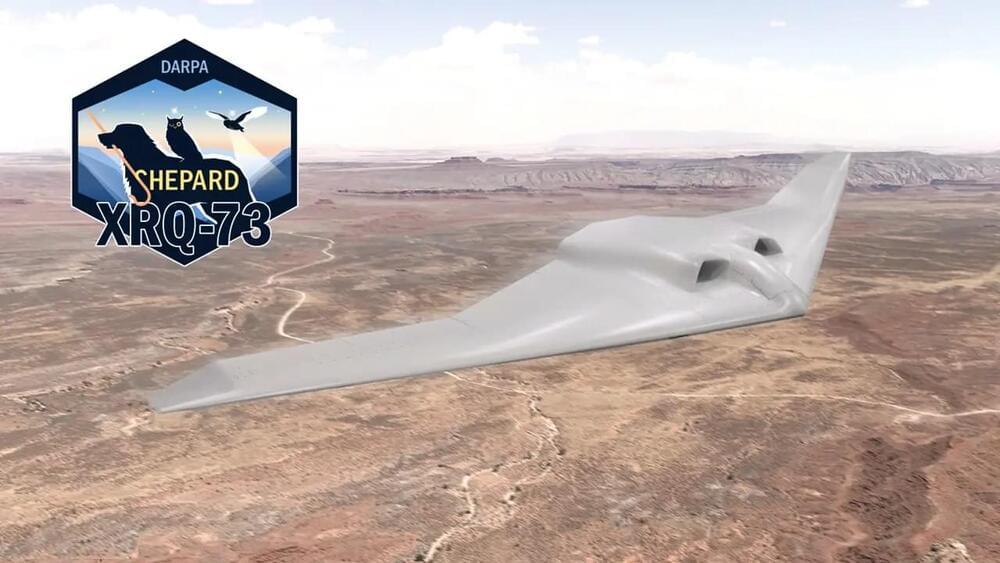
Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE: NOC) has announced the design and construction of the Series Hybrid Electric Propulsion AiRcraft Demonstration (SHEPARD) vehicle. The uncrewed air system developed for DARPA recently received its official X-plane designation of XRQ-73. Built in collaboration with Scaled Composites, a Northrop Grumman subsidiary, the XRQ-73 SHEPARD is a DARPA “X-prime” program leveraging hybrid electric architecture and component technologies to quickly mature a new mission-focused aircraft design with propulsion architecture and power class for the Department of Defense.
“The idea behind a DARPA X-prime program is to take emerging technologies and burn down system-level integration risks to quickly mature a new missionized long endurance aircraft design that can be fielded quickly. The SHEPARD program is maturing a specific propulsion architecture and power class as an exemplar of potential benefits for the Department of Defense,” said Steve Komadina, SHEPARD program manager.
The DARPA team includes members from the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), the Office of Naval Research (ONR), and warfighters. The prime contractor for SHEPARD is Northrop Grumman Corporation’s Aeronautics Systems sector in Redondo Beach, CA. Scaled Composites, LLC is a major supplier, along with Cornerstone Research Group, Inc., Brayton Energy, LLC, PC Krause and Associates, and EaglePicher Technologies, LLC. The XRQ-73 aircraft hybrid-electric uncrewed aircraft system (UAS) will be a Group 3 UAS weighing approximately 1,250 pounds. First flight of the XRQ-73 is expected by year-end 2024.