Although it’s not the first time this was hypothesized, this study is the first time researchers looked at the presence of gingipains within the brains of diseased patients. Even more, the patients themselves were never even diagnosed with Alzheimer’s.
“Our identification of gingipain antigens in the brains of individuals with AD and also with AD pathology but no diagnosis of dementia argues that brain infection with P. gingivalis is not a result of poor dental care following the onset of dementia or a consequence of late-stage disease, but is an early event that can explain the pathology found in middle-aged individuals before cognitive decline,” the authors explained.
While this isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer to what causes Alzheimer’s, it’s a step in the right direction to finding the reasoning behind this life-altering disease.
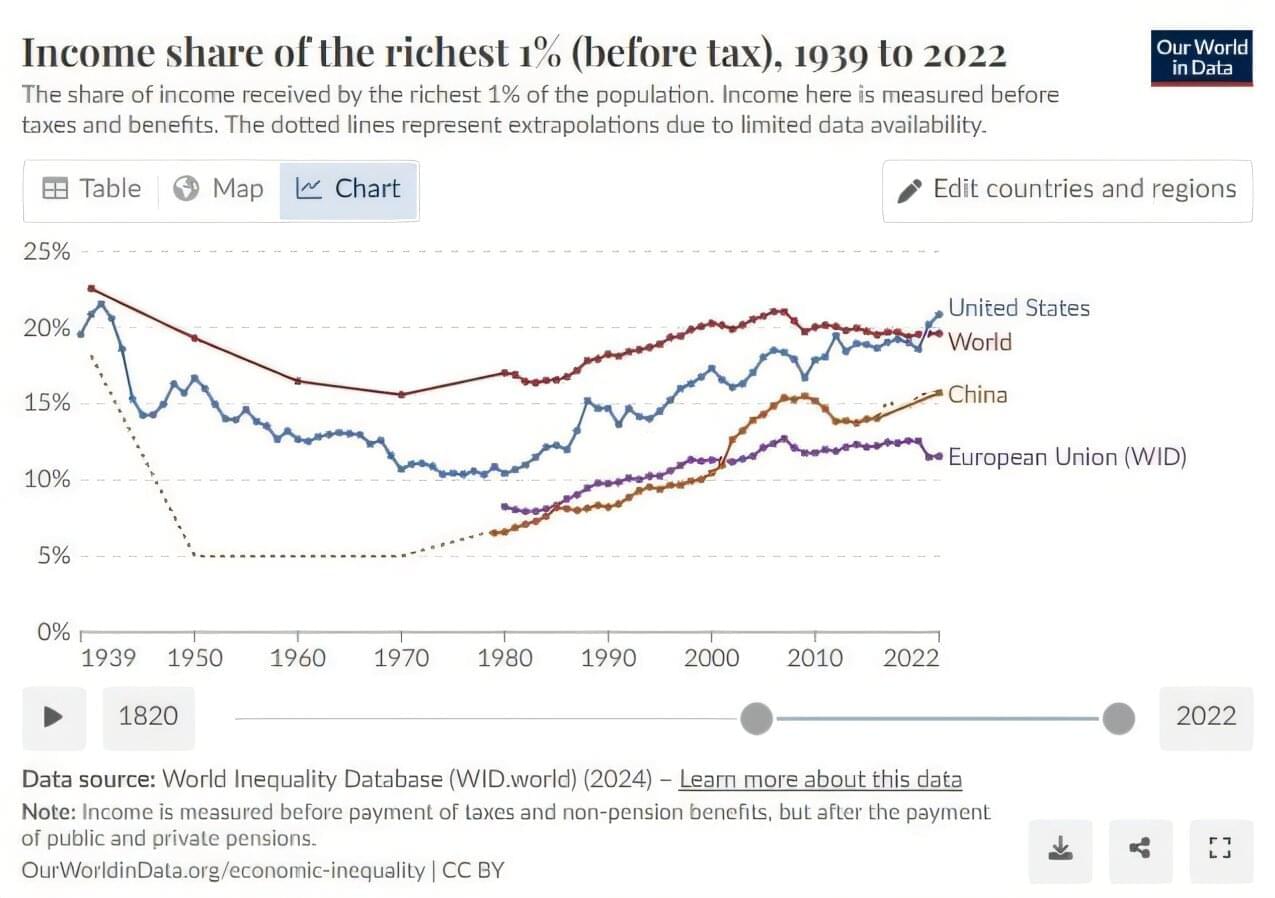
How will artificial intelligence affect the distribution of income and wealth this century? After falling through much of the 20th century, income inequality, measured as the fraction of income going to the richest 1% of residents, has been rising since the 1980s. The fraction has doubled in both China and the United States during that time, increased by 50% in Europe and one-third worldwide.
Industrialization dominated the economy before then, but starting in the ’70s and ’80s, capital took over as globalization increased, tax changes reduced progressivity and game-changing technologies were introduced rapidly.
The computer and personal computer revolution came first, followed by the Internet and the World Wide Web. Now artificial intelligence (AI) is beginning to make its mark in the world as a next-generation general-purpose technology.
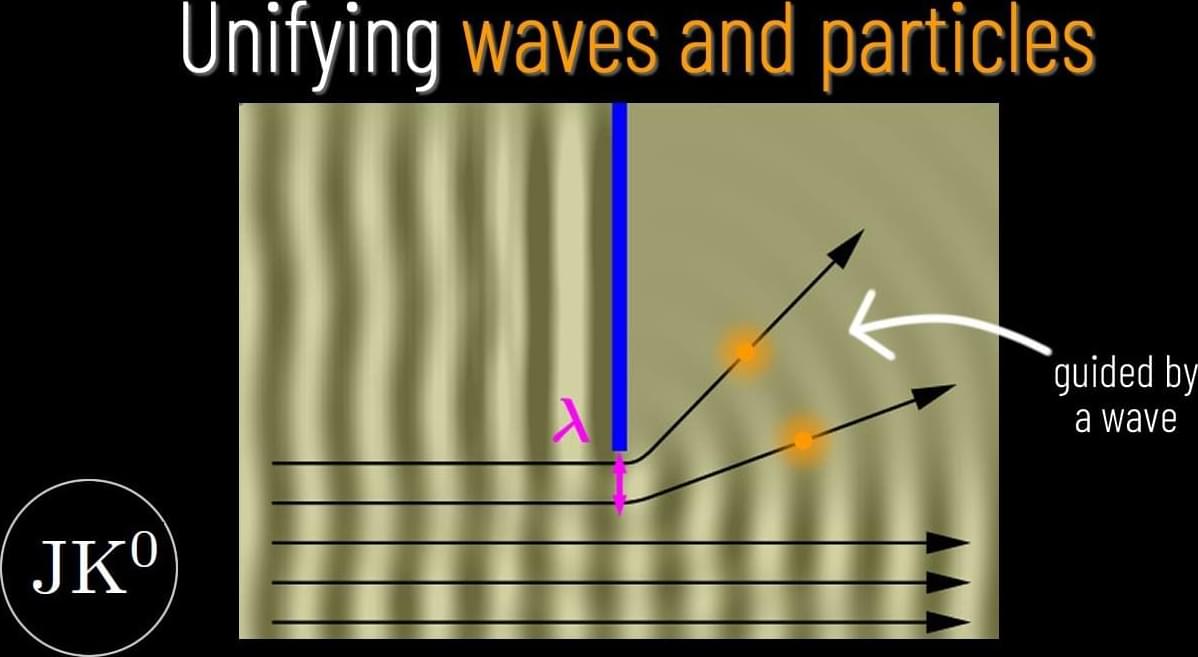
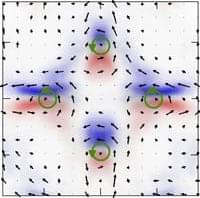
Real-space quantum vortices are key to many phenomena in modern physics. New experiments provide the first proof of vortices in momentum space, raising the prospect of exploring novel orbitronic phenomena.
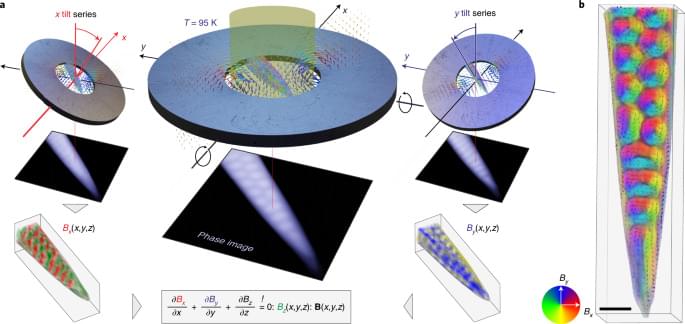
Holographic vector-field electron tomography reveals the three-dimensional magnetic texture of Bloch skyrmion tubes in FeGe at nanometre resolution, including complex three-dimensional modulations and fundamental skyrmion formation principles.
Prostate cancer statistics can look scary: 34,250 U.S. deaths in 2024. 1.4 million new cases worldwide in 2022. Dr. Bruce Montgomery, a UW Medicine oncologist, hopes that patients won’t see these numbers and just throw up their hands in fear or resignation.
“Being diagnosed with prostate cancer is not a death knell,” said Montgomery, senior author of a literature and trial review that appeared in JAMA today. Montgomery is the clinical director of Genitourinary Oncology at Fred Hutch Cancer Center and University of Washington Medical Center, and a professor of medicine and urology at the UW School of Medicine.
He encourages patients to ask their primary-care doctor specific questions about this cancer too. Montgomery also encourages his fellow doctors to bring up the question of prostate cancer screening with their patients.
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells.
Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate in our blood stem cells as we age is important to understand how and why blood cancers develop and hopefully how to intervene before the onset of clinical symptoms.
As we age, stem cells in the bone marrow naturally accumulate mutations and with this, we see the emergence of clones, which are groups of blood cells that have a slightly different genetic makeup. Sometimes, specific clones can lead to blood cancers like leukemia.
A team of environmental researchers, Earth scientists and pollution specialists at Nanjing University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and colleagues from Germany and the U.S. has found evidence that microplastics have a negative impact on photosynthesis in terrestrial, marine, and freshwater ecosystems.
In their study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the group conducted a meta-analysis of data from more than 150 studies involving the impact of microplastics on plants.
Prior research has shown that microplastics have made their way to nearly every ecosystem on the planet, and now contaminate plants and animals, including humans. For this new study, the research team wondered if microplastics might have an unknown impact on plants living in the ocean, in fresh water or growing on land, and they conducted a study of prior research to find out.
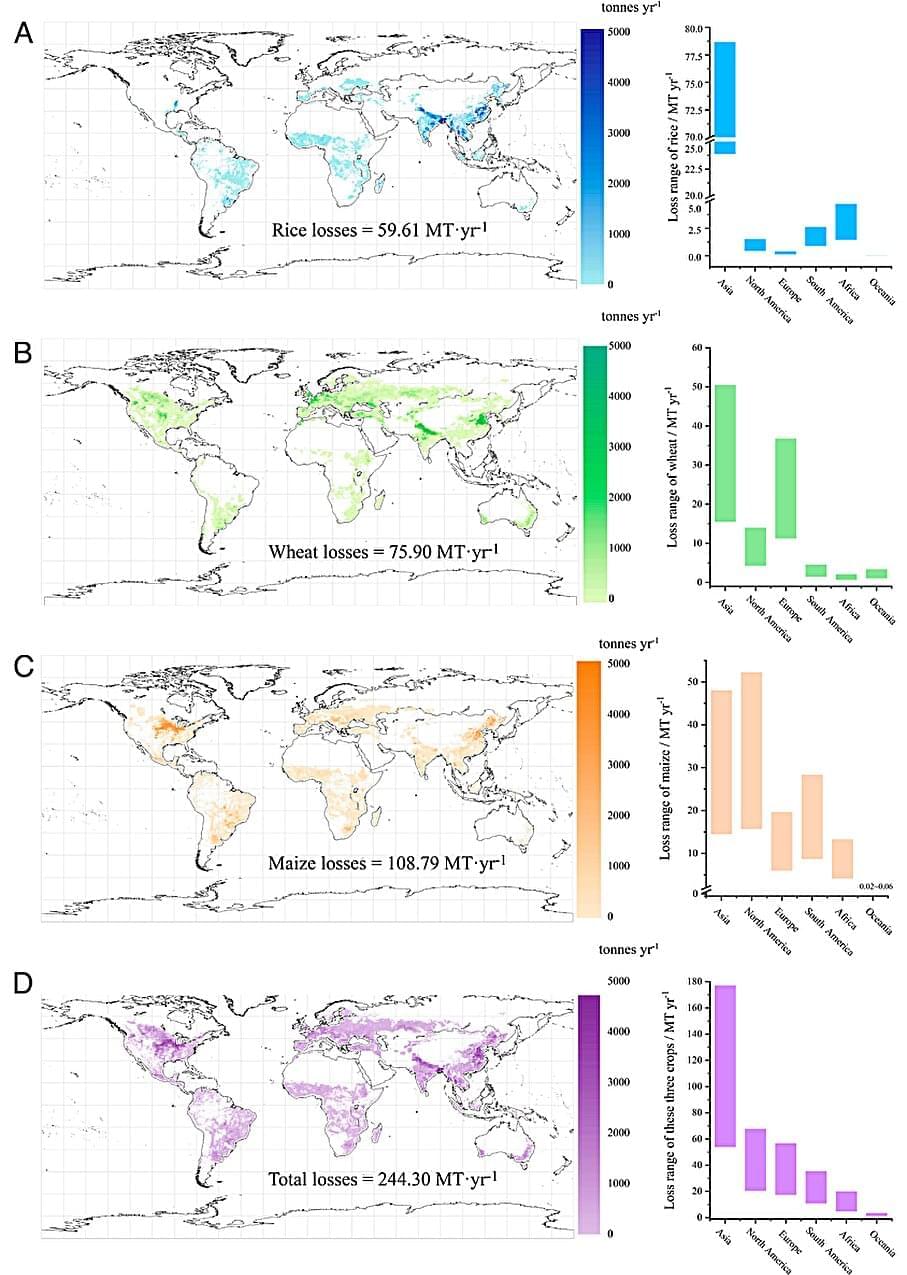
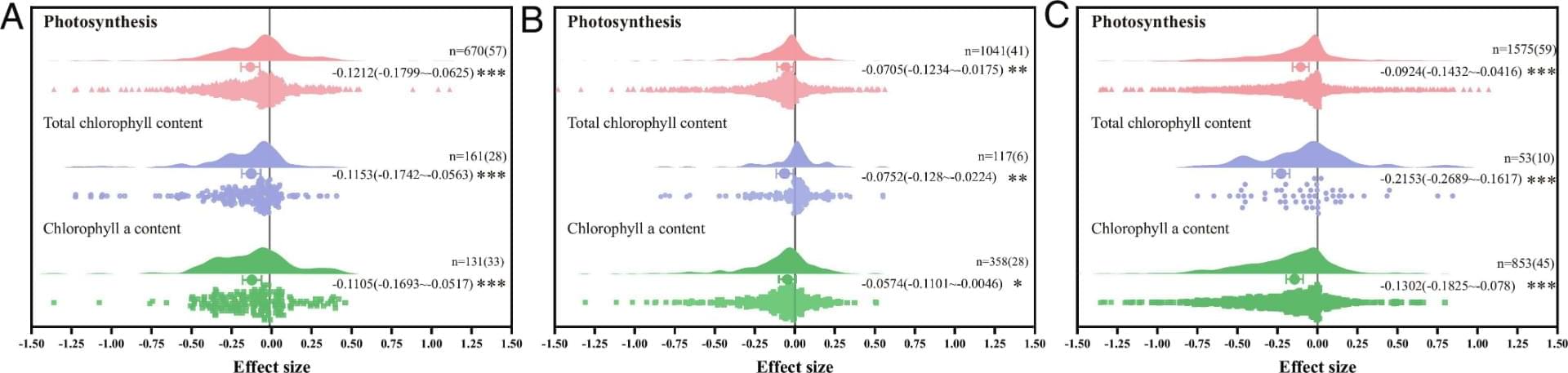
Understanding how ecosystems respond to ubiquitous microplastic (MP) pollution is crucial for ensuring global food security. Here, we conduct a multiecosystem meta-analysis of 3,286 data points and reveal that MP exposure leads to a global reduction in photosynthesis of 7.05 to 12.12% in terrestrial plants, marine algae, and freshwater algae. These reductions align with those estimated by a constructed machine learning model using current MP pollution levels, showing that MP exposure reduces the chlorophyll content of photoautotrophs by 10.96 to 12.84%. Model estimates based on the identified MP-photosynthesis nexus indicate annual global losses of 4.11 to 13.52% (109.73 to 360.87 MT·y−1) for main crops and 0.31 to 7.24% (147.52 to 3415.11 MT C·y−1) for global aquatic net primary productivity induced by MPs. Under scenarios of efficient plastic mitigation, e.g.
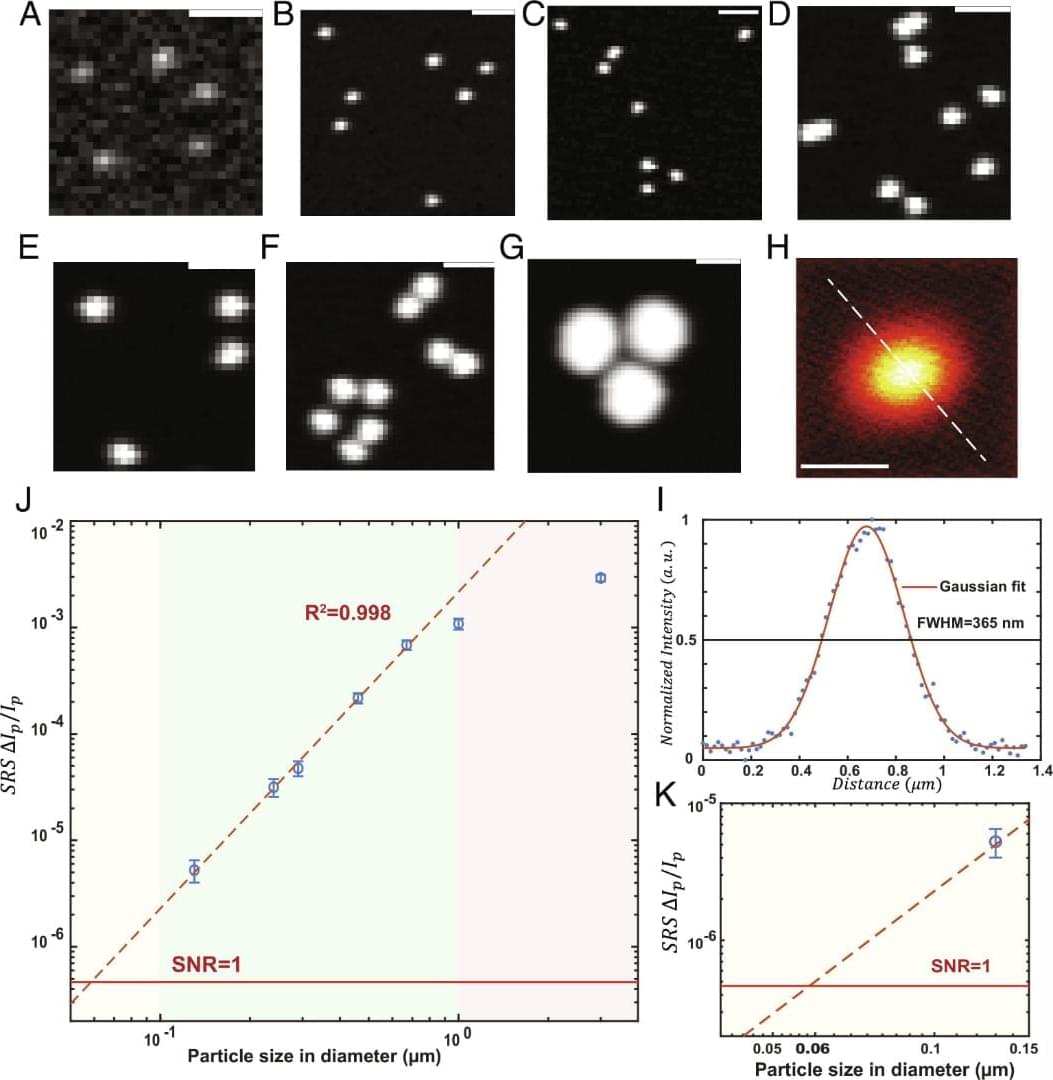
The shape is another important morphological feature that matters as a critical aspect of nanotoxicity. Studies have shown that shape plays a role in determining the cellular uptake of micro-nano particles (65, 66). SRS images of plastic particles confirmed the existence of shape diversity for micro-nano plastics in bottled water. To account for the shape of plastic particles in a statistical manner, we measure the aspect ratio of individual particles above the diffraction limit (Fig. 6 H). The aspect ratio is widely acknowledged in nanotoxicology studies (67, 68). The aspect ratio of the plastic particles detected ranges from 1 to 6, and the average aspect ratio for particles is around 1.7. Fig. 6 I–M provides a pictorial view of how the aspect ratio is related to the particle shape. Particles with an aspect ratio of above 3 are most likely to be fibrous in shape, while particles with an aspect ratio of below 1.4 will be largely spherical. Shape variation on plastic particles has been found in all polymers detected, confirming the widely recognized idea that real-world micro-nano plastics have diverse morphological prosperities. This dimension is hard to be resembled by engineered polymer nanoparticles commonly studied in research laboratories, and the toxicological consequences pertaining to real-life plastic particle exposures and their differing physicochemical properties (i.e., size, shape) have yet to be determined.