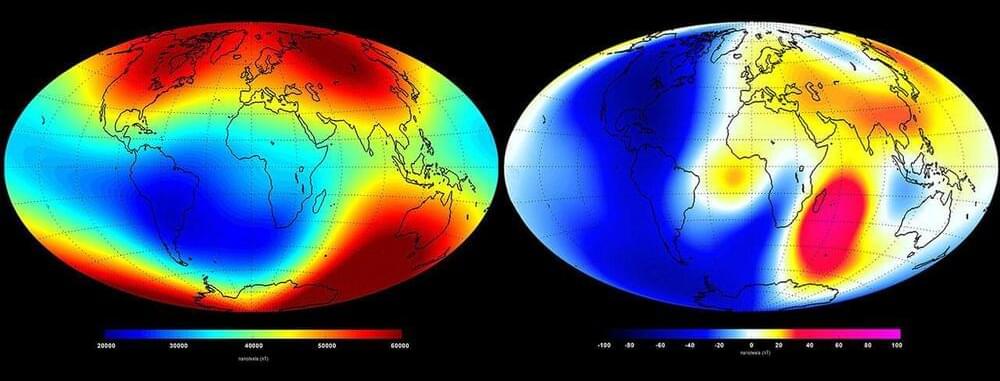
The Earth’s liquid molten outer core, composed mostly of iron and nickel, exerts an electromagnetic field extending from the north and south pole that protects the planet from harmful solar particle radiation.


Researchers from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and collaborators from the Institute of Physics of CAS have directly observed polar Bloch points in strained ferroelectric films.
Their work is published in Nature Communications.
Based on their previous work on the polar meron lattice, the researchers considered the model of a tensile-strained ultrathin ferroelectric PbTiO3 film sandwiched by symmetric electrodes in phase-field simulations and found that the merons transform into Bloch points with the increase of the electrode thickness.
Researchers at European XFEL in Schenefeld near Hamburg have taken a closer look at the formation of the first crystallization of nuclei in supercooled liquids. They found that the formation starts much later than previously assumed. The findings could help to better understand the creation of ice in clouds in the future and to describe some processes inside the Earth more precisely.
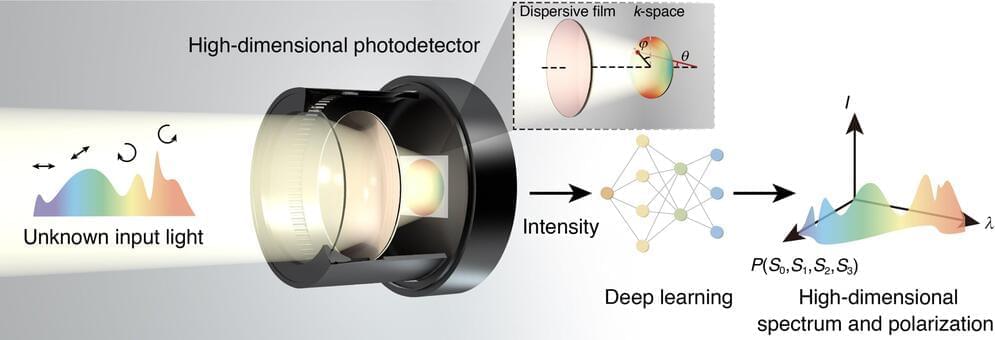
Our photodetector is capable of demonstrating high spectral resolution and accurate reconstruction of full-Stokes polarization states in both theoretical and experimental settings. Precision detection of high-dimensional information by our photodetector, such as a two-color laser field with different polarization states or broadband reflection from a gold interface exhibiting varying polarization states, is achieved beyond the capabilities of commercial polarimeter and spectrometer.
Additionally, this approach can be extended to imaging applications by sandwiching the film with a commercial microlens array and sensor array to realize ultra-compact high-dimensional imager, said Assistant Professor Chunqi Jin from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Looking ahead, Prof. Wei Li envisions that ultra-broadband detection can be achieved by integrating broadband commercial photodetectors; the detection resolution can be further improved by using photonic crystals, metasurfaces, and two-dimensional materials instead of existing thin film schemes; and the detection capability can be stepped up in higher dimensions by integrating functionalities such as image processing, and distance measurement.
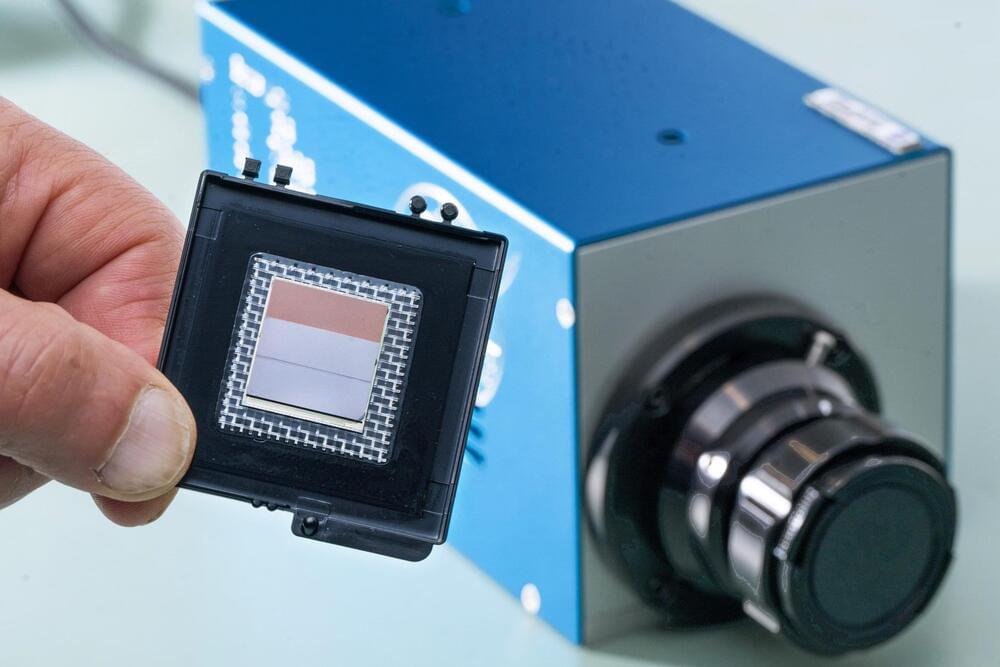
Innovative infrared sensors developed by NASA increase resolution for Earth and space imaging, promising advancements in environmental monitoring and planetary science.
A newly developed infrared camera featuring high resolution and equipped with a range of lightweight filters has the potential to analyze sunlight reflected from Earth’s upper atmosphere and surface, enhance forest fire alerts, and uncover the molecular composition of other planets.
These cameras are equipped with sensitive, high-resolution strained-layer superlattice sensors, originally developed at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, funded through the Internal Research and Development (IRAD) program.

New research combining experimental and computational approaches provides deeper insights into proton spin contributions from gluons.
Nuclear physicists have been tirelessly exploring the origins of proton spin. A novel approach, merging experimental data with cutting-edge calculations, has now illuminated the spin contributions from gluons—the particles that bind protons. This advancement also sets the stage for three-dimensional imaging of the proton structure.
Joseph Karpie, a postdoctoral associate at the Center for Theoretical and Computational Physics (Theory Center) at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, led this groundbreaking research.

Sensory hypersensitivity in mice with the Grin2b gene mutation found in patients is related to hyperactivity of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and hyperconnectivity between the ACC and other brain regions. Credit: Institute for Basic Science.
Director Kim Eunjoon states, “This new research demonstrates the involvement of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), which has been known for its deep association with cognitive and social functions, in sensory hypersensitivity in autism.”
The hyperactivity of the ACC was also associated with the enhanced functional connectivity between the ACC and other brain areas. It is believed both hyperactivity and the hyperconnectivity of the ACC with various other brain regions are involved with sensory hypersensitivity in Grin2b-mutant mice.

Enhanced neuron growth in the hippocampus, achieved through exercise or genetic methods, aids mice in forgetting strong, maladaptive memories, offering potential for new treatments for PTSD or drug addiction.
Researchers at the University of Toronto, Canada, and Kyushu University, Japan, discovered that enhancing neuron production and subsequently altering neural connections in the hippocampus—through exercise or genetic intervention—enables mice to forget memories associated with trauma or drugs. The findings, reported in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, could offer a new approach to treating mental health conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or drug addiction.
PTSD is a mental health condition that can be triggered by experiencing or seeing a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, serious accident, or attack. Worldwide, around 3.9% of the general population has PTSD, with symptoms including vivid flashbacks and avoidance behaviors, such as staying away from places or pushing away people that remind them of the traumatic event.

How can rapidly emerging #AI develop into a trustworthy, equitable force? Proactive policies and smart governance, says Salesforce.
These initial steps ignited AI policy conversations amid the acceleration of innovation and technological change. Just as personal computing democratized internet access and coding accessibility, fueling more technology creation, AI is the latest catalyst poised to unlock future innovations at an unprecedented pace. But with such powerful capabilities comes large responsibility: We must prioritize policies that allow us to harness its power while protecting against harm. To do so effectively, we must acknowledge and address the differences between enterprise and consumer AI.
Enterprise versus consumer AI
Salesforce has been actively researching and developing AI since 2014, introduced our first AI functionalities into our products in 2016, and established our office of ethical and human use of technology in 2018. Trust is our top value. That’s why our AI offerings are founded on trust, security and ethics. Like many technologies, there’s more than one use for AI. Many people are already familiar with large language models (LLMs) via consumer-facing apps like ChatGPT. Salesforce is leading the development of AI tools for businesses, and our approach differentiates between consumer-grade LLMs and what we classify as enterprise AI.
Our guest in this episode is Dr. Mark Kotter. Mark is a neurosurgeon, stem cell biologist, and founder or co-founder of three biotech start-up companies that have collectively raised hundreds of millions of pounds: bit.bio, clock.bio, and Meatable.
In addition, Mark still conducts neurosurgeries on patients weekly at the University of Cambridge.
We talk to Mark about all his companies, but we start by discussing Meatable, one of the leading companies in the cultured meat sector. This is an area of technology which should have a far greater impact than most people are aware of, and it’s an area we haven’t covered before in the podcast.
Selected follow-ups:
• Dr Mark Kotter at the University of Cambridge (https://www.stemcells.cam.ac.uk/peopl…)
• Meatable (https://meatable.com/)
• bit.bio (https://www.bit.bio/)
• clock.bio (https://clock.bio/)
• After 25 years of hype, embryonic stem cells are still waiting for their moment (https://www.technologyreview.com/2023…) — Article in MIT Technology Review.
• The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 (https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/med…)
• Moo’s Law: An Investor’s Guide to the New Agrarian Revolution (https://www.harriman-house.com/mooslaw) — book by Jim Mellon.
• What is the climate impact of eating meat and dairy? (https://interactive.carbonbrief.org/w…)
• Guidance for businesses on cell-cultivated products and the authorisation process (https://www.food.gov.uk/business-guid…)
• Wild mammals make up only a few percent of the world’s mammals (https://ourworldindata.org/wild-mamma…) — Our World In Data.
• BlueRock Therapeutics (https://www.bluerocktx.com/)
• Therapies under development at bit.bio (https://www.bit.bio/therapeutics2023)
• Stem Cell Gene Therapy Shows Promise in ALS Trial (https://www.technologynetworks.com/ne…) — from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center.
Music: Spike Protein, by Koi Discovery, available under CC0 1.0 Public Domain Declaration.