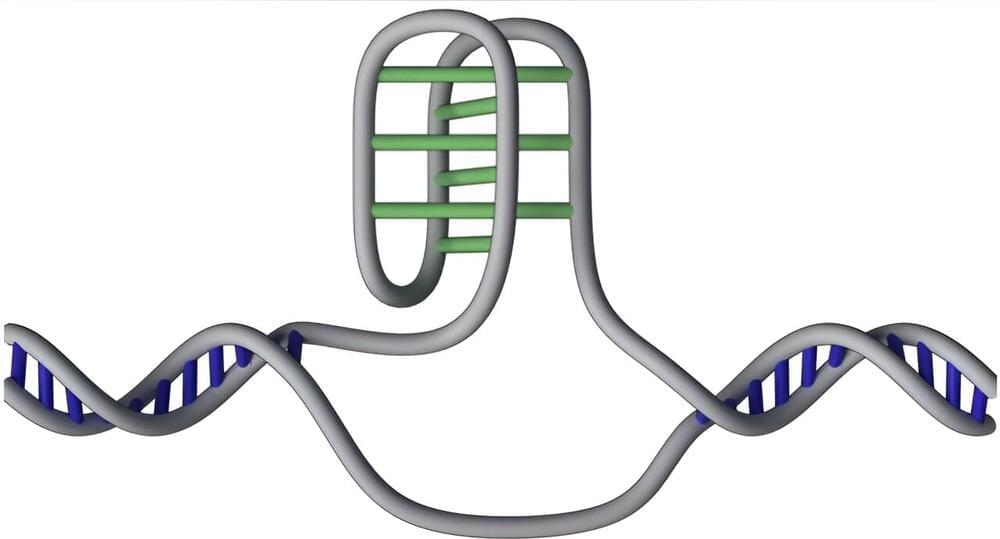
Researchers have mapped 50,000 of DNA’s mysterious “knots” in the human genome. The innovative study of DNA’s hidden structures may open up new approaches for treatment and diagnosis of diseases, including cancer.

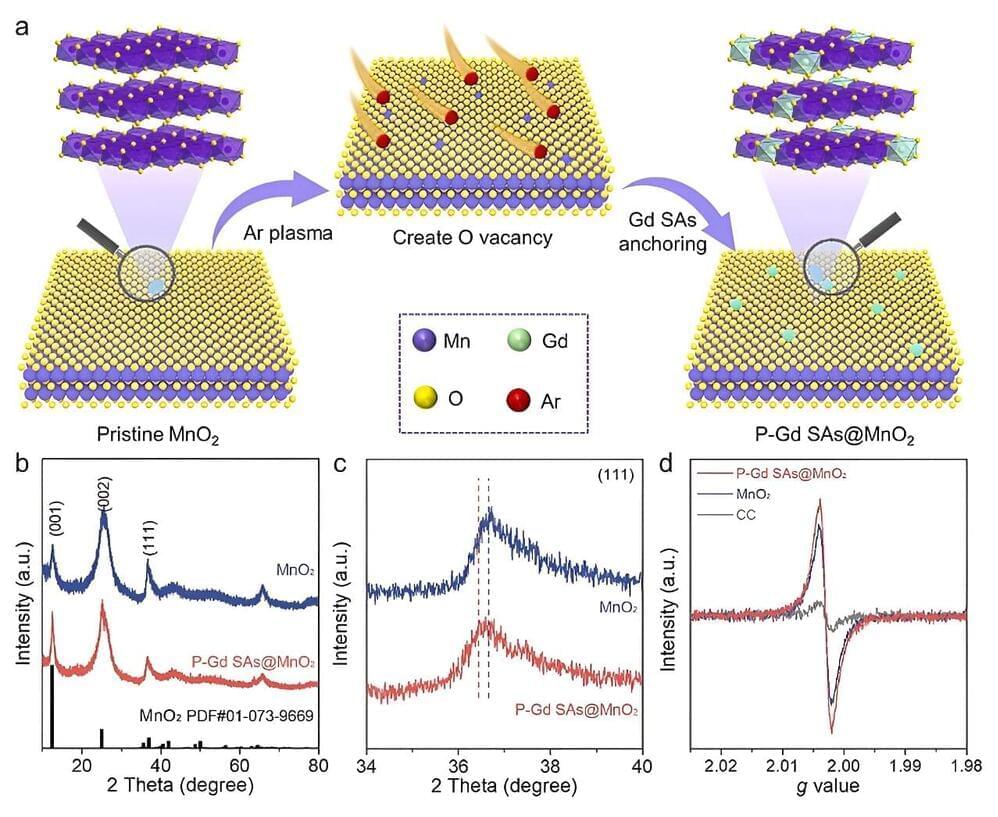
An international group of researchers has developed a novel approach that enhances the efficiency of the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), a key process in renewable energy technologies. By introducing rare earth single atoms into manganese oxide (MnO2), the group successfully modulated oxygen electronic states, leading to unprecedented improvements in OER performance.
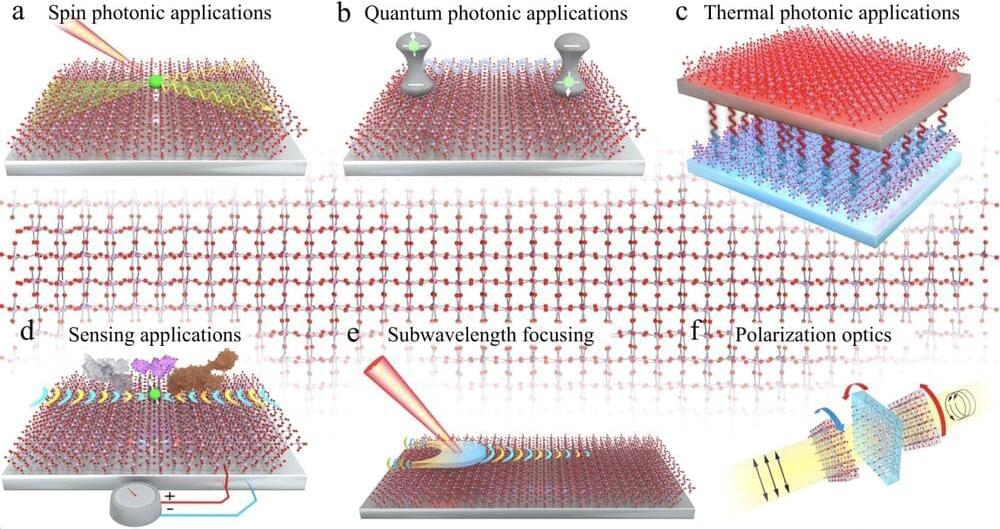
A recent study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers provides fundamental insight into how light, electrons, and crystal vibrations interact in materials. The research has implications for developing on-chip architectures for quantum information processing, significantly reducing fabrication constraints, and thermal management.
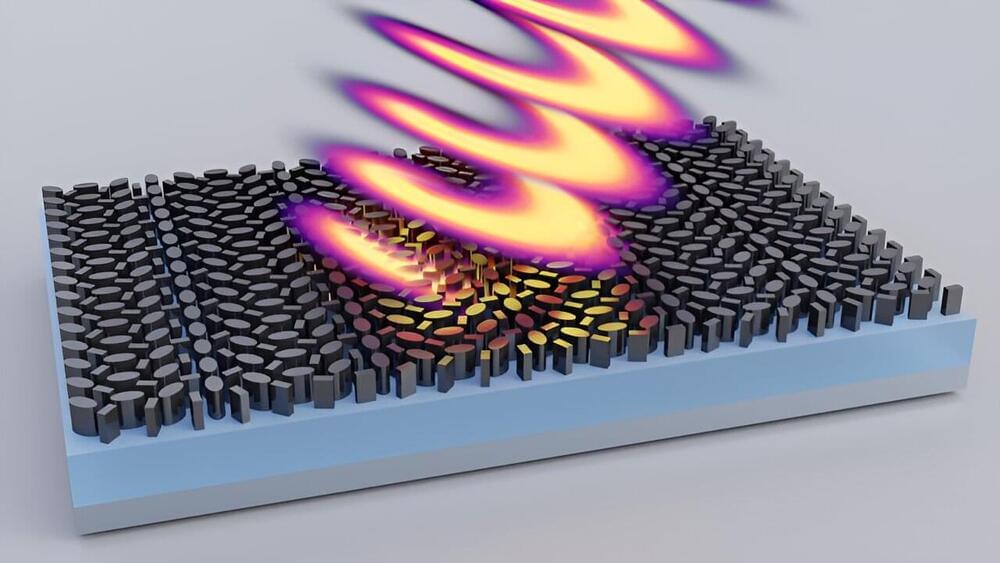
Researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have experimentally demonstrated that metasurfaces (two-dimensional materials structured at the nanoscale) can precisely control the optical properties of thermal radiation generated within the metasurface itself. This pioneering work, published in Nature Nanotechnology, paves the way for creating custom light sources with unprecedented capabilities, impacting a wide array of scientific and technological applications.
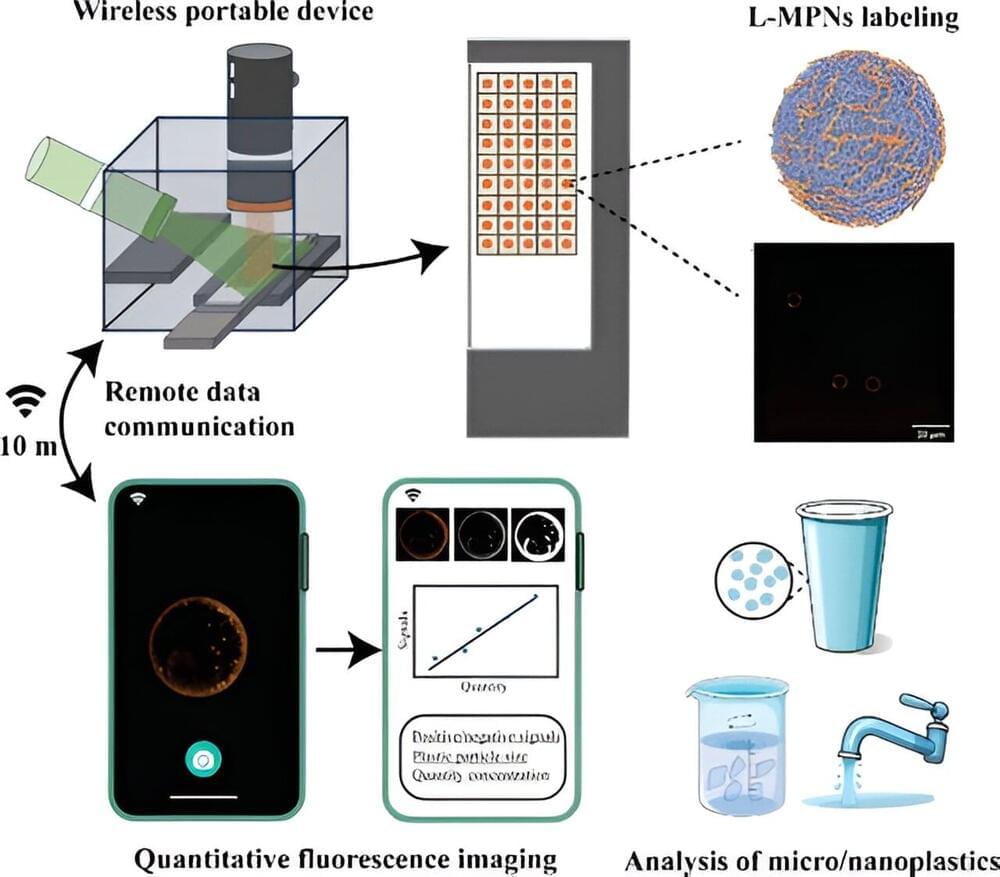
Micro-and nanoplastics are in our food, water and the air we breathe. They are showing up in our bodies, from testicles to brain matter. Now, University of British Columbia researchers have developed a low-cost, portable tool to accurately measure plastic released from everyday sources like disposable cups and water bottles.
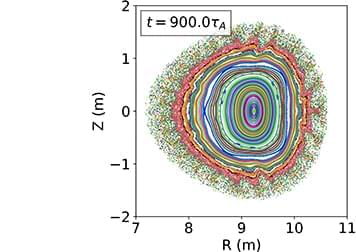
We use the new simulation capabilities of the extended-magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) code, M3D-C1, to investigate the nonlinear MHD properties of a reactor-scale quasisymmetric stellarator equilibrium. Our model captures the self-consistent evolution of the magnetic field, temperature, density, and flow profiles without imposing restrictions on the structure of the first. We include the effects of resistivity using a realistic temperature-dependent Spitzer model, along with a model for heat transport that captures the key physical characteristic, namely, strongly anisotropic diffusion in directions perpendicular and parallel to the magnetic field. We consider a quasi-axisymmetric, finite-pressure equilibrium that was optimized for self-consistent bootstrap current, quasi-symmetry, and energetic particle confinement. Our assessment finds that the equilibrium is highly unstable to interchange-like pressure-driven instabilities near the plasma edge. The initially unstable modes rapidly destabilize other modes in the direction of the N-fold rotational symmetry (toroidal, in this case). For this equilibrium, N = 2, meaning destabilization of a large number of even-numbered toroidal Fourier modes. Thus, field-periodicity is likely to be an important factor in the nonlinear MHD stability characteristics of optimized stellarators.
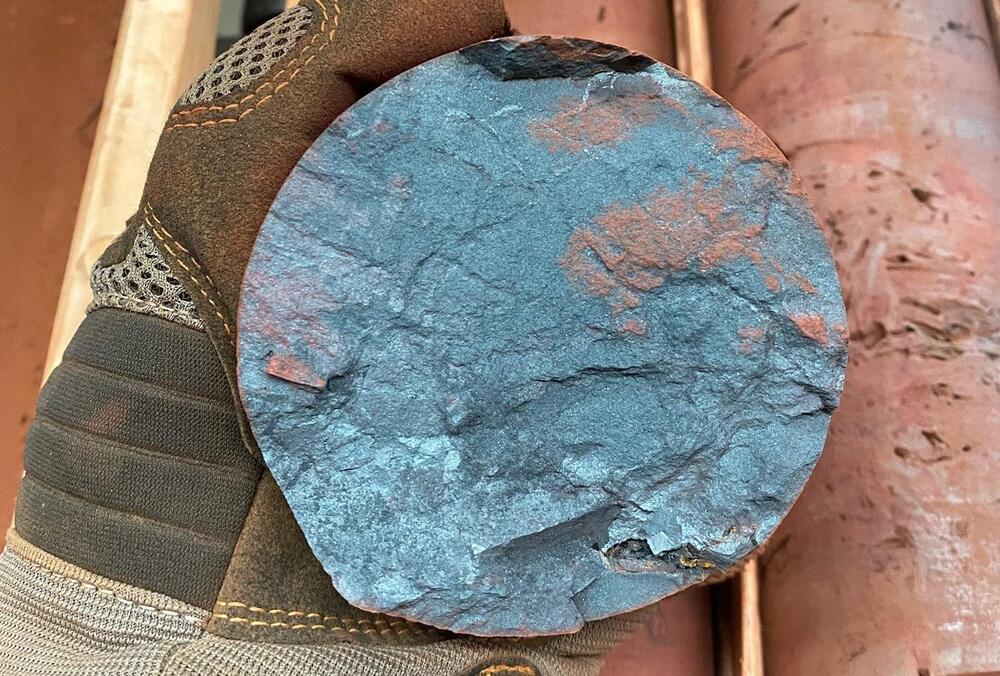

Curtin University researchers found that Western Australia’s Hamersley iron ore deposits are one billion years younger than previously believed, formed during significant geological events 1.4 to 1.1 billion years ago.
Research conducted by Curtin University has uncovered that the vast iron ore deposits in Western Australia’s Hamersley Province are approximately one billion years younger than previously estimated. This finding could significantly boost the search for more of the resource.
Using a new geochronology technique to accurately measure the age of iron oxide minerals, researchers found the Hamersley deposits formed between 1.4 and 1.1 billion years ago, rather than 2.2 billion years ago as previously estimated.
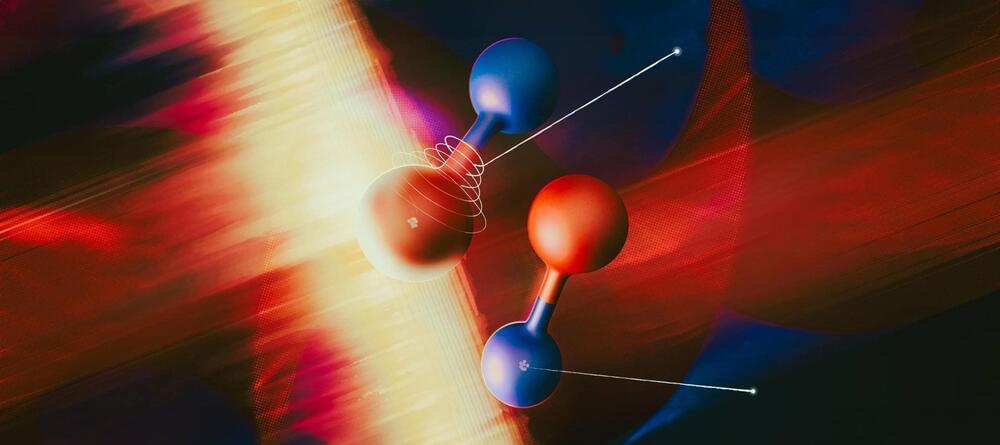
Researchers at SLAC have made groundbreaking strides in understanding the photoelectric effect, initially described by Einstein.
They’ve developed a technique using attosecond X-ray pulses to measure electron-emission delays, revealing discrepancies in existing theories by showing larger-than-expected delays. Their method provides a new tool to study electron-electron interactions, which are fundamental to many technologies, including semiconductors and solar cells.
New Photoelectric Effect Insights
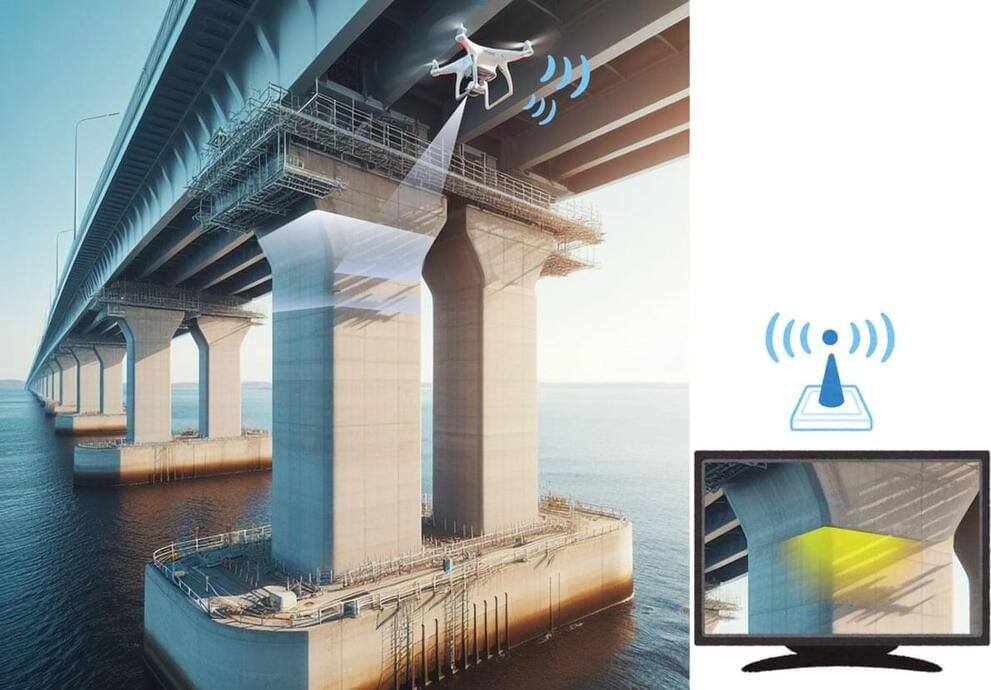

A new material developed by Tohoku University records and stores stress history in structures through a luminescent effect, offering an innovative solution to monitor aging infrastructure without needing power or complex equipment.
Identifying deteriorating infrastructure can be as challenging as fixing it. However, researchers at Tohoku University have made this process easier with the development of an innovative new material.
The material responds to mechanical stimuli by recording stress history through a luminescent effect called an afterglow. This information is stored for a long time, and by applying the material to the surfaces of structures, researchers can observe changes in the afterglow to determine the amount of stress the material has experienced.