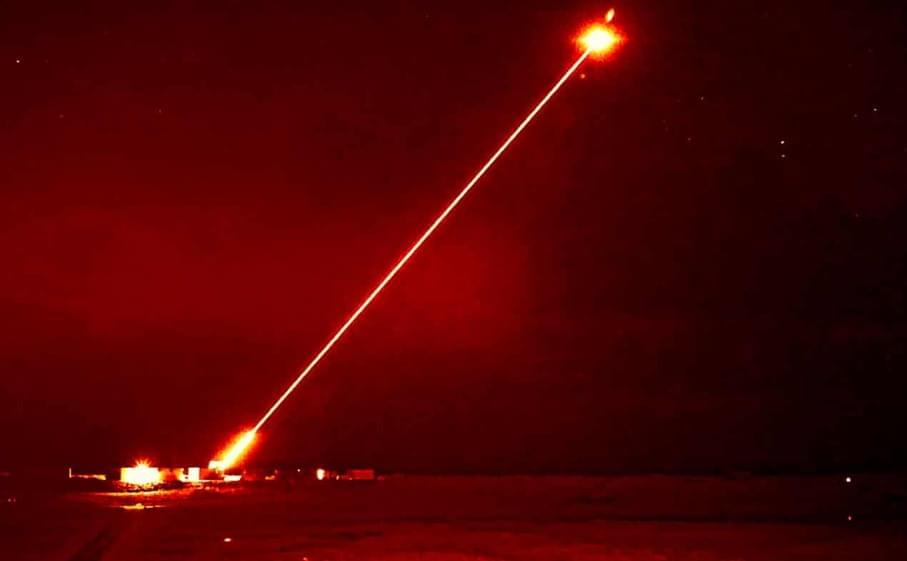
The DragonFire laser-directed energy weapon (LDEW) system has achieved the UK’s first high-power firing of a laser weapon against aerial targets during a trial at the MOD’s Hebrides Range.
The DragonFire is a line-of-sight weapon and can engage with any visible target, and its range is classified. The system is able to deliver a high-power laser over long ranges and requires precision equivalent to hitting a £1 coin from a kilometer away.
Laser-directed energy weapons are incredibly powerful and can engage targets at lightning-fast speeds. They use a concentrated beam of light to cut through their target, resulting in structural failure or other devastating outcomes if the warhead is targeted.