Group theory and first-principles calculations combine to predict which antiferromagnets have potentially useful net surface magnetization.
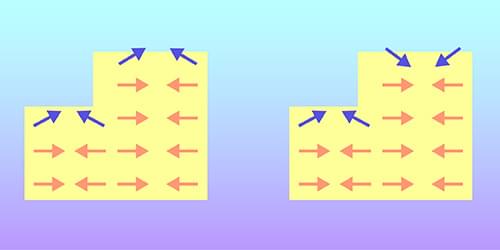
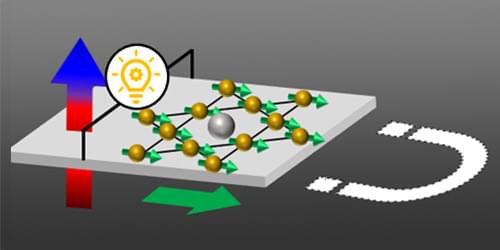
Antiferromagnetism was discovered in the 1930s by Louis Néel but had long been considered of scientific, not practical, interest. Antiferromagnets (AFM) are internally magnetic, but the magnetic moments of their atoms and molecules are antiparallel to each other, canceling out and resulting in no net magnetization. This cancellation renders bulk antiferromagnets effectively invisible to external magnetic fields, so that their magnetic properties are difficult to harness in applications. Recently, however, a new paradigm has appeared—antiferromagnetism-based spintronics—which seeks to apply antiferromagnets’ unique properties (such as fast spin dynamics, the absence of strong stray fields, and the stability of these materials) to the processing and storage of information [1].