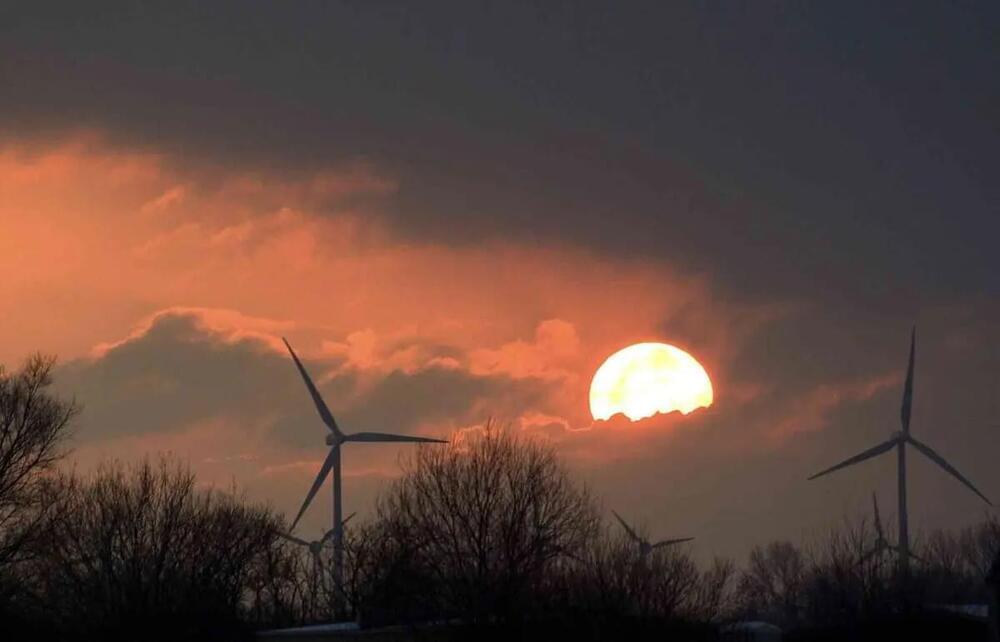
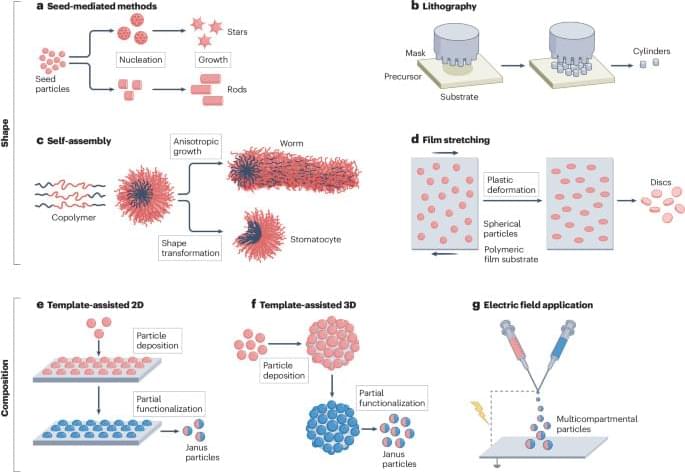
As summer approaches, electricity demand surges in the U.S., as homes and businesses crank up the air conditioning. To meet the rising need, many East Coast cities are banking on offshore wind projects the country is building in the Atlantic Ocean.
For electric grid operators, knowing how much wind power these offshore turbines can harvest is critical, but making accurate predictions can be difficult. A team of CU Boulder scientists and their collaborators are working to tackle the challenge.
In a paper published March 14 in Wind Energy Science, a team led by Dave Rosencrans, a doctoral student, and Julie K. Lundquist, a professor in the Department of Atmospheric and Ocean Sciences, estimates that offshore wind turbines in the Atlantic Ocean region, where the U.S. plans to build large wind farms, could take away wind from other turbines nearby, potentially reducing the farms’ power output by more than 30%.