Could it be used to find the origin of 3D-printed guns?



A research team affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a novel extracorporeal blood purification technology that captures and removes bacteria from the bloodstream by leveraging sticky, clot-like surfaces. This breakthrough could pave the way for new treatments against deadly systemic infections, including sepsis, even those caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The work is published in Advanced Science.
Led by Professor Joo H. Kang, from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UNIST, the research team announced the development of an innovative extracorporeal bacterial purification device that utilizes artificial blood clots. Similar to dialysis, the technique involves extracting infected blood outside the body, adsorbing bacteria onto artificial thrombi, and then returning the purified blood to the patient.
The newly developed extracorporeal blood purification device (eCDTF) features a spiral structure inserted into the central tube. Inside this spiral, artificial blood clots are embedded, which attract and trap bacteria flowing through the tube. Composed solely of plasma proteins without any cellular components like white blood cells, these artificial thrombi facilitate effective bacterial adhesion to the device’s surface.

The universe is decaying much faster than thought. This is shown by calculations of three scientists at Radboud University on the so-called Hawking radiation. They calculate that the last stellar remnants take about 1078 years (a 1 with 78 zeros) to perish. That is much shorter than the previously postulated 101100 years (a 1 with 1100 zeros).

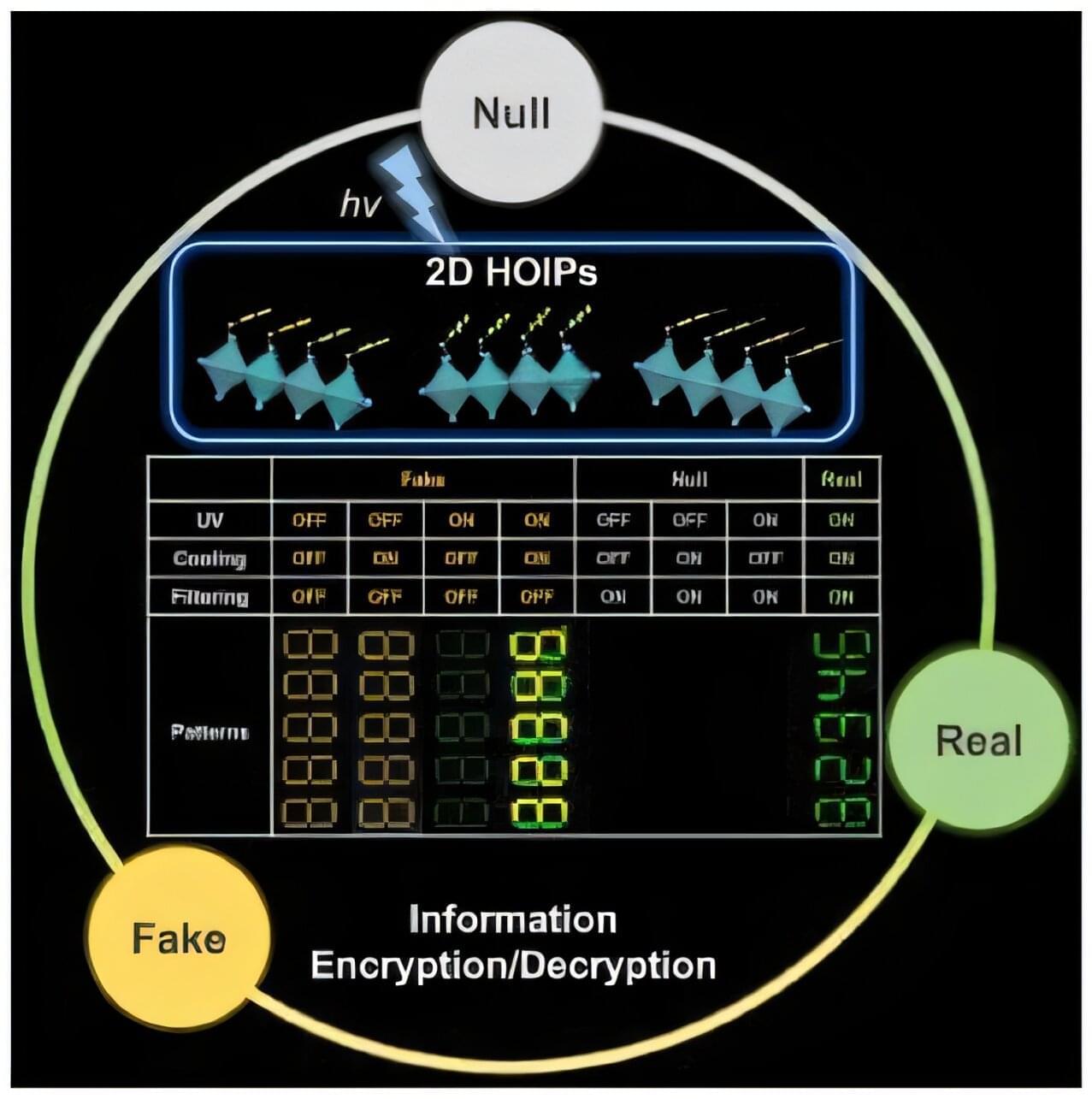
To guarantee high data security, encryption must be unbreakable while the data remains rapidly and easily readable. A novel strategy for optical encryption/decryption of information has now been introduced in the journal Angewandte Chemie by a Chinese research team. It is based on compounds with carefully modulated luminescent properties that change in response to external stimuli.
The compounds are hybrid two-dimensional organic-inorganic metal-halide perovskites, whose structure consists of inorganic layers formed from lead and iodide ions (linked PbI6 octahedra) with organic cations arranged between them. They are easy to produce, inexpensive, and printable, while demonstrating interesting optoelectronic properties.
A team led by Shenlong Jiang, Qun Zhang, and Yi Luo at the University of Science and Technology of China (Hefei) worked with three perovskites with only slight variations in their cations (phenethylammonium lead iodide perovskite (PEA)2PbI4 and its fluoridated (2-F-PEA)2PbI4 and brominated (4-Br-PEA)2PbI4 derivatives).


Scientists have uncovered a critical role for rapid DNA repair in maintaining genome stability. A new study reveals that repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in nuclear DNA in plants serves as a powerful safeguard against the integration of foreign DNA from chloroplasts—a phenomenon that, while important for evolution, can be highly destabilizing to the genome. The research expands our knowledge about plant genome evolution and also has relevance to the medical field.
The findings, presented by Dr. Enrique Gonzalez-Duran and Prof. Dr. Ralph Bock from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology in Nature Plants, shed new light on endosymbiotic gene transfer (EGT)—an ongoing evolutionary process in which genes from organelles such as chloroplasts and mitochondria are relocated into the nuclear genome.
While successful gene transfers help the nucleus to better coordinate its function with that of the organelles, they also pose risks: Mutations arising from DNA insertion can disrupt essential nuclear genes and provoke harmful rearrangements.
