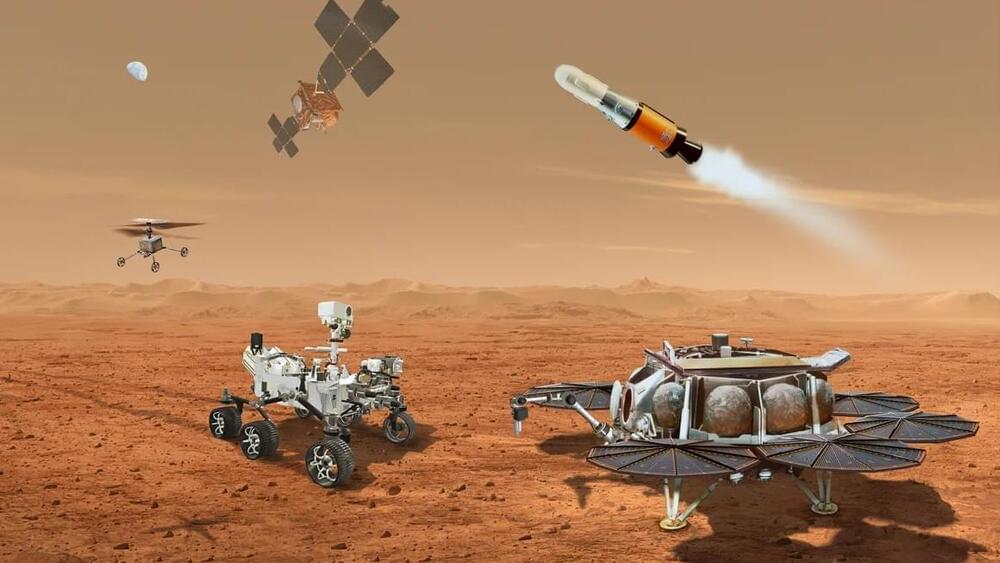
In 2021, NASA’s Perseverance rover landed in the Jezero Crater on Mars. For the next three years, this astrobiology mission collected soil and rock samples from the crater floor for eventual return to Earth. The analysis of these samples is expected to reveal much about Mars’ past and how it transitioned from being a warmer, wetter place to the frigid and desiccated place we know today. Unfortunately, budget cuts have placed the future of the proposed NASA-ESA Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission in doubt.
As a result, NASA recently announced that it was seeking proposals for more cost-effective and rapid methods of bringing the samples home. This will consist of three studies by NASA and the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHUAPL).
In addition, NASA has selected seven commercial partners for firm-fixed-price contracts for up to $1.5 million to conduct their own 90-day studies. Once complete, NASA will consider which proposals to integrate into the MSR mission architecture.