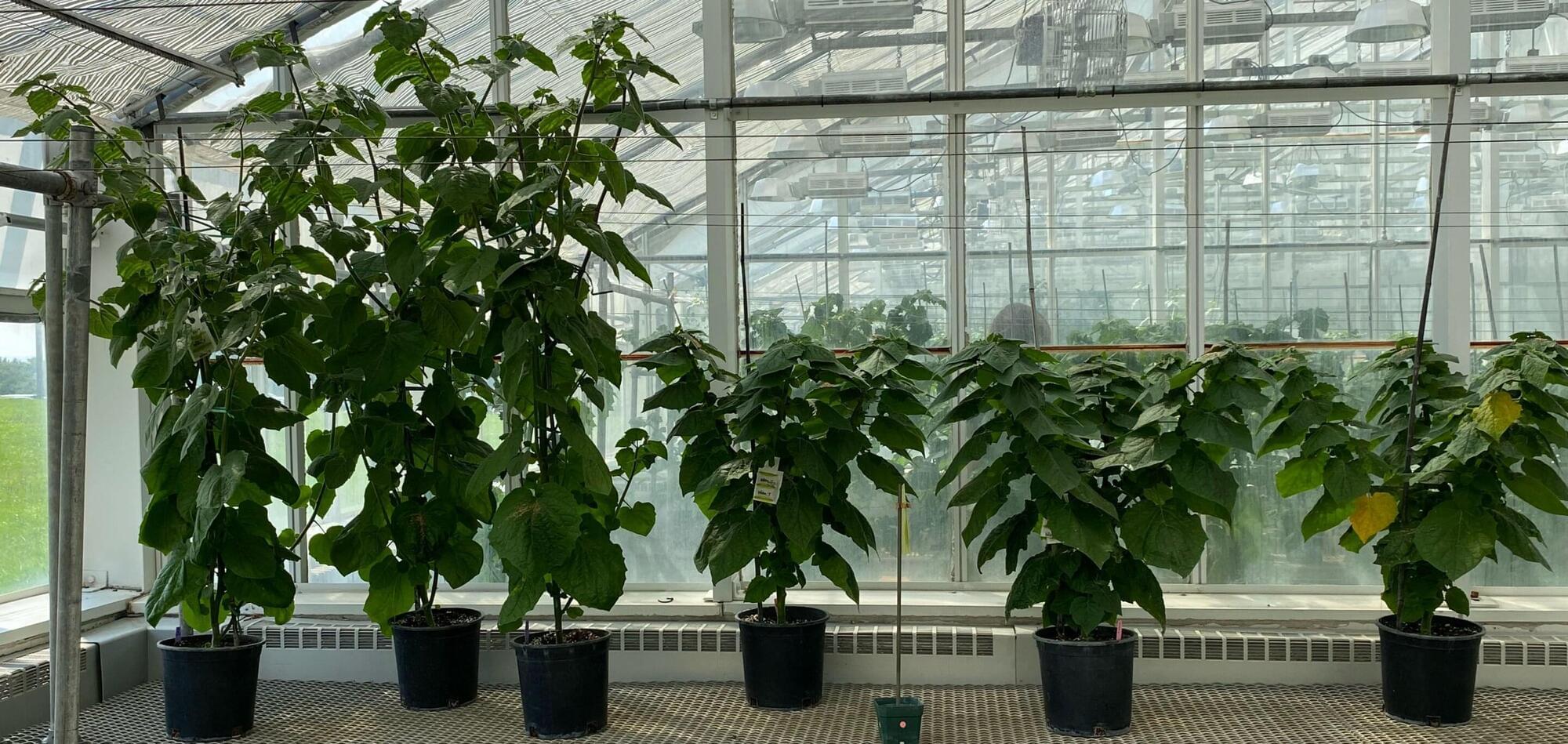
Goldenberries taste like a cross between pineapple and mango, pack the nutritional punch of a superfood, and are increasingly popular in U.S. grocery stores. But the plants that produce these bright yellow-orange fruits grow wild and unruly—reaching heights that make large-scale farming impractical.
Researchers at the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) helped solve that problem. Using CRISPR gene editing, a collaborative team including BTI professor Joyce Van Eck engineered compact goldenberry plants that are 35% shorter than their wild relatives, making them viable for commercial agriculture.
“Goldenberry has tremendous potential as a nutritious crop, but its large, bushy growth habit has hindered commercial production,” said Van Eck. “These new compact plants can be grown at higher density, don’t require extensive staking or trellising, and are much easier to maintain and harvest.”