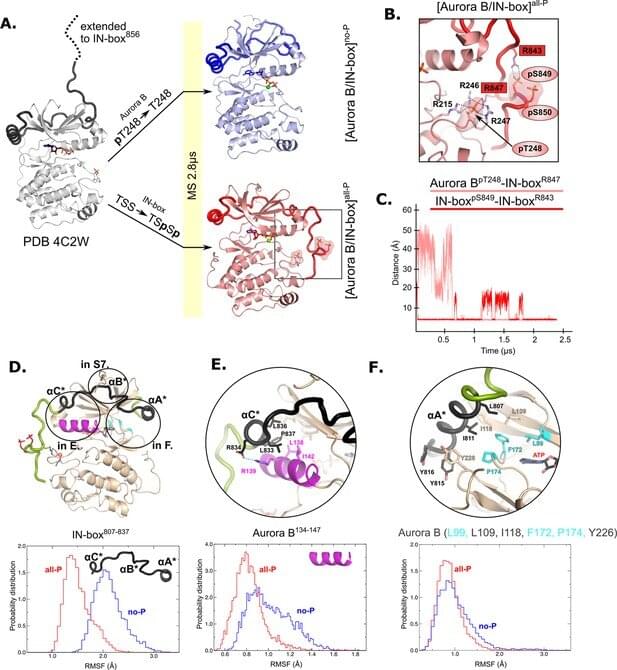
There has been a lot of buzz about all the ways that Artificial Intelligence could change the world, from the workplace to schools and day-to-day life as a whole, but the recent advancements in the field could spell the end of the traditional school classroom. In an interview with the British media outlet, The Guardian, reported on Friday (July 7) one of the world’s leading experts on AI made the prediction that for better or worse, AI might change classrooms.
How would things change?
Speaking about how AI could potentially change traditional school classrooms, a British computer scientist at the University of California, Berkeley, Professor Stuart Russell told The Guardian, “Education is the biggest benefit that we can look for in the next few years.”