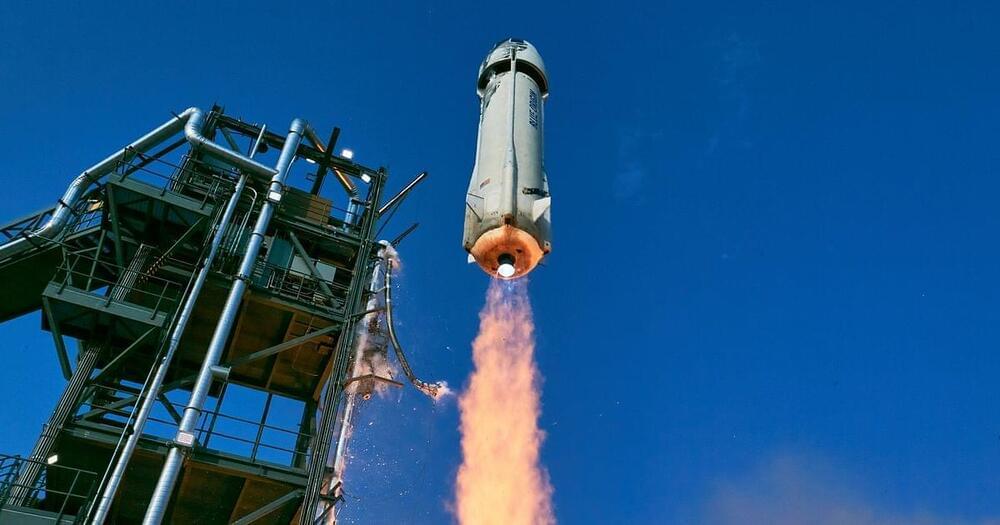
As part of the SERA-Blue Origin collaboration, Brazilian civil engineer Victor Hespanha flew on a New Shepard, in June 2022.


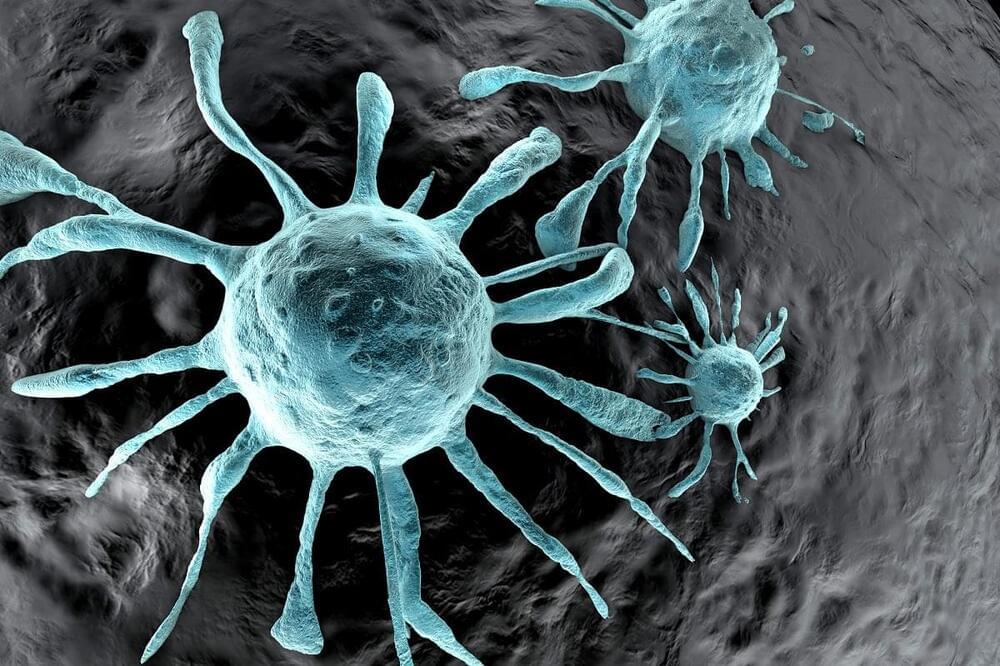
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem say they have developed a way to accurately predict the behavior of cancer cells, which will advance diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
The new diagnostic tool uses AI machine learning combined with nanoinformatics (observing nanomaterials) to classify cancer cell behavior in individual patient biopsies, potentially paving the way for personalized monitoring of the progression of the disease and the impact of treatments.
The study was led by Hebrew University doctoral student Yoel Goldstein and Prof. Ofra Benny from its School of Pharmacy in the Faculty of Medicine, working with Prof. Tommy Kaplan, the head of the Department of Computational Biology at the School of Engineering and Computer Science.
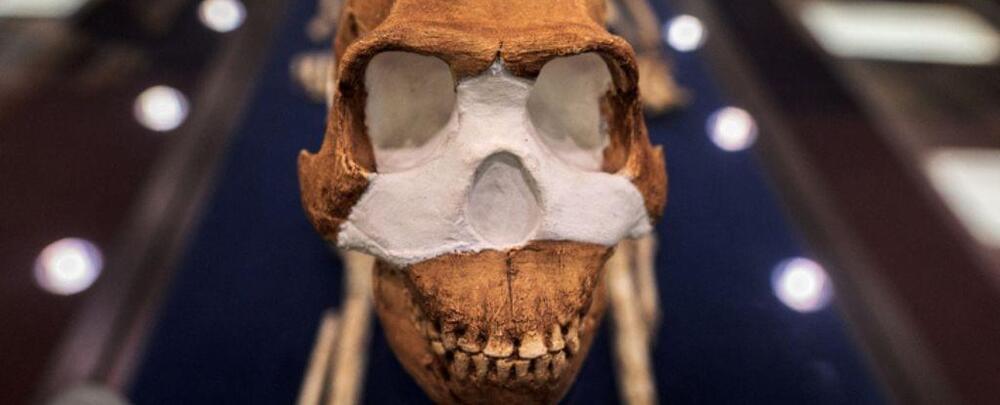

Paleontologists in South Africa said they have found the oldest known burial site in the world, containing remains of a small-brained distant relative of humans previously thought incapable of complex behavior.
Led by renowned paleoanthropologist Lee Berger, researchers said in 2023 they had discovered several specimens of Homo naledi – a tree-climbing, Stone Age hominid – buried about 30 meters (100 feet) underground in a cave system within the Cradle of Humankind, a UNESCO world heritage site near Johannesburg.
“These are the most ancient interments yet recorded in the hominin record, earlier than evidence of Homo sapiens interments by at least 100,000 years,” the scientists wrote in a series of preprint papers published in eLife.
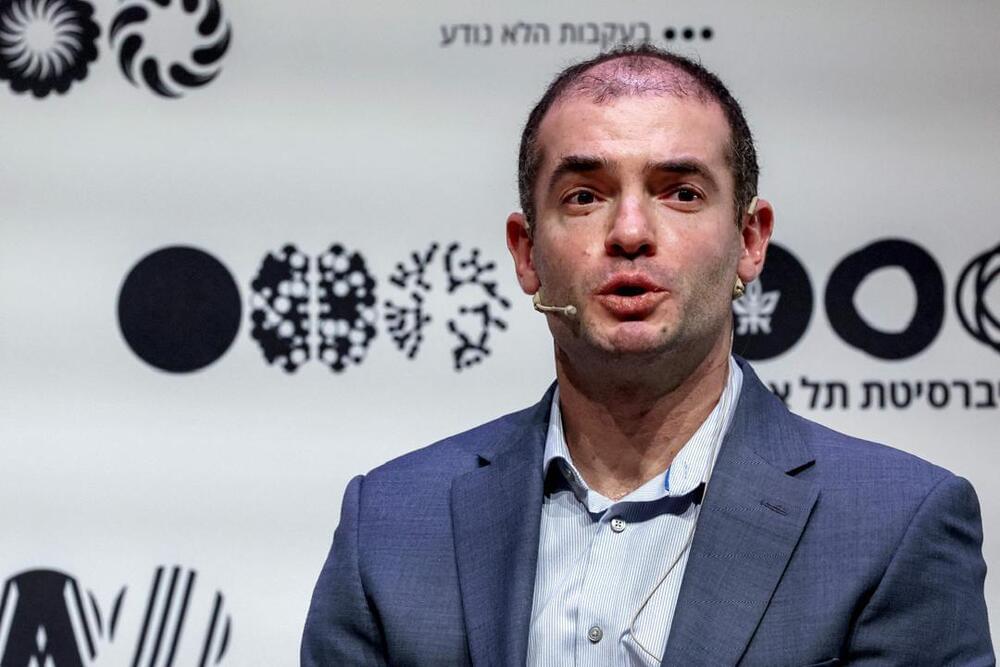

Ilya Sutskever, one of OpenAI’s co-founders, has launched a new company, Safe Superintelligence Inc. (SSI), just one month after formally leaving OpenAI.
Sutskever, who was OpenAI’s longtime chief scientist, founded SSI with former Y Combinator partner Daniel Gross and ex-OpenAI engineer Daniel Levy.
At OpenAI, Sutskever was integral to the company’s efforts to improve AI safety with the rise of “superintelligent” AI systems, an area he worked on alongside Jan Leike, who co-led OpenAI’s Superalignment team. Yet both Sutskever and then Leike left the company in May after a dramatic falling out with leadership at OpenAI over how to approach AI safety. Leike now heads a team at rival AI shop Anthropic.


Lakes and seas of liquid methane exist on Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, due to the moon’s bone-chilling cold temperatures at-290 degrees Fahrenheit (−179 degrees Celsius), whereas it can only exist as a gas on Earth. But do these lakes and seas of liquid methane strewn across Titan’s surface remain static, or do they exhibit wave activity like the lakes and seas of liquid water on Earth? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances hopes to address as a team of researchers have investigated coastal shoreline erosion on Titan’s surface resulting from wave activity. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the formation and evolution of planetary surfaces throughout the solar system and how well they relate to Earth.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of shoreline analogs on Earth, orbital images obtained by NASA’s now-retired Cassini spacecraft, coastal evolution models, and several mathematical equations to ascertain the processes responsible for shoreline morphology across Titan’s surface. Through this, the researchers were able to construct coastal erosion models depicting how wave activity could be responsible for changes in shoreline morphology at numerous locations across Titan’s surface.
“We can say, based on our results, that if the coastlines of Titan’s seas have eroded, waves are the most likely culprit,” said Dr. Taylor Perron, who is a Cecil and Ida Green Professor of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a co-author on the study. “If we could stand at the edge of one of Titan’s seas, we might see waves of liquid methane and ethane lapping on the shore and crashing on the coasts during storms. And they would be capable of eroding the material that the coast is made of.”
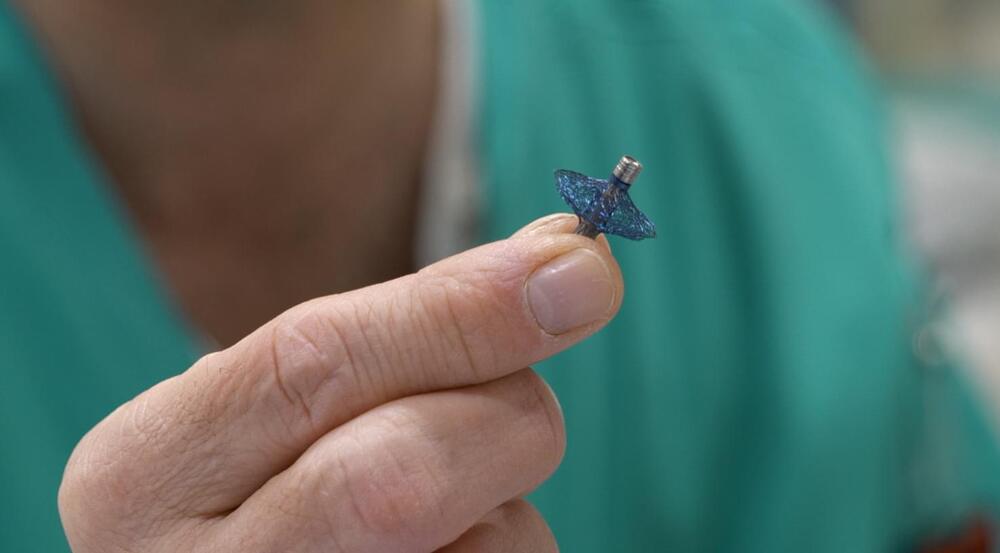


A groundbreaking way of measuring fluid buildup in the body allows chronic heart failure patients to monitor their condition and treat it independently with a physician-approved response.
Tel Aviv-based startup Vectorious has created a tiny pressure sensor that is implanted directly into the heart. It is the only sensor in the world that measures the pressure in the left atrium (one of the heart’s two upper chambers) and is able to identify increases in that pressure caused by a buildup of fluid in the body.
This data on the left atrial pressure (LAP) is then transmitted to an app for the patient and their doctor.


Researchers at the National Graphene Institute have made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionise energy harnessing and information computing. Their study, published in Nature (“Control of proton transport and hydrogenation in double-gated graphene”), reveals how electric field effects can selectively accelerate coupled electrochemical processes in graphene.
Electrochemical processes are essential in renewable energy technologies like batteries, fuel cells, and electrolysers. However, their efficiency is often hindered by slow reactions and unwanted side effects. Traditional approaches have focused on new materials, yet significant challenges remain.
The Manchester team, led by Dr Marcelo Lozada-Hidalgo, has taken a novel approach. They have successfully decoupled the inseparable link between charge and electric field within graphene electrodes, enabling unprecedented control over electrochemical processes in this material. The breakthrough challenges previous assumptions and opens new avenues for energy technologies.