New telomere supplements claim to slow aging with botanicals like ashwagandha. New research reveals the gap between marketing and human evidence.

Jim Al-Khalili explores emerging technologies powering the future of quantum, and looks at how we got here.
This Discourse was recorded at the Ri on 7 November 2025, in partnership with the Institute of Physics.
Watch the Q&A session for this talk here (exclusively for our Science Supporter members):
Join this channel as a member to get access to perks:
/ @theroyalinstitution.
Physicist and renowned broadcaster Jim Al-Khalili takes a look back at a century of quantum mechanics, the strangest yet most successful theory in all of science, and how it has shaped our world. He also looks forward to the exciting new world of Quantum 2.0 and how a deeper understanding of such counterintuitive concepts as quantum superposition and quantum entanglement is leading to the development of entirely new technologies, from quantum computers and quantum sensors to quantum cryptography and the quantum internet.
The United Nations has proclaimed 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, to celebrate the centenary of quantum mechanics and the revolutionary work of the likes of Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger. Together with the Institute of Physics, join us to celebrate the culmination of the International Year of Quantum at the penultimate Discourse of our Discover200 year.
-
The Math Inc. team is excited to introduce Gauss, a first-of-its-kind autoformalization agent for assisting human expert mathematicians at formal verification. Using Gauss, we have completed a challenge set by Fields Medallist Terence Tao and Alex Kontorovich in January 2024 to formalize the strong Prime Number Theorem (PNT) in Lean (GitHub).
The translation of human mathematics into verifiable machine code has long been a grand challenge. However, the cost of doing so is prohibitive, requiring scarce human expertise. In particular, after 18 months, Tao and Kontorovich recently announced intermediate progress in July 2025 toward their goal, obstructed by core difficulties in the field of complex analysis.
In light of such difficulties, we are pleased to announce that with Gauss, we have completed the project after three weeks of effort. Gauss can work autonomously for hours, dramatically compressing the labor previously reserved for top formalization experts. Along the way, Gauss formalized the key missing results in complex analysis, which opens up future initiatives previously considered unapproachable.
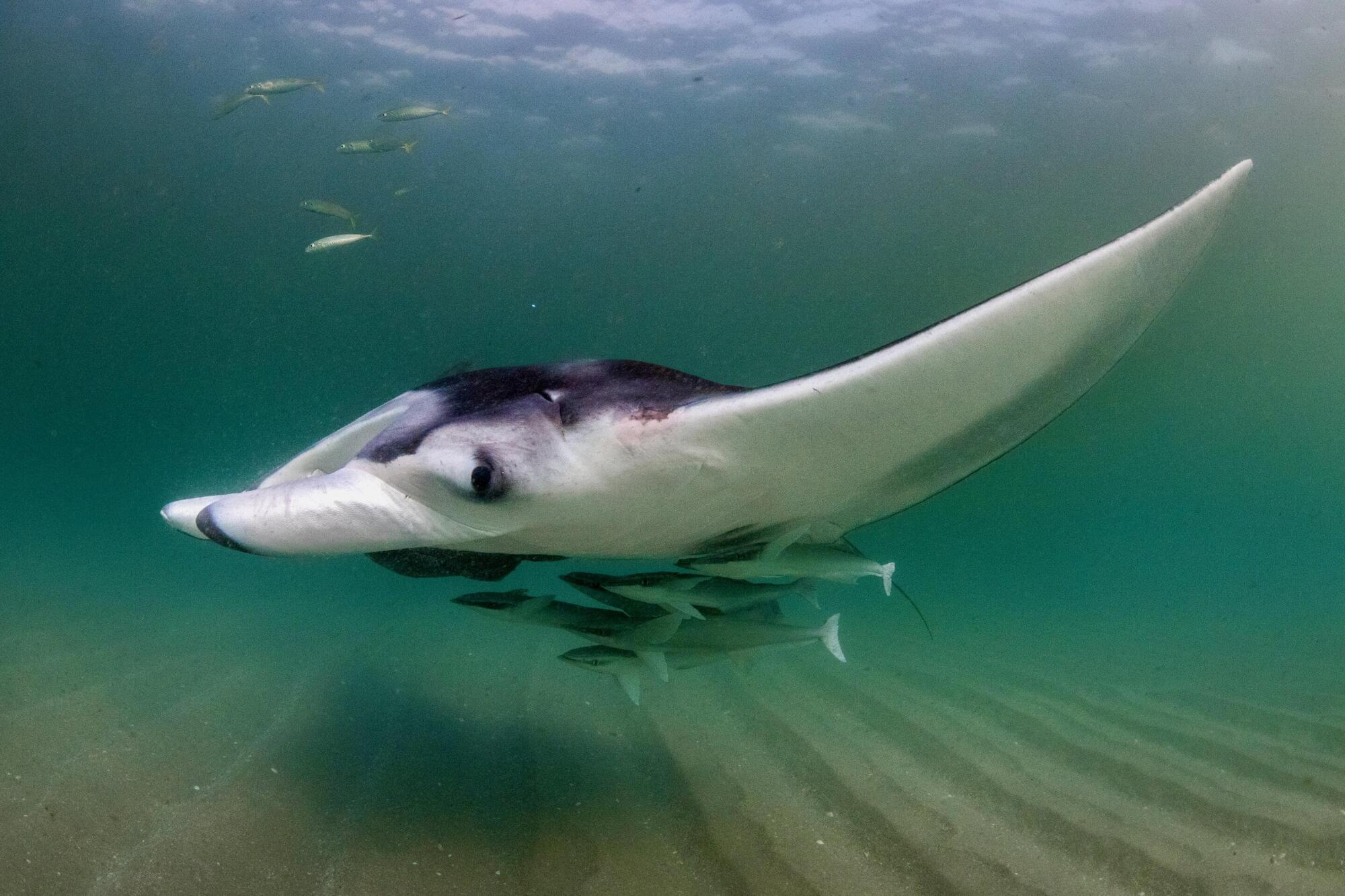

A new study from the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Marine Megafauna Foundation finds that young Caribbean manta rays (Mobula yarae) often swim with groups of other fish, creating small, moving ecosystems that support a variety of marine species.
The paper is published in the journal Marine Biology.
South Florida —particularly Palm Beach County—serves as a nursery for juvenile manta rays. For nearly a decade, the Marine Megafauna Foundation has been studying these rays and documenting the challenges they face from human activities near the coast, such as boat strikes and entanglement in fishing gear, which can pose significant threats to juvenile mantas.
But the report was also marked by the flaws of its technocratic conception. Crucially, the broader stakes of the global energy transition went ignored. This is a mistake in urgent need of correction. The decarbonization agenda is not simply about reordering markets or industrial policies, but in fact represents the crucible for a new geopolitical order.
Four years ago, the International Energy Agency (IEA) published a landmark report, “Net Zero by 2050: A Roadmap for the Global Energy Sector,” that proposed a technical blueprint for a global green energy transition by the middle of this century. The report focused on the economic and technological dimensions of this energy transition. It was an admirable effort that calls for careful study.
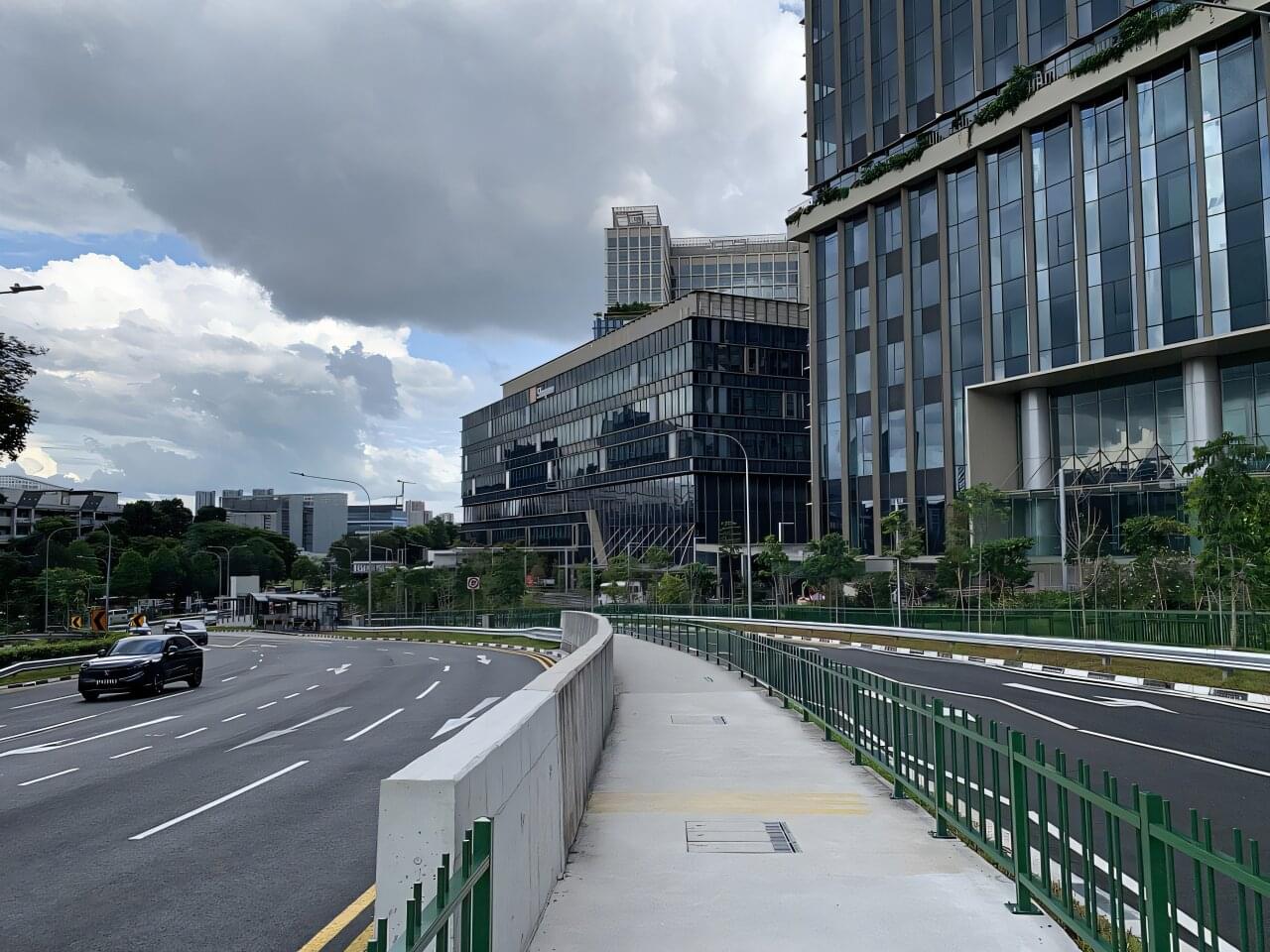

Compact, mixed-use districts are often assumed to naturally produce cleaner travel patterns, but the reality on the ground is far more complex.
In Singapore, for instance, two adjacent employment hubs—One-North and Science Park—share similar locations but differ sharply in how people move through them.
A new study from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) reveals why and offers a high-resolution approach to understanding where emissions accumulate within districts rather than across entire cities.
Researchers in the US have used quantum chemistry to explain why ozone catalysts degrade during water electrolysis.
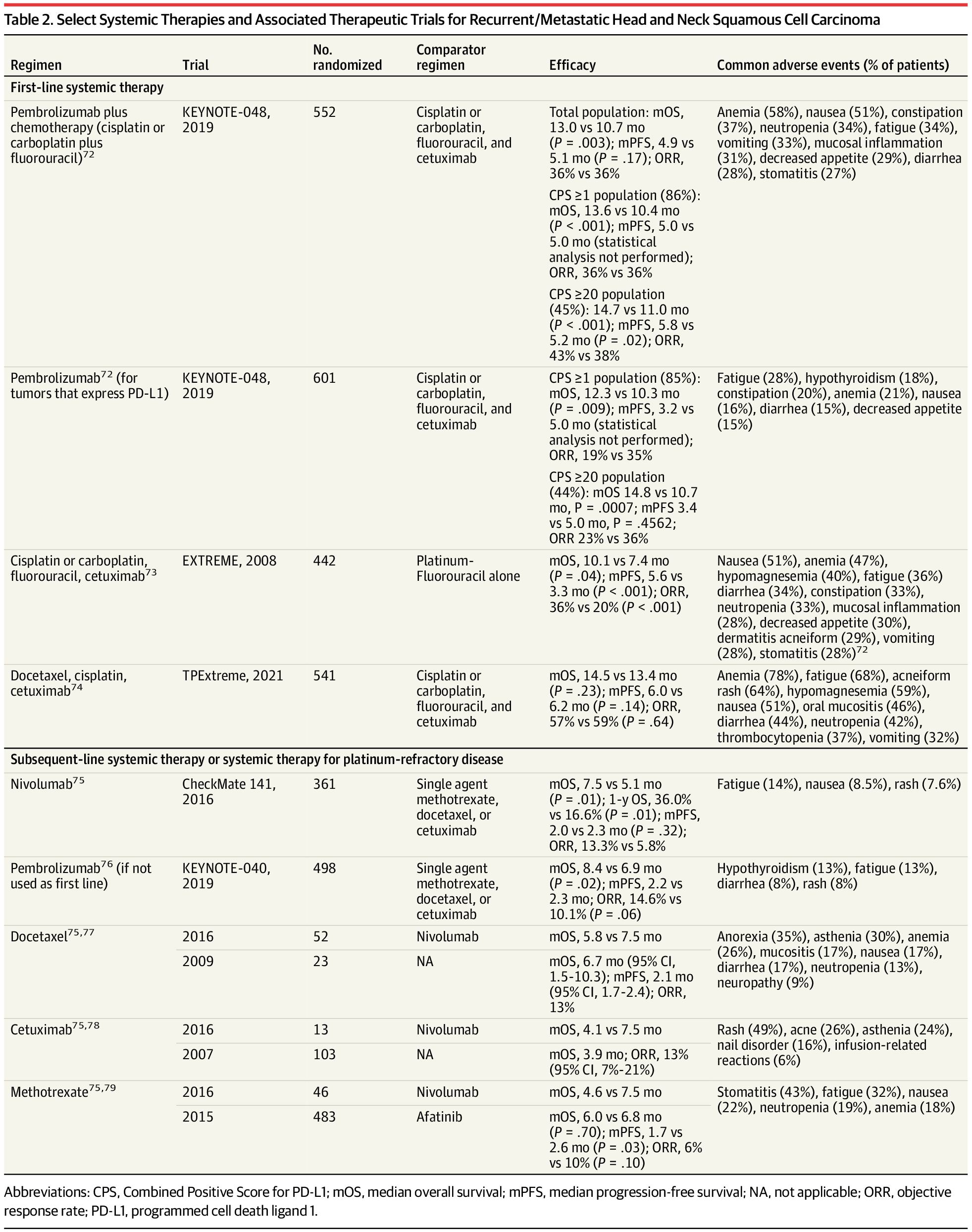
Head and neck cancer is the seventh most common cancer worldwide. In 2024, approximately 58 450 individuals were diagnosed with oral cavity and pharynx cancer and 12 650 were diagnosed larynx cancer in the US.
Although many malignancies originate in the head and neck region, the term head and neck cancer typically applies to tumors arising in the lining or mucosa of the upper aerodigestive tract. Approximately 90% of head and neck cancers are caused by squamous cell carcinoma.
This Review summarizes the epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) of the upper aerodigestive tract.
This review examines the epidemiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.

Check out Lokendens’ film, created in the style of found footage.