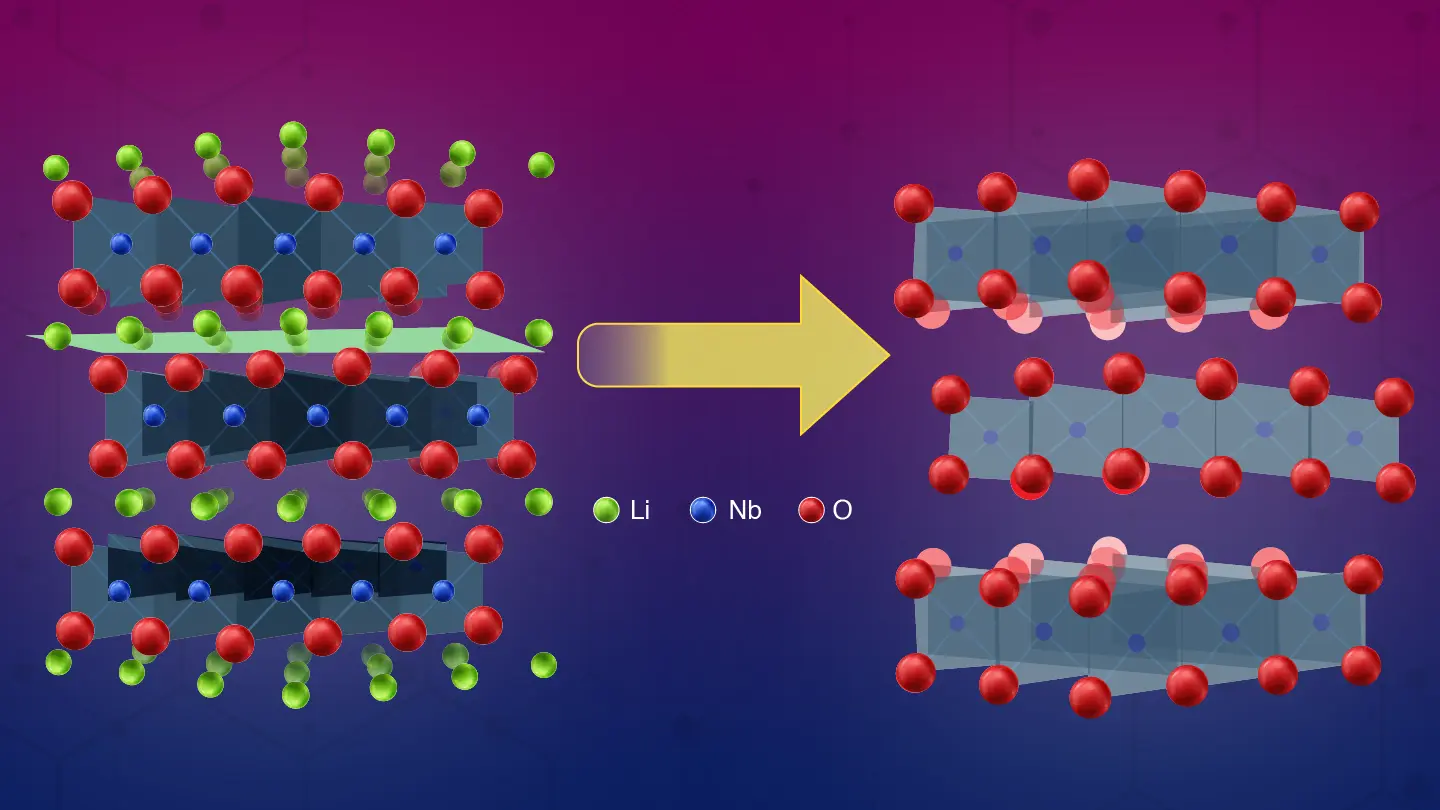
A new van der Waals oxide combines strongly correlated properties with 2D features—opening doors to next-generation materials.


Researchers at Örebro University have developed two new AI models that can analyse the brain’s electrical activity and accurately distinguish between healthy individuals and patients with dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
“Early diagnosis is crucial in order to be able to take proactive measures that slow down the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life,” says Muhammad Hanif, researcher in informatics at Örebro University.
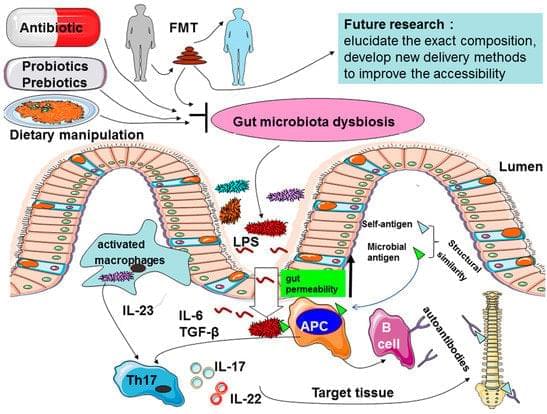
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease primarily affecting the sacroiliac joints and the spine, for which the pathogenesis is thought to be a result of the combination of host genetic factors and environmental triggers. However, the precise factors that determine one’s susceptibility to AS remain to be unraveled. With 100 trillion bacteria residing in the mammalian gut having established a symbiotic relation with their host influencing many aspects of host metabolism, physiology, and immunity, a growing body of evidence suggests that intestinal microbiota may play an important role in AS. Several mechanisms have been suggested to explain the potential role of the microbiome in the etiology of AS, such as alterations of intestinal permeability, stimulation of immune responses, and molecular mimicry.



Researchers Rachel Ruttan and Katherine DeCelles of the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management are anything but neutral on neutrality. The next time you’re tempted to play it safe on a hot-button topic, their evidence-based advice is to consider saying what you really think.
That’s because their recent research, based on more than a dozen experiments with thousands of participants, reveals that people take a dim view of others’ professed neutrality on controversial issues, rating them just as morally suspect as those expressing an opposing viewpoint, if not worse.
“Neutrality gives you no advantage over opposition,” says Prof. Ruttan, an associate professor of organizational behavior and human resource management with an interest in moral judgment and prosocial behavior. “You’re not pleasing anyone.”
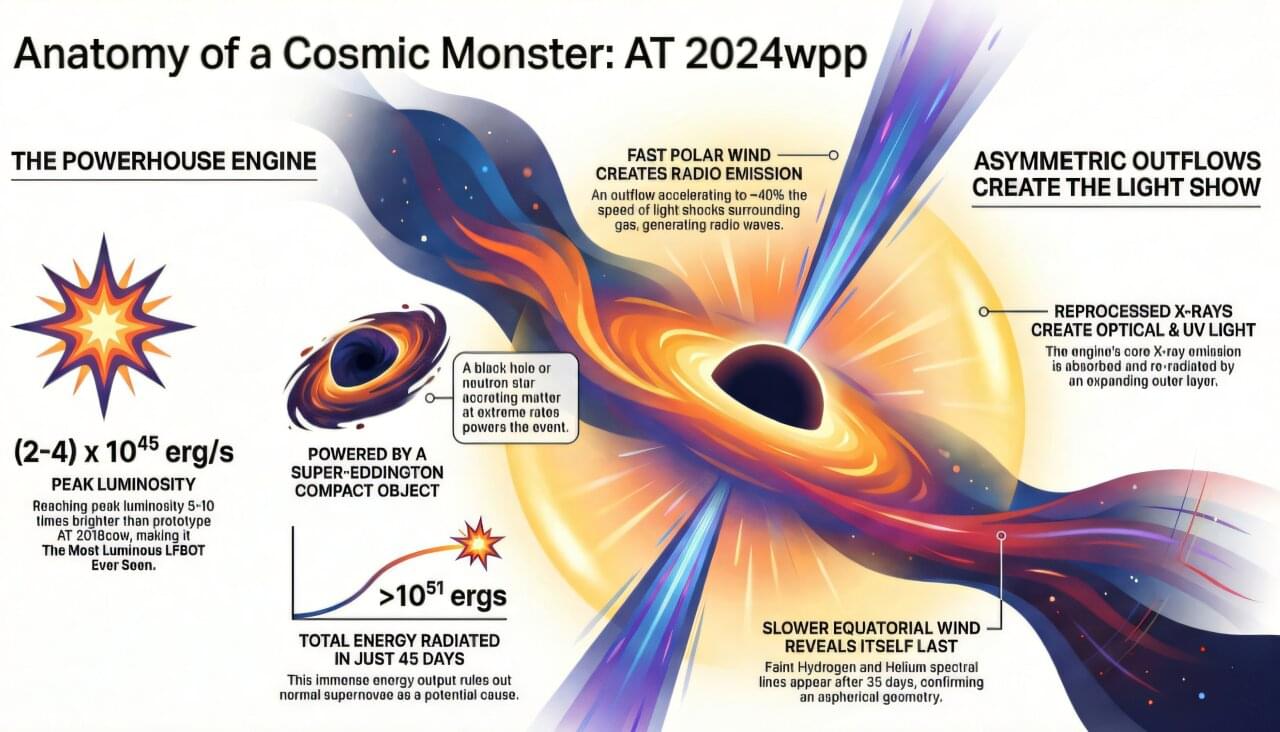
Among the more puzzling cosmic phenomena discovered over the past few decades are brief and very bright flashes of blue and ultraviolet light that gradually fade away, leaving behind faint X-ray and radio emissions. With slightly more than a dozen discovered so far, astronomers have debated whether they are produced by an unusual type of supernova or by interstellar gas falling into a black hole.
Analysis of the brightest such burst to date, discovered last year, shows that they’re neither.
Instead, a team of astronomers led by researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, concluded that these so-called luminous fast blue optical transients (LFBOTs) are caused by an extreme tidal disruption, where a black hole of up to 100 times the mass of our sun completely shreds its massive star companion within days.
When the most massive stars reach the ends of their lives, they blow up in spectacular supernova explosions, which seed the universe with heavy elements such as carbon and iron. Another type of explosion—the kilonova—occurs when a pair of dense dead stars, called neutron stars, smash together, forging even heavier elements such as gold and uranium. Such heavy elements are among the basic building blocks of stars and planets.
So far, only one kilonova has been unambiguously confirmed to date, a historic event known as GW170817, which took place in 2017. In that case, two neutron stars smashed together, sending ripples in space-time, known as gravitational waves, as well as light waves across the cosmos.
The cosmic blast was detected in gravitational waves by the National Science Foundation’s Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) and its European partner, the Virgo gravitational-wave detector, and in light waves by dozens of ground-based and space telescopes around the world.
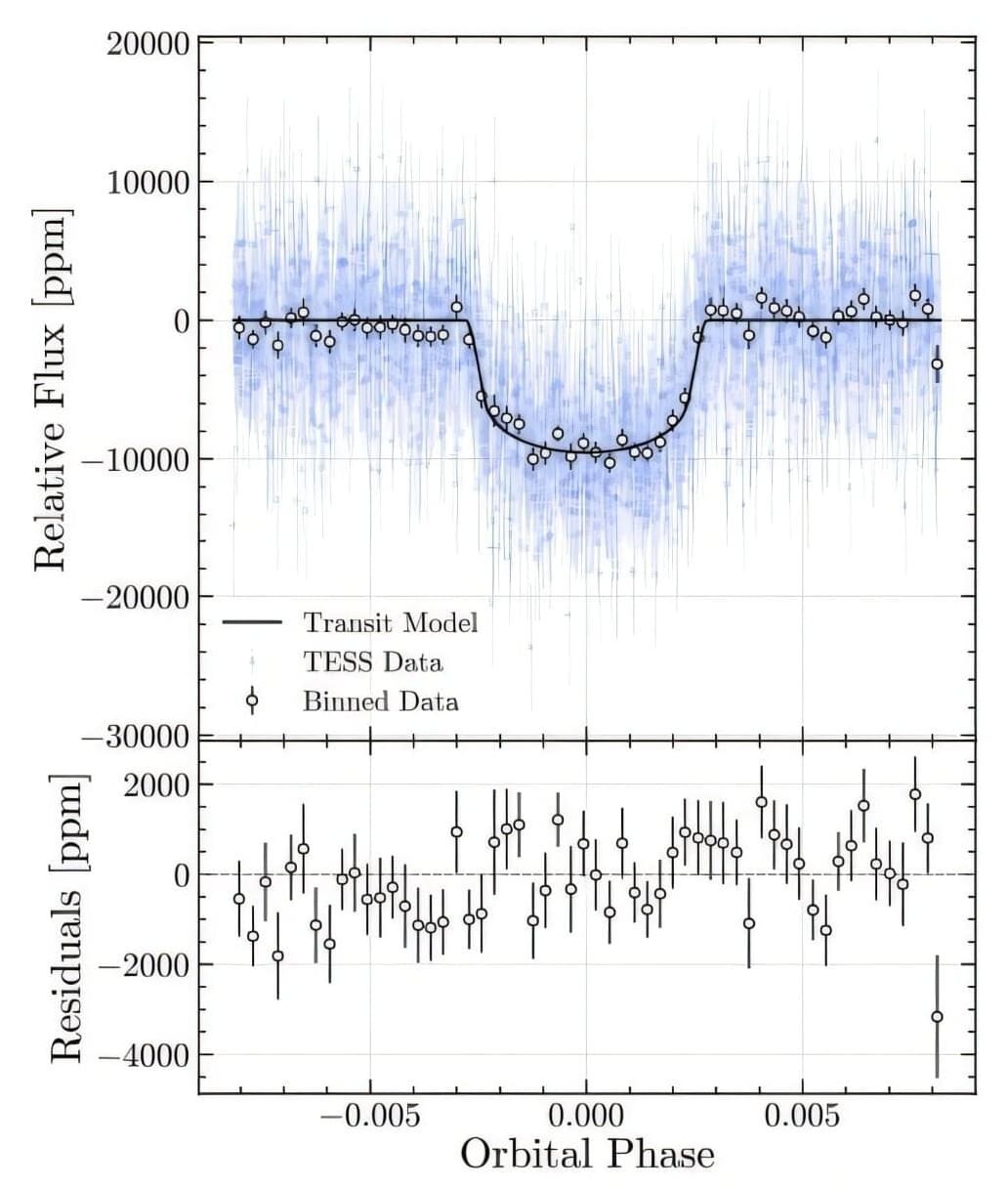
Astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) and elsewhere report the discovery of a new brown dwarf about 60 times more massive than Jupiter. The newfound substellar object, designated TOI-7019 b, is a brown dwarf known to orbit a star that is part of the Milky Way’s ancient thick disk. The finding is detailed in a paper published December 5 on the arXiv preprint server.
Brown dwarfs (BDs) are intermediate objects between planets and stars, occupying the mass range between 13 and 80 Jupiter masses (0.012 and 0.076 solar masses). However, although many brown dwarfs have been detected to date, these objects orbiting other stars are a rare find.
Recently, a team of astronomers led by CfA’s Jea Adams Redai found another rare brown dwarf, which is a companion to the star TOI-7019. This star was initially observed with NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), which detected a transit signal in its light curve. Now, follow-up observations of this star confirmed that the transit signal is produced by a substellar object.

In a review of previous studies, McMaster University researchers observe a stronger signal for psilocybin as a treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder than cannabinoids.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder involves persistent, intrusive thoughts and repetitive mental or physical behaviors, and requires long-term treatment to alleviate symptoms. The ethology of the disorder appears complex, involving multiple biological pathways. Imbalances in central serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate activities are widely thought to play a causative role, placing neurochemistry at the center of many treatment strategies.
First-line treatment includes selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behavioral therapy using exposure and response prevention. Roughly 40–60% of patients remain unresponsive to psychotherapy or pharmacotherapy, alone or combined, placing many people in the category of treatment-resistant OCD.