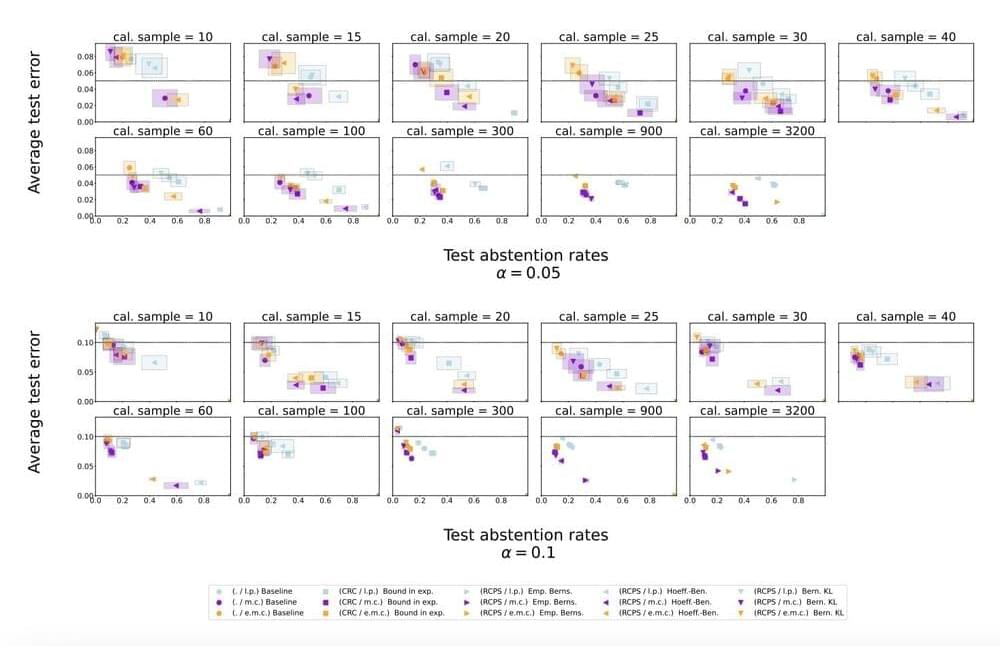
Autonomous and AI-enabled systems increasingly rely on optical and radio frequency sensors and significant computer power. They face growing vulnerabilities from directed-energy laser and microwave weapons.
In May the U.S. secretary of the Air Force flew in an F-16 that engaged in a mock dogfight over the California desert while controlled by artificial intelligence. Carmakers from San Francisco to Boston are jousting to deliver driverless cars. In Norway a crewless cargo ship carries fertilizer from port to port. On the land, sea and in the air, we face the coming of such autonomous platforms—some envisioned to benefit humanity, and others meant for destruction—available to everyone, to governments, businesses and criminals.