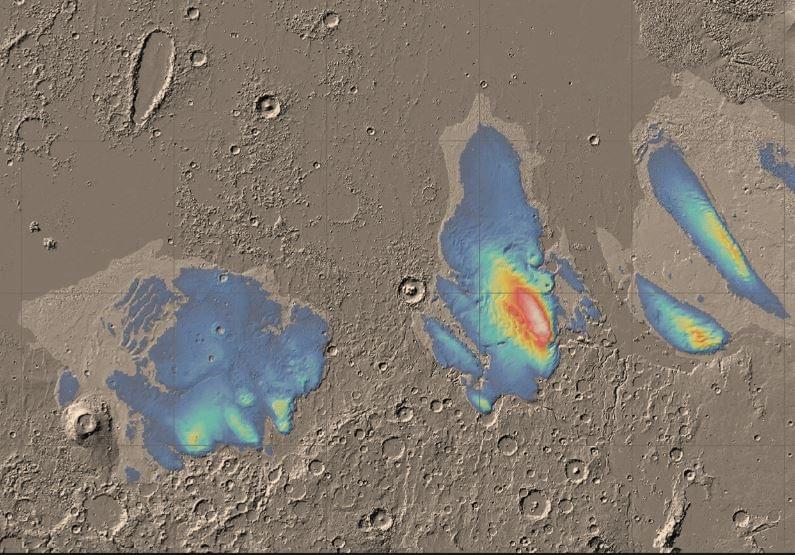
Windswept piles of dust, or layers of ice? ESA’s Mars Express has revisited one of Mars’s most mysterious features to clarify its composition. Its findings suggest layers of water ice stretching several kilometers below ground—the most water ever found in this part of the planet.
Over 15 years ago, Mars Express studied the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), revealing massive deposits up to 2.5 km deep. From these early observations, it was unclear what the deposits were made of—but new research now has an answer.
“We’ve explored the MFF again using newer data from Mars Express’s MARSIS radar, and found the deposits to be even thicker than we thought: up to 3.7 km thick,” says Thomas Watters of the Smithsonian Institution, U.S., lead author of both the new research, published in Geophysical Research Letters, and the initial 2007 study. “Excitingly, the radar signals match what we’d expect to see from layered ice, and are similar to the signals we see from Mars’s polar caps, which we know to be very ice rich.”