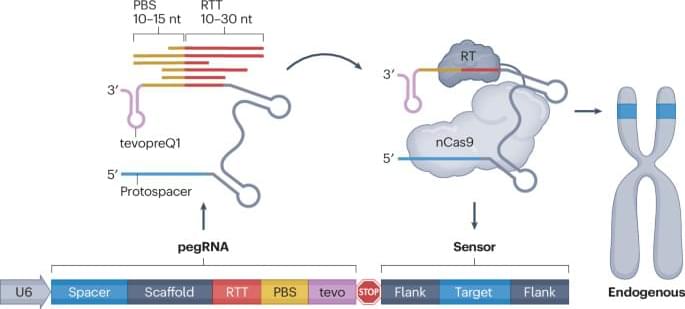
In this Tools of the Trade article, Samuel Gould explains how prime editing sensors can improve experimental efficiency and can be designed using a computational tool he created and named PEGG.

Download Opera for free using https://opr.as/Opera-browser-anastasiintech Thanks Opera for sponsoring this video!Timestamps:00:00 — Intro00:52 — Computing w…



A team at HZB has investigated a new, simple method at BESSY II that can be used to create stable radial magnetic vortices in magnetic thin films.
In some materials, spins form complex magnetic structures within the nanometre and micrometer scale in which the magnetization direction twists and curls along specific directions. Examples of such structures are magnetic bubbles, skyrmions, and magnetic vortices.
Spintronics aims to make use of such tiny magnetic structures to store data or perform logic operations with very low power consumption, compared to today’s dominant microelectronic components. However, the generation and stabilization of most of these magnetic textures is restricted to a few materials and achievable under very specific conditions (temperature, magnetic field…).
For more: https://news.cgtn.com/news/2024-04-28/China-unveils-.…htmlChina has unveiled its first self-develop…
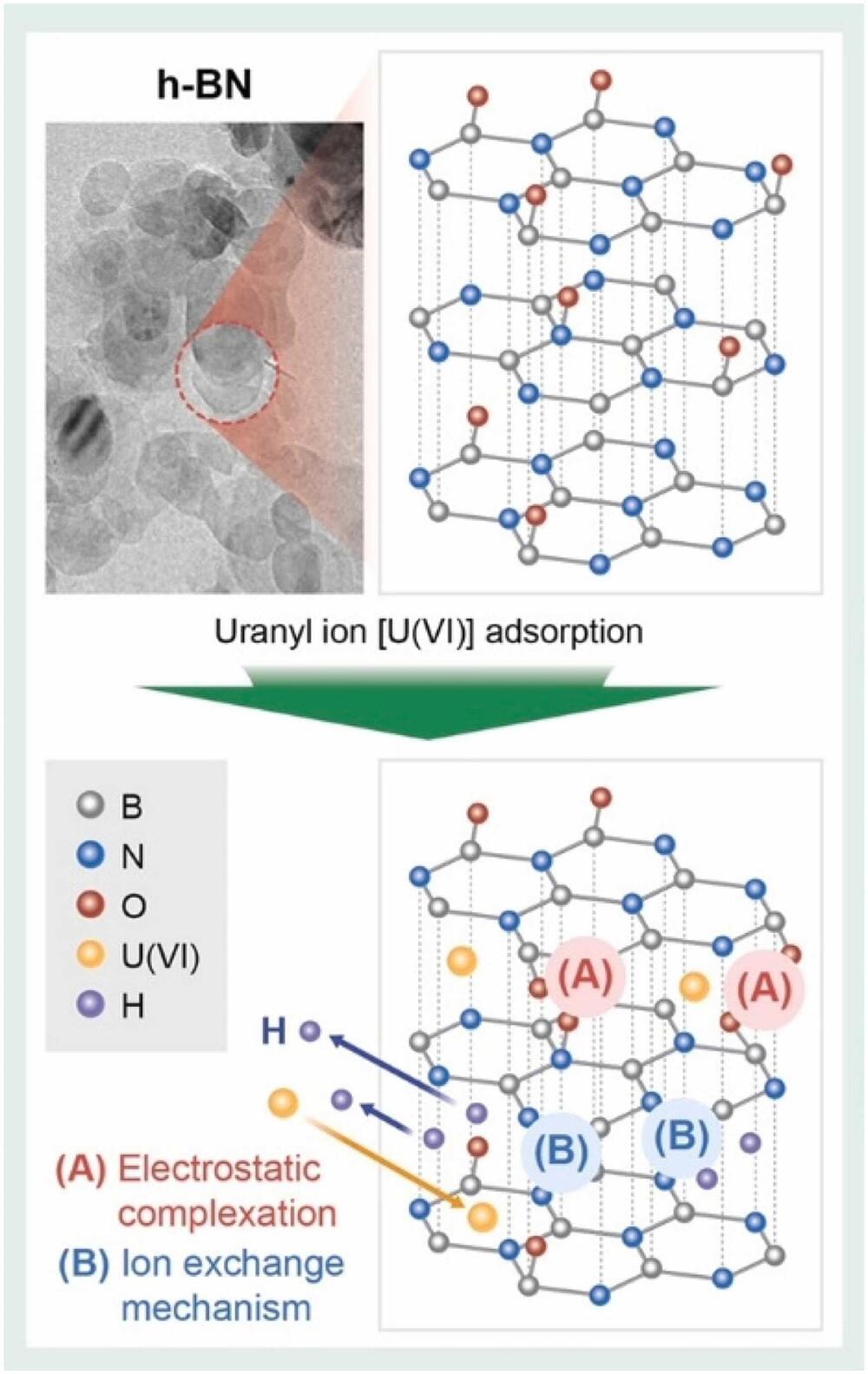
Nuclear energy has long been regarded as a next-generation energy source, and major countries around the world are competing to secure cutting-edge technologies by leveraging the high economic efficiency and sustainability of nuclear power. However, uranium, which is essential for nuclear power generation, has serious implications for both soil ecosystems and human health.
Despite being a key radioactive material, uranium poses significant health risks due to its chemical toxicity to the kidneys, bones, and cells. As a result, both the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the World Health Organization recommend allowing and advocating for uranium concentrations in wastewater to be below 30 μg/L.
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) has conducted research on a nano-material-based adsorption process to efficiently remove uranium wastewater extracted from actual radioactive-contaminated soil. They have also proposed its applicability to prevent secondary environmental pollutions.
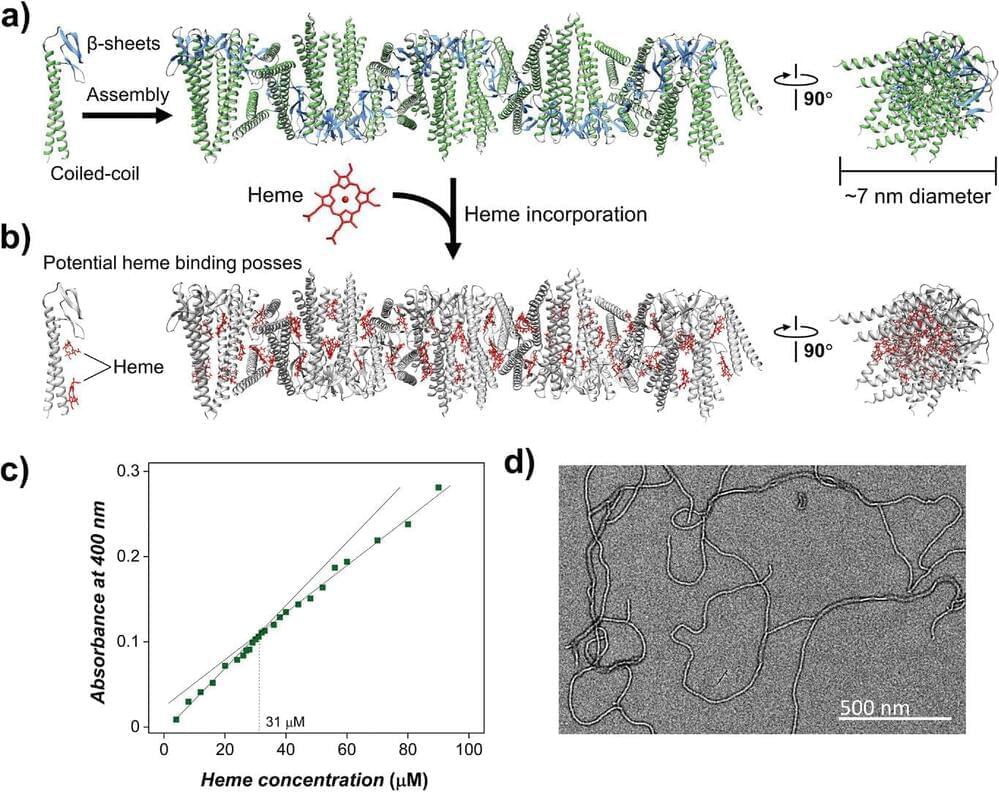
Engineered protein filaments originally produced by bacteria have been modified by scientists to conduct electricity. In a study published recently in the journal Small, researchers revealed that protein nanowires—which were modified by adding a single compound—can conduct electricity over short distances and harness energy from moisture in the air.
“Our findings open up possibilities for developing sustainable and environmentally friendly electrical components and devices, based on proteins,” says Dr. Lorenzo Travaglini, lead author on the paper. “These engineered nanowires could one day lead to innovations in energy harvesting, biomedical applications and environmental sensing.”
Developments in the interdisciplinary field that combine protein engineering and nanoelectronics also hold promise for developing cutting-edge technologies that bridge the gap between biological systems and electronic devices.
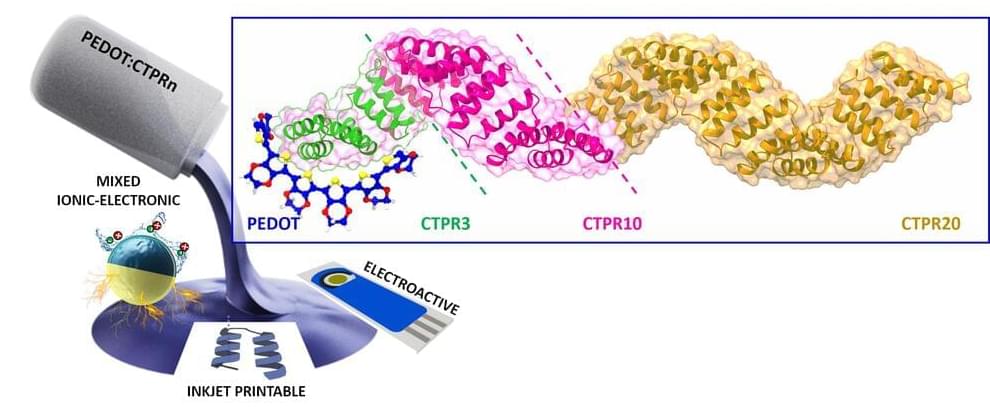
Bioelectronics is a field of research in which biology and electronics converge. In medicine, for example, an external electric current is used to cure or monitor diseases of the nervous system, and also to monitor biomarkers in situ. Devices made of conductive materials are used for these applications.
The most widely used conductive polymer so far in energy and biomedical applications is PEDOT doped with PSS, known as PEDOT: PSS. Despite its exceptional properties, new conductive materials that can improve some of its limitations, such as biocompatibility, still need to be developed.
A study conducted by CIC biomaGUNE’s Biomolecular Nanotechnology group is proposing a mechanism for doping PEDOT using a robust engineered protein (PEDOT: Protein); the outcome is a hybrid material with ionic and electronic conductivity, which is quite similar to PEDOT: PSS in some cases. The paper is published in the journal Small.
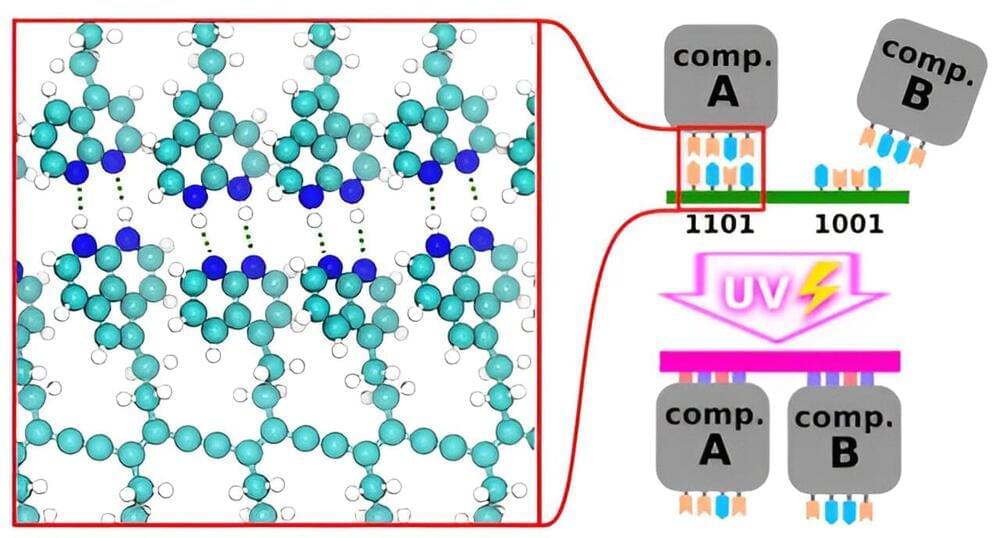
Molecular computer components could represent a new IT revolution and help us create cheaper, faster, smaller, and more powerful computers. Yet researchers struggle to find ways to assemble them more reliably and efficiently.
To help achieve this, scientists from the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences investigated the possibilities of molecular machine self-assembly building upon solutions honed by natural evolution and using synergy with current chip manufacturing.
There is a limit to the miniaturization of current silicon-based computer chips. Molecular electronics, using single-molecule-sized switches and memories, could provide a revolution in the size, speed and capabilities of computers while cutting down on their increasing power consumption, but their mass production is a challenge. Large-scale, low-defect, accessible nanofabrication and assembly of the components remains elusive. Inspiration taken from living nature could change this status quo.