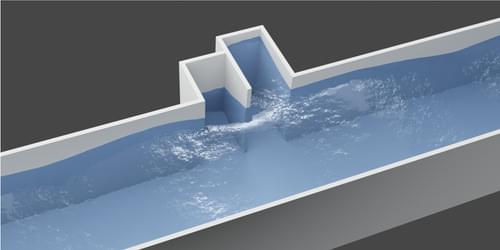
Cavities at the sides of a water channel can cause waves to be completely absorbed, suggesting new techniques for protecting coastlines.
If waves of water, light, or sound were to impinge upon a hypothetical object called a perfect absorber, they would be neither reflected nor transmitted; they would simply vanish. Researchers have now demonstrated perfect absorption using ordinary water waves traveling down a narrow channel [1]. The waves are canceled out by their own reflections from cavities built into the side of the channel. With further development, the researchers believe that the effect could be used to reduce erosion or protect sensitive structures by using an array of elements deployed near coastlines.
“We were motivated by the need to control or absorb waves in rivers or to protect coastlines,” says mathematical physicist Agnes Maurel of ESPCI Paris. “Completely absorbing wave energy is even better than redirecting it, and you can also imagine perhaps harvesting such energy.”