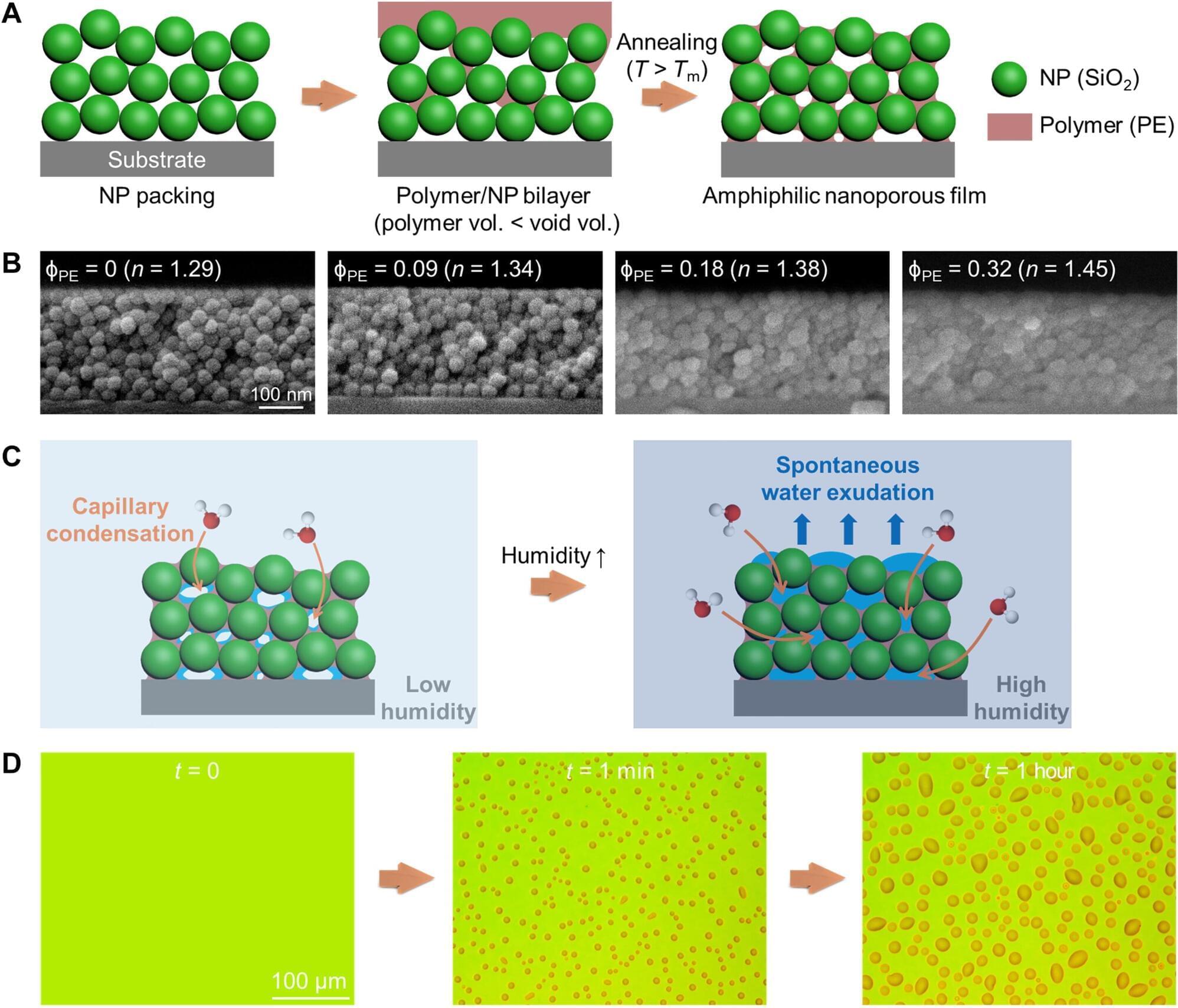
A serendipitous observation in a Chemical Engineering lab at Penn Engineering has led to a surprising discovery: a new class of nanostructured materials that can pull water from the air, collect it in pores and release it onto surfaces without the need for any external energy.
The research, published in Science Advances, describes a material that could open the door to new ways to collect water from the air in arid regions and devices that cool electronics or buildings using the power of evaporation.
The interdisciplinary team includes Daeyeon Lee, Russell Pearce and Elizabeth Crimian Heuer Professor in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE); Amish Patel, Professor in CBE; Baekmin Kim, a postdoctoral scholar in Lee’s lab and first author; and Stefan Guldin, Professor in Complex Soft Matter at the Technical University of Munich.