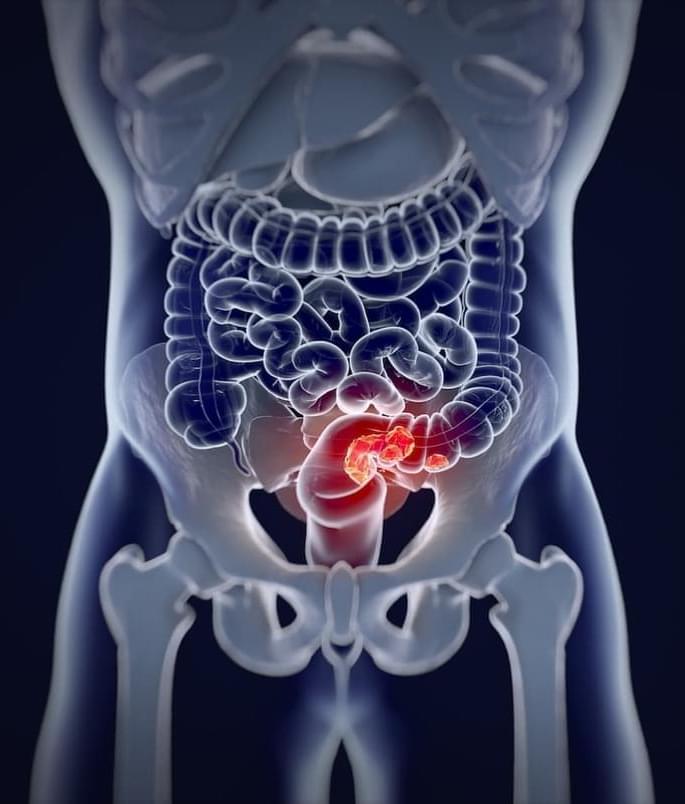
In what researchers have called an “unprecedented” response, a new drug that treats locally advanced rectal cancer has shown to have completely eradicated tumors in all 42 patients who took part in the Phase II trial.
The drug, Jemperli (dostarlimab-gxly), had earlier shown great potential for eliminating mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) cancers, which make up 5–10% of colorectal cancers. Following the Phase II trial, the first 24 patients assessed showed a “sustained complete clinical response” – no cancer evident – after an average of 26.3 months.
“These findings demonstrate the potential of dostarlimab-gxly as a novel approach to treating locally advanced dMMR rectal cancer that leads to durable complete tumor regression without the need for life-altering treatment,” said Dr Andrea Cercek, researcher and oncologist at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). “As a clinician, I’ve seen firsthand the debilitating impact of standard treatment of dMMR rectal cancer and am thrilled about the potential of dostarlimab-gxly in these patients.”