SpaceX LabPadre Space
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
SpaceX’s Starship Launch 5 and Elon Musk’s Ambitious Plans
SpaceX’s upcoming Starship launch and Elon Musk’s ambitious plans for the rocket’s production and capabilities have generated excitement and anticipation among fans and industry observers Questions to inspire discussion What is SpaceX’s upcoming Starship launch? —The upcoming Starship launch refers to SpaceX’s ambitious plans for the rocket’s production and capabilities, generating excitement and anticipation among fans and industry observers.
This Invention Made Disney MILLIONS, but Then They LOST It!
Destro Robotics

Consistently Exercising 2–3 times a week over the Long Term linked to Lower Current Insomnia Risk
Consistently exercising 2–3 times a week over the long term is linked to a lower current risk of insomnia as well as the ability to clock up the recommended 6–9 hours of shut-eye every night, suggests an international 10-year study published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Regular exercise is associated with better overall health, and several studies have suggested that physical activity promotes better quality sleep and may improve symptoms of chronic insomnia, note the researchers.
But it’s not entirely clear how much gender, age, weight (BMI), overall fitness, general health, and exercise type contribute to this association, they add.

Researchers find the “recipe” for growing new limbs
For as long as superheroes have been imagined, there’s been a superhero who can regrow limbs. Other animals (like salamanders and sharks) do it, why couldn’t we? Scientists have also tackled this question because, obviously, humans don’t naturally regrow limbs. But before we move on to regrowing limbs ourselves, we need to understand how other species do it.
In a new study, researchers mapped the proteins that kick off limb creation in mice and chicks, finding that a cocktail of just three proteins performs the initial magic.
“People in the field have known a lot of the proteins critical for limb formation, but we found that there are proteins we missed,” said study co-first author ChangHee Lee, research fellow in genetics in the lab of Cliff Tabin at Harvard Medical School.
Cancer Stem Cells
Long suspected to exist, cancer stem cells were discovered in solid tumors about 20 years ago. Is this the long-sought root cause of cancer? Thousands of scientists now believe so. Then why haven’t you heard about this from your oncologist? We delve into the debate on CSCs, and explore which foods and food supplements are most effective in the lab at killing or blocking cancer stem cells.
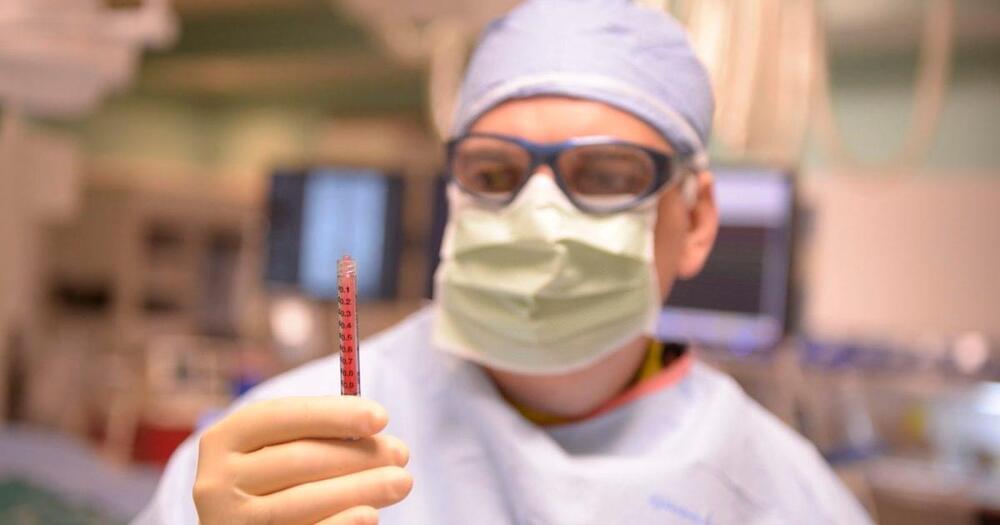
A single injection of stem cells slashes risk of heart attack or stroke by 58%
Treated participants’ risk of heart attack or stroke dropped by 58%.
The trial: Mesoblast has now tested the therapy, called “rexlemestrocel-L,” in a double-blind, randomized phase 3 trial, which it says is the largest trial of a cell therapy in patients with chronic heart failure. The results have been published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
During this trial, 537 patients with HFrEF received an injection of about 150 million MPCs straight into the muscular tissue of their hearts — or a sham treatment with no injection. All of the participants were also receiving standard heart failure treatment at the time of the trial.