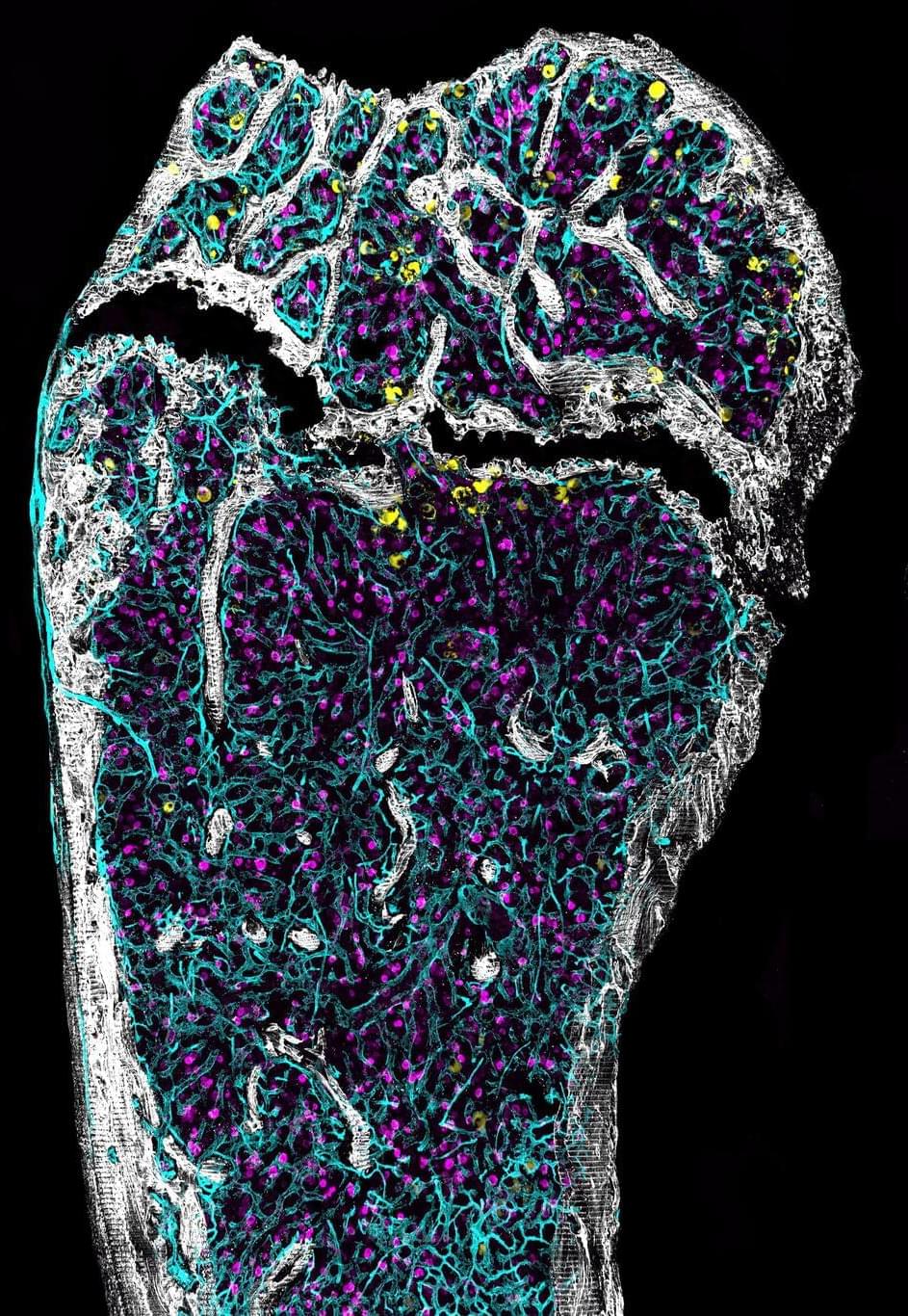
Our bone marrow—the fatty, jelly-like substance inside our bones—is an unseen powerhouse quietly producing 500 billion new blood cells every day. That process is driven by hematopoietic stem cells that generate all of the various types of blood cells in our bodies and regenerating themselves to keep the entire assembly line of blood production operating smoothly.
As with any complex system, hematopoietic stem cells lose functionality as they age—and, in the process, contribute to the risk of serious diseases, including blood cancers. We know that the risk of developing aging-associated diseases is different among different individuals. Surprisingly, however, little is known about whether hematopoietic stem cells age differently between individuals.
“If you take a room full of 50-year-olds, some will be completely gray-haired, others will be salt-and-pepper, and a few will not have any gray hairs at all,” said Jennifer Trowbridge, Dattels Family Endowed Chair and professor at the Jackson Laboratory. “Logically, you’d expect to see the same kind of variation in the function of hematopoietic stem cells—but until now, nobody has studied that directly.”