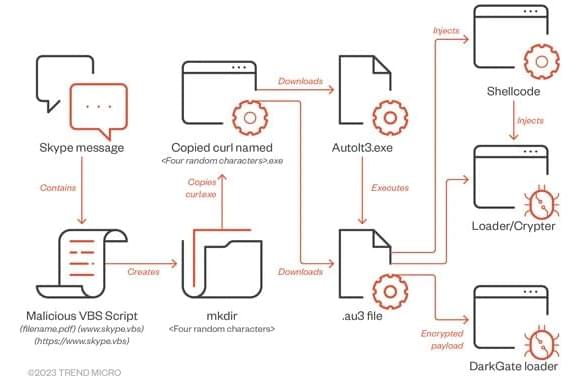
🚨 Beware! DarkGate #malware is now spreading through instant messaging apps like Skype & #Microsoft Teams. Stay cautious and don’t open suspicious documents!
Patch now if you haven’t already: Adobe Acrobat Reader exploits are in the wild. #Adobe
The Cybersecurity Infrastructure & Security Agency (CISA) this week added to its catalog of known exploited vulnerabilities an Adobe Acrobat Reader use-after-free bug.
Adobe Acrobat and Reader Document Cloud Versions 22.003.20282 and 22.003.20281 and earlier contain the flaw (CVE-2023–21608), as do Adobe Acrobat and Reader 20.005.30418 and earlier. The use-after-free vuln allows an attacker to remotely execute malicious code on a compromised account, and execute the exploit when a victim opens the rigged PDF file.
CISA recommends applying the latest updates to the affected software, which was patched in January of this year. Researchers who discovered and reported the vuln shared details of their findings in a February 2023 blog post.
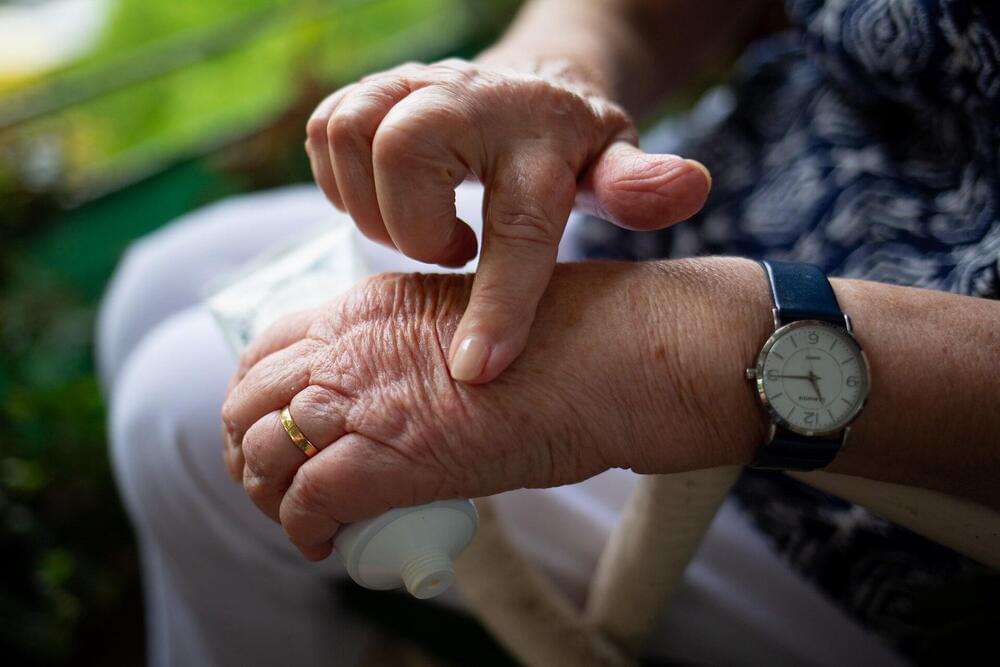
Relief could be on the way for people with painful hand osteoarthritis after a Monash University and Alfred Health-led study found an affordable existing drug can help. Until now there has been no effective treatment.
Published in The Lancet, the paper investigated methotrexate, a low-cost, effective treatment for inflammatory joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. It has been widely used in Australia and globally since the early 1980s.
Researchers found that methotrexate reduced symptoms in those with hand osteoarthritis (OA). A 20mg weekly oral dose over six months had a moderate effect in reducing pain and stiffness in patients with symptomatic hand OA.
🥼 Researchers from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience and the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain and Disease Research have shown that microRNA-132 can significantly affect different brain cells, with potential implications for Alzheimer’s disease ✔️
🔗
Research shows that microRNA-132 can significantly affect different brain cells, with potential implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Find out more.
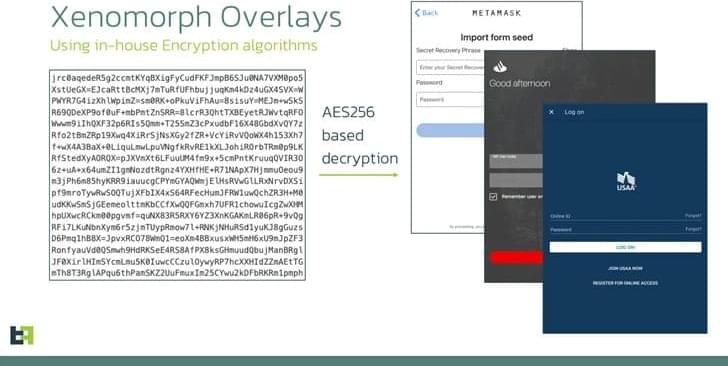
Beware of the new Xenomorph Android banking trojan variant.
Its Automatic Transfer System can initiate transactions, access balances, and even transfer funds – all without your knowledge.
Read:
A new variant of the Xenomorph Banking Trojan has been uncovered, targeting 35+ U.S. financial institutions.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have adapted their novel metasurface process to create an all-glass metasurface with birefringence, or dual refraction, properties. Learn how this achievement could transform waveplate technology for high-power laser systems such as the National Ignition Facility:
We support diverse research activities with talented staff, state-of-the-art facilities and core competencies. From internal collaboration to external partnerships, we work together to advance scientific discovery.
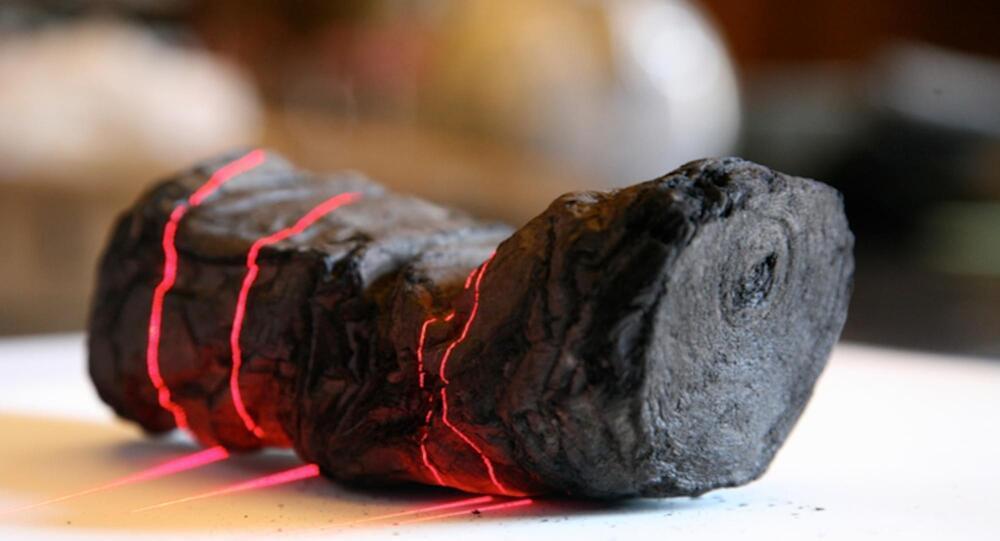
The carbonized scrolls are too delicate for human hands, but AI analysis found ‘purple’ amid the charred papyrus.
This week saw the release of a treasure trove of data from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Gaia mission, a space-based observatory that is mapping out the Milky Way in three dimensions. The newly released data includes half a million new stars and details about more than 150,000 asteroids within our solar system.
The overall aim of the Gaia mission is to create a full 3D map of our galaxy that includes not only stars, but also other objects like planets, comets, asteroids, and more. The mission was launched in 2013 and the data it collected is released in batches every few years, with previous releases including data on topics like the positions of over 1.8 billion stars.
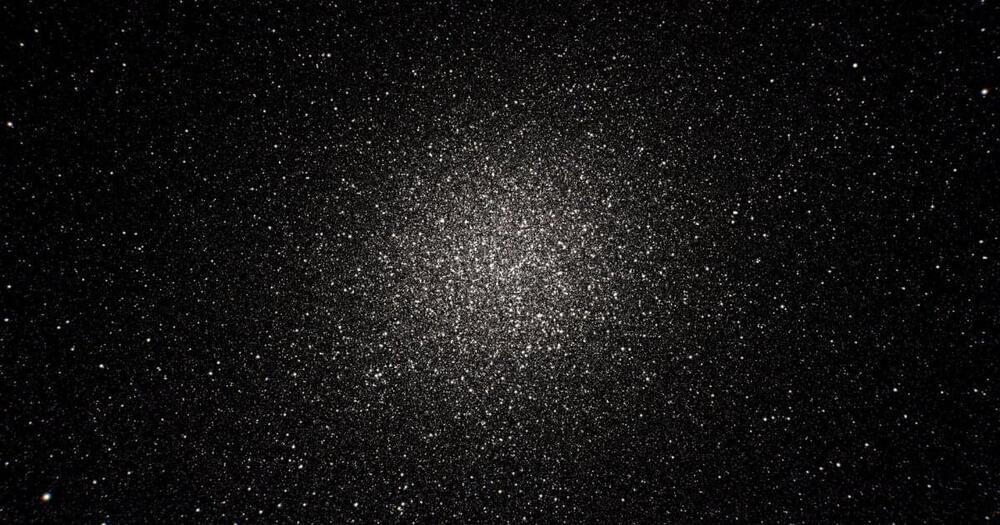
The new data release fills in some gaps from previous releases, particularly in areas of the sky that are densely packed with stars — such as the Omega Centauri globular cluster, shown above. The new view of this cluster shows 10 times as many stars as the previous data, with a total of 526,587 new stars identified.
The research paper explores the multifaceted role of the IL-17 family in immune response, covering everything from infection control to pathological conditions like autoimmune diseases and cancer. Future therapies may exploit IL-17’s unique signaling pathways to offer more targeted and cost-effective treatments.
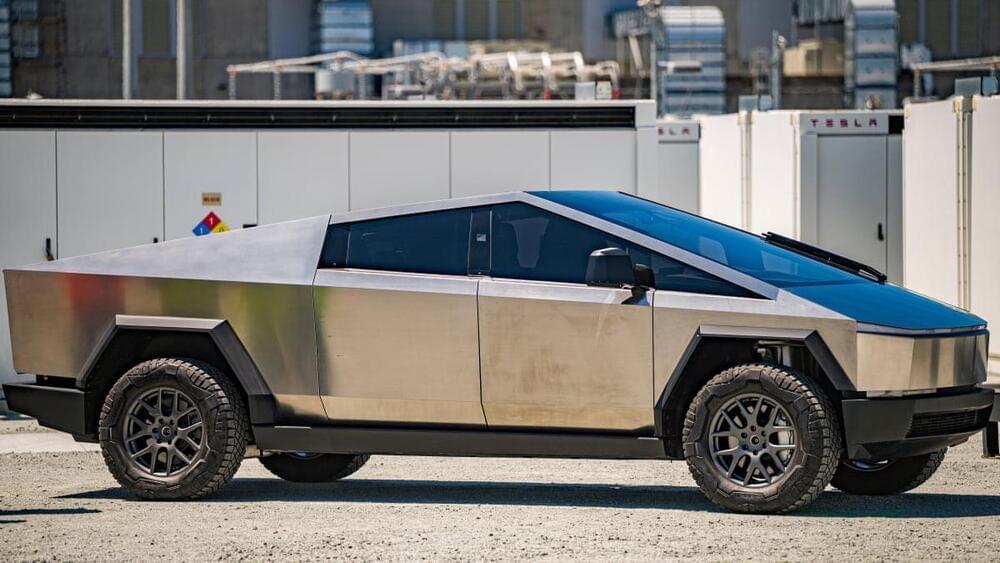
Tesla’s Cybertruck shows off its off-road capabilities on a notoriously tough Baja track.