This talk is part of a workshop on “To be or not to be… conscious. Phenomenal Realism and Illusionism”, held at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (Germany) on September 29–30, 2022, organized by François Kammerer and Tobias Schlicht.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Rita El Zaghloul — Director, High Ambition Coalition for Nature & People Secretariat
Championing a global deal for nature and people — rita maria el zaghloul — director, high ambition coalition for nature and people secretariat.
Dr. Masayuki Goto, MD, PhD — Director, Space Medical Accelerator — Keeping People Healthy In Space
Keeping people healthy in space and developing novel therapies with space technologies — dr. masayuki goto, MD, phd — director, space medical accelerator.
Dr. Masayuki Goto, MD, PhD is Director and President of the Space Medical Accelerator (https://space-healthcare.jp/), an organization founded in 2022 in Japan with a mission to keep people healthy in space and to develop terrestrial medicine by utilizing space technology and research.
Dr. Goto is a Medical Doctor, a Neurosurgeon, and a Space Medicine researcher with degrees from University of Tsukuba and Yamagata University.
Dr. Goto has been certified by the Japanese Society of Aerospace Medicine and Environmental Medicine.
Elizabeth Reynolds, Managing Director, US, Starburst Aerospace; Championing An Aerospace Renaissance
Championing an aerospace renaissance — elizabeth reynolds, managing director, US, starburst aerospace.
Elizabeth Reynolds is Managing Director, US of Starburst Aerospace (https://starburst.aero/), a global Aerospace and Defense (A\&D) startup accelerator and strategic advisory practice championing today’s aerospace renaissance, aligning early-stage technology innovators with government and commercial stakeholders and investors to modernize infrastructure in space, transportation, communications, and intelligence.
Elizabeth’s team works alongside hundreds of technology startups developing new aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, drones, sensors, autonomy, robotics, and much more.
Elizabeth brings 15 years of experience in deep tech entrepreneurship, growth, business operations, and strategy to the team. Prior to joining Starburst, she served as an executive for biotech, medtech, mobility, and interactive media companies, from founding through IPO. She is also an advisor to a number of startups and nonprofits supporting STEM education.
Starburst has offices in Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., Paris, Munich, Singapore, Seoul, Tel Aviv, and Madrid, has grown into a global team of 70 dedicated team members with a portfolio of 140+ startups, 20 accelerator programs, and 2 active venture funds which strive to provide enabling growth services for deep tech leaders disrupting the industry and working towards a safer, greener, and more connected world.
Dr. Diane DiEuliis — NDU — Preparing National Security Leaders For The Next Generation Of Threats
Episode Disclaimer — The views presented in this episode are those of the speaker and do not necessarily represent the views of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) or its components.
Dr. Diane DiEuliis, Ph.D. is a Distinguished Research Fellow at National Defense University (NDU — https://www.ndu.edu/), an institution of higher education, funded by the United States Department of Defense, aimed at facilitating high-level education, training, and professional development of national security leaders. Her research areas focus on emerging biological technologies, biodefense, and preparedness for biothreats. Specific topic areas under this broad research portfolio include dual-use life sciences research, synthetic biology, the U.S. bioeconomy, disaster recovery, and behavioral, cognitive, and social science as it relates to important aspects of deterrence. Dr. DiEuliis currently has several research grants in progress, and teaches in foundational professional military education.
Prior to joining NDU, Dr. DiEuliis was Deputy Director for Policy, and served as Deputy Assistant Secretary for Policy and Planning in the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR), Department of Health and Human Services. She coordinated policy and research in support of domestic and international health emergencies, such as Hurricane Sandy, and Ebola outbreaks. She was responsible for implementation of the Pandemic All-Hazards Preparedness Act, the National Health Security Strategy, and supported the Public Health Emergency Medical Countermeasures Enterprise (PHEMCE).
From to 2007 to 2011, Dr. DiEuliis was the Assistant Director for Life Sciences and Behavioral and Social Sciences in the Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) in the Executive Office of the President. During her tenure at the White House, she was responsible for developing policy in areas such as biosecurity and biodefense, synthetic biology, social and behavioral science, scientific collections, and biotechnology. Dr. DiEuliis also worked to help coordinate agency response to public health issues such as the H1N1 flu.
Prior to working at OSTP, Dr. DiEuliis was a program director at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), where she managed a diverse portfolio of neuroscience research in neurodegenerative diseases. She completed a fellowship at the University of Pennsylvania in the Center for Neurodegenerative Disease Research and completed her postdoctoral research in the NIH Intramural research program, where she focused on cellular and molecular neuroscience.
Dr. DiEuliis is a National Merit Scholar, and has a Ph.D. in biology from the University of Delaware in Newark, Delaware. She is the author of over 70 publications.
What If We Accessed The 10th Dimension?
This video explores the 4th to the 10th dimensions of time. Watch this next video about the 10 stages of AI: • The 10 Stages of Artificial Intelligence.
🎁 5 Free ChatGPT Prompts To Become a Superhuman: https://bit.ly/3Oka9FM
🤖 AI for Business Leaders (Udacity Program): https://bit.ly/3Qjxkmu.
☕ My Patreon: / futurebusinesstech.
➡️ Official Discord Server: / discord.
💡 Future Business Tech explores the future of technology and the world.
Examples of topics I cover include:
• Artificial Intelligence \& Robotics.
• Virtual and Augmented Reality.
• Brain-Computer Interfaces.
• Transhumanism.
• Genetic Engineering.
SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO
Disclaimer:
Some links in this description are affiliate links.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
This video explores the 4th to the 10th dimensions of time. Other related terms: advanced civilization, ai, artificial intelligence, future business tech, future technology, future tech, future business technologies, future technologies, aliens, higher dimensions, 10th dimension, 4th dimension, 5th dimension, 6th dimension, 7th dimension, 8th dimension, 9th dimension, time travel, etc.
These two scientists have mapped out the insides or “reachable space” of a language model using control theory, what they discovered was extremely surprising
Please support us on Patreon to get access to the private Discord server, bi-weekly calls, early access and ad-free listening.
/ mlst.
Aman Bhargava from Caltech and Cameron Witkowski from the University of Toronto to discuss their groundbreaking paper, “What’s the Magic Word? A Control Theory of LLM Prompting.” They frame LLM systems as discrete stochastic dynamical systems. This means they look at LLMs in a structured way, similar to how we analyze control systems in engineering. They explore the “reachable set” of outputs for an LLM. Essentially, this is the range of possible outputs the model can generate from a given starting point when influenced by different prompts. The research highlights that prompt engineering, or optimizing the input tokens, can significantly influence LLM outputs. They show that even short prompts can drastically alter the likelihood of specific outputs. Aman and Cameron’s work might be a boon for understanding and improving LLMs. They suggest that a deeper exploration of control theory concepts could lead to more reliable and capable language models.
What’s the Magic Word? A Control Theory of LLM Prompting (Aman Bhargava, Cameron Witkowski, Manav Shah, Matt Thomson)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.
LLM Control Theory Seminar (April 2024)
• LLM Control Theory Seminar (April 2024)
Society for the pursuit of AGI (Cameron founded it)
https://agisociety.mydurable.com/

‘Noise’ in the Machine: Human Differences in Judgment Lead to Problems for AI
New research says that quantifying progress in AI must account for the fact that the humans AI is measured against are actually a variable, noisy benchmark.
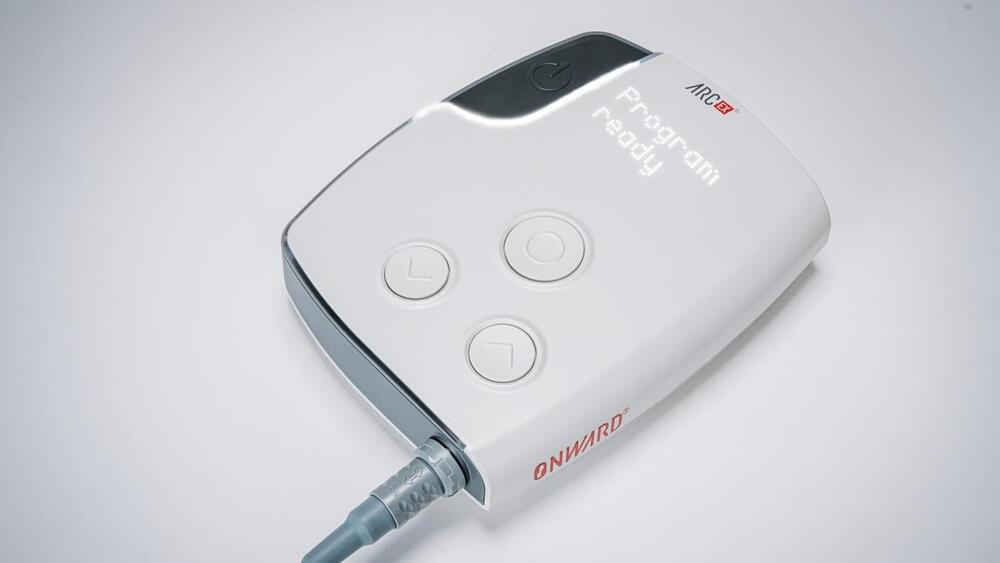
This Device Zaps the Spinal Cord to Give Paralyzed People Use of Their Hands Again
Reid was part of a 60-participant clinical trial that looked to use spinal cord stimulation to regain control of both hands. Similar treatments have shown promise in paraplegic patients, restoring the ability to walk in just a day. But those required surgery to place electrodes on the spinal cord.
ARC-EX therapy, by contrast, delivers two different types of electrical pulses through the skin—no surgery required. Developed by Grégoire Courtine and colleagues at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, the device improved hand strength, pinch, and other movements in 72 percent of participants.
Because the device is non-invasive, it’s a simple addition to physical rehabilitation programs—a sort of pilates for the fingers, explained the team. The trial only included two months of stimulation, and extending the timeline could potentially further improve results.