Nanoscale materials present us with astonishing chemical and physical properties that help materialize applications such as single molecular sensing and minimally invasive photothermal therapy—which were once just theories—into reality.

Nanostructured high entropy alloys—metals made from a chaotic mix of several different elements—show a lot of promise for use in industries such as aerospace and automotive because of their strength and stability at high temperatures compared with regular metals.
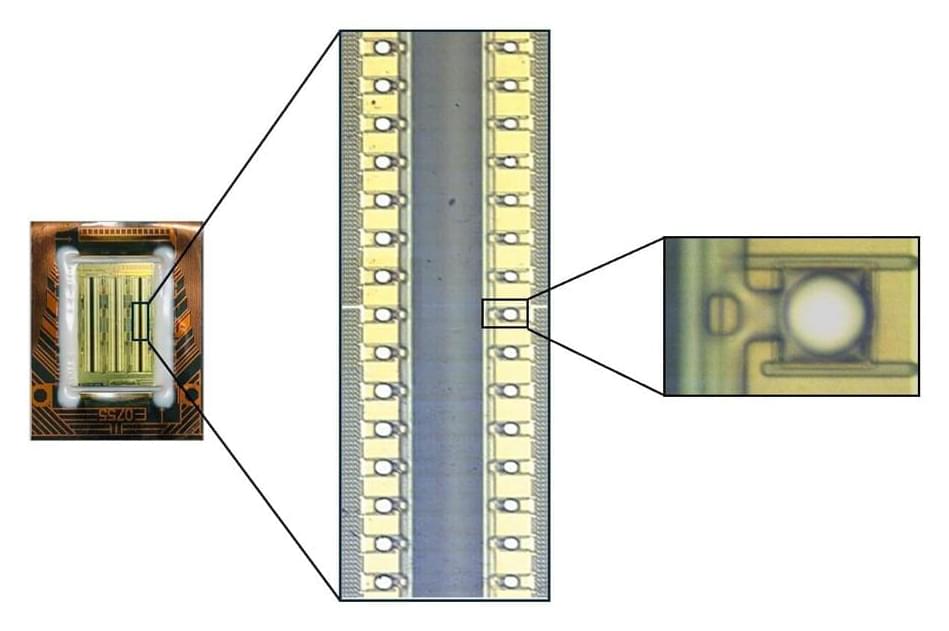
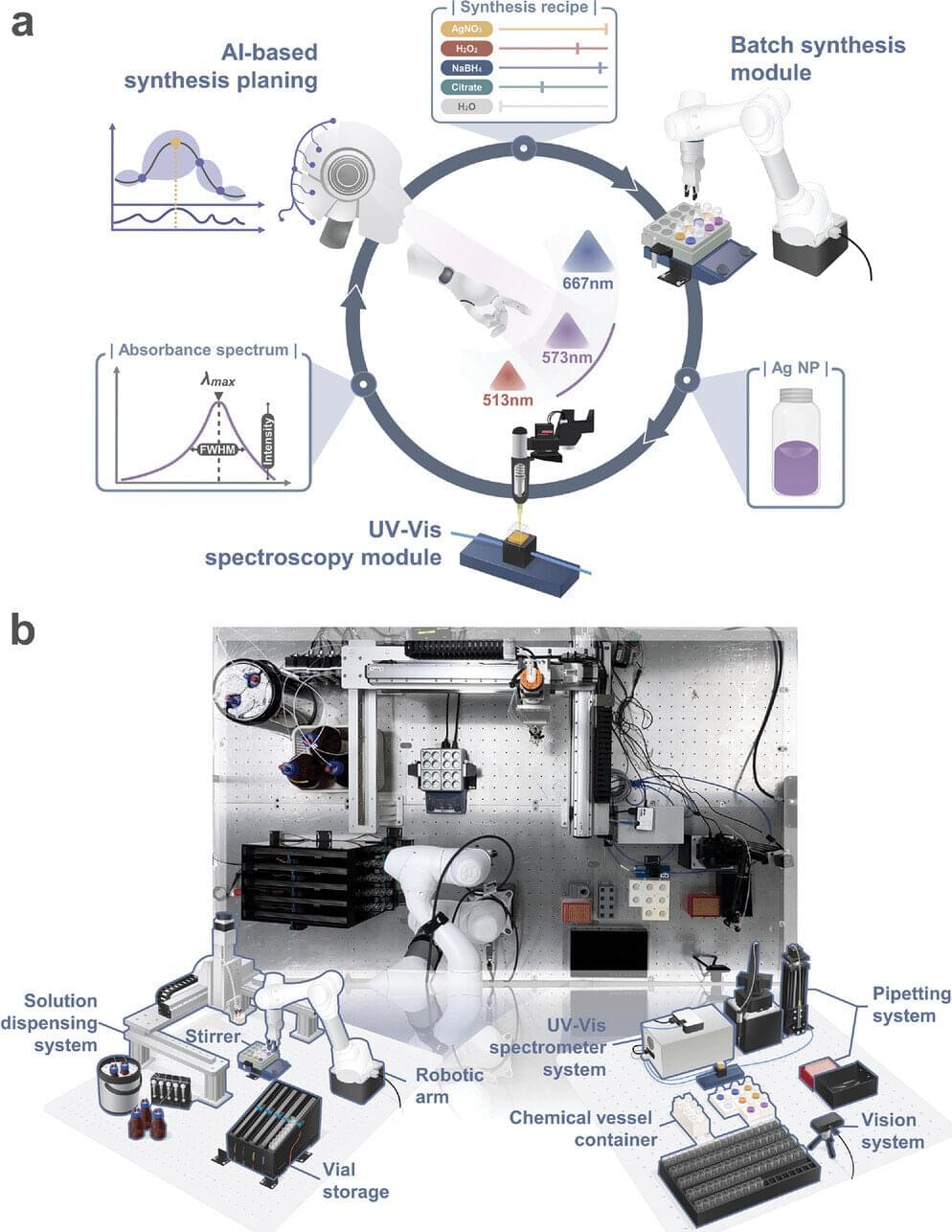
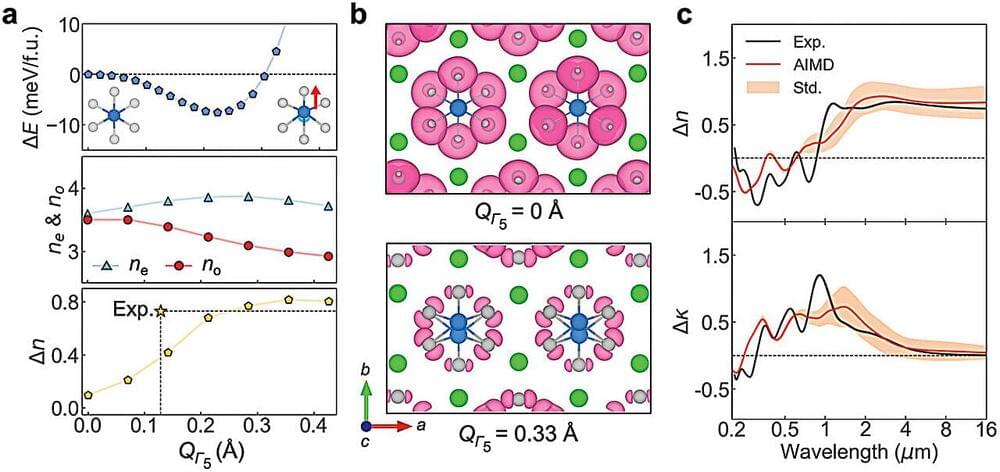
While we usually think of disorder as a bad thing, a team of materials science researchers led by Rohan Mishra, from Washington University in St. Louis, and Jayakanth Ravichandran, from the University of Southern California, have revealed that—when it comes to certain crystals—a little structural disorder might have big impacts on useful optical properties.

Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have developed a nanoparticle that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Their goal is to kill primary breast cancer tumors and brain metastases in one treatment, and their research shows the method can shrink breast and brain tumors in laboratory studies.

The team, led by Dipanjan Pan, Dorothy Foehr Huck & J. Lloyd Huck Chair Professor in Nanomedicine and professor of materials science and engineering and of nuclear engineering, published their work —the first of its kind, they said—in ACS Nano.
“Borophene is a very interesting material, as it resembles carbon very closely including its atomic weight and electron structure but with more remarkable properties. Researchers are only starting to explore its applications,” Pan said.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to understand the biological interactions of borophene and the first report of imparting chirality on borophene structures.”
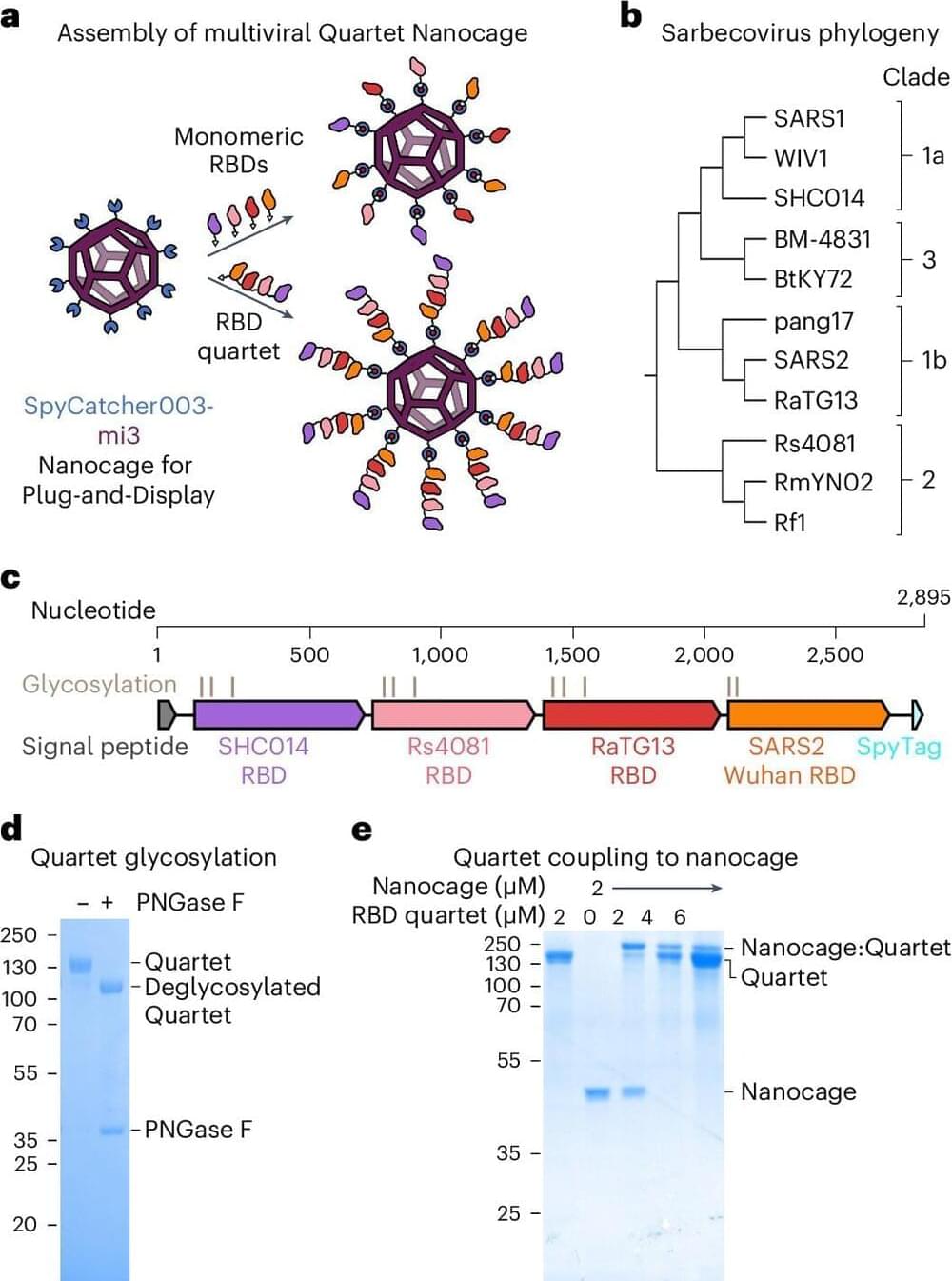

A Birmingham researcher has developed a new high-throughput device that produces libraries of nanomaterials using sustainable mechanochemical approaches.
Dr. Jason Stafford from the University’s School of Engineering invented the platform to create highly controllable reaction conditions and reduce the substantial amount of time researchers spend generating materials in the laboratory.
The benchtop device is a fully automated unit that can be programmed for parallel synthesis to produce a series of novel materials made in subtly different ways, so creating a library of advanced materials or product formulations for further testing and optimization.
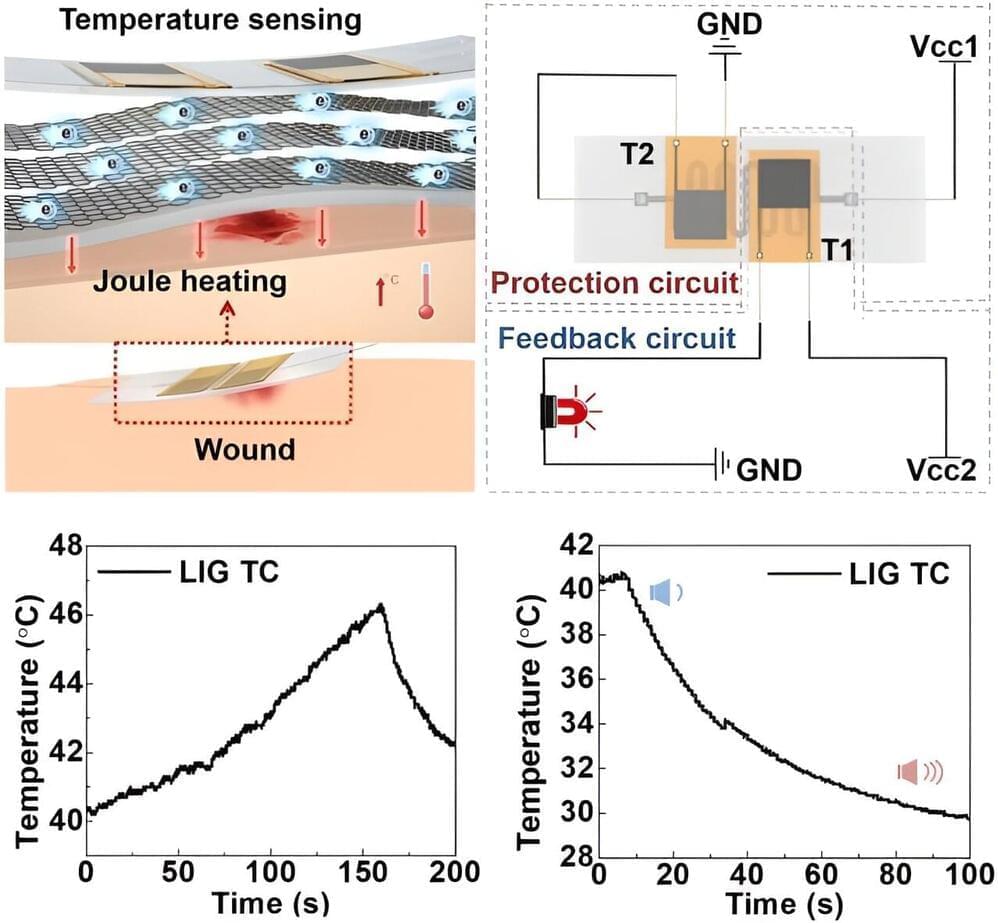
Skin functions as a sophisticated sensorial system in the human body, capable not only of detecting environmental stimuli—such as temperature, pressure, strain, and vibration—but also of actively responding to these changes. Among these, the temperature regulation capability of the skin plays a critical role in maintaining the stability of homeothermic animals.