Join the discussion on this paper page.


Almost 1 in 5 Indian adults aged 60+ show signs of mild neurocognitive disorder, according to a study.
Given an estimated 138 million adults over 60 years of age in India, these estimates suggest approximately 24 million and 9.9 million older adults in India are living with mild and major neurocognitive disorder, respectively, revealed the study published in the journal PLOS One.
An advanced human heart organoid system can be used to model embryonic heart development under pregestational diabetes-like conditions, researchers report in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
The organoids recapitulate hallmarks of pregestational diabetes-induced congenital heart disease found in mice and humans. The findings also showed that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and lipid imbalance are critical factors contributing to these disorders, which could be ameliorated with exposure to omega-3s.
“The new stem cell-based organoid technology employed will enable physiologically relevant studies in humans, allowing us to bypass animal models and obtain more information about relevant disease mechanisms, accelerating drug discovery and medical translation,” says senior study author Aitor Aguirre of Michigan State University.
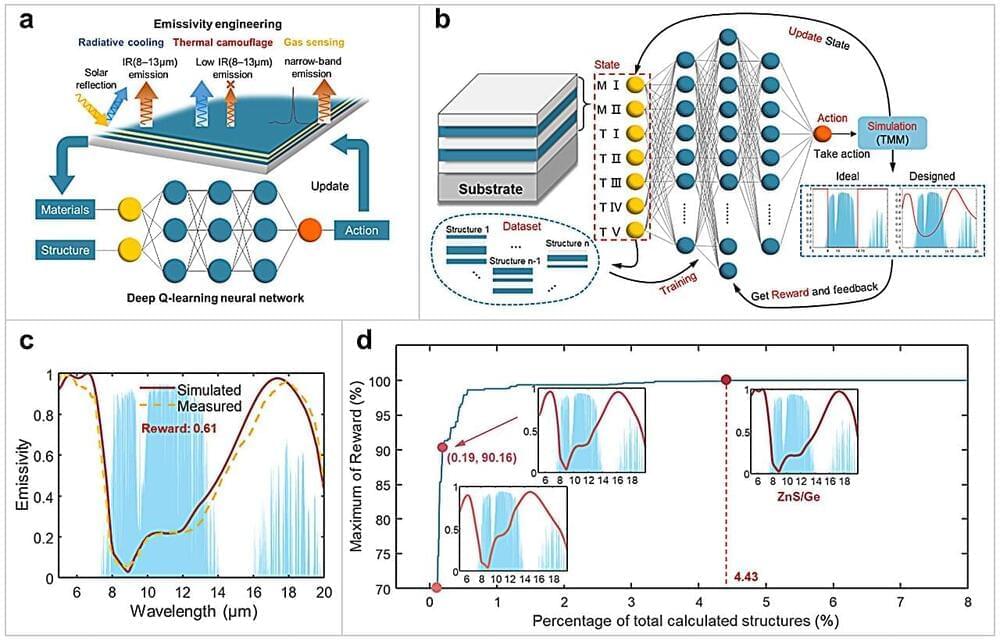
Wavelength-selective thermal emitters (WS-TEs) have been frequently designed to achieve desired target emissivity spectra, as in typical emissivity engineering, for broad applications such as thermal camouflage, radiative cooling, and gas sensing, etc.
However, previous designs required prior knowledge of materials or structures for different applications, and the designed WS-TEs usually vary from application to application in terms of materials and structures, thus there is no general design framework for emissivity engineering across different applications. Moreover, previous designs fail to tackle the simultaneous design of both materials and structures, as they either fix materials to design structures or fix structures to select suitable materials.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Run Hu from School of Energy and Power Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China, and coworkers have proposed a general deep learning framework based on the deep Q-learning network algorithm (DQN) for efficient optimal design of WS-TEs across different applications.
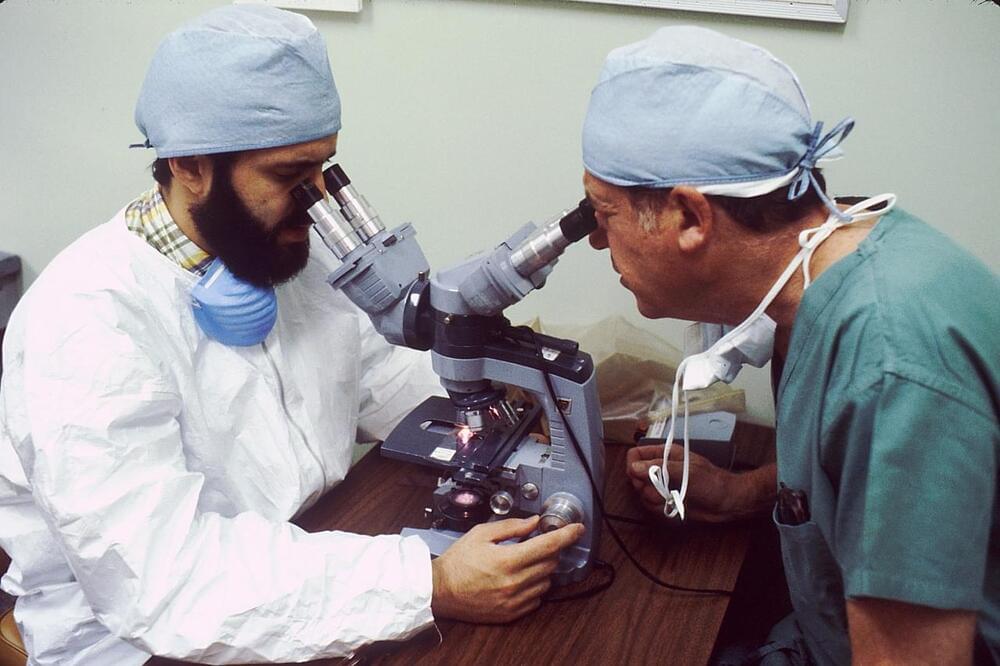
Histopathology describes the process of examining pieces of tissue using a microscope. Light microscopic (LM) examination of tissue helps diagnose several types of cancer by allowing pathologists to view cellular changes within a biopsy sample.
The workload of pathologists has increased in recent years due to policies that encourage screening for early cancer diagnoses. In addition, longer life expectancies and scientific advances have led to an increased number of cancer survivors, further increasing the need for pathology evaluations. Thus, strategies to efficiently utilize the limited pathology resources have become essential to maintaining standards of care and the health and safety of patients.
Digital pathology (DP) has emerged as an alternative method for analyzing tissue samples by stitching together digital images from histopathology slides. Automated slide scanners can rapidly generate these high-resolution images with minimal human interaction. In addition to the speed, DP does not require a microscope, offering remote viewing possibilities. Pathologists and other healthcare professionals can easily share images.
This is a sci-fi documentary, looking at how warp drive technology and warp spaceships work. As well as the negative energy needed to travel at warp speed. The faster than light journey to Mars takes 18.6 seconds, but how long does it take to reach the nearest black hole?
It is a journey showing the future science of space travel, exploration, and future space technology.
Personal inspiration in creating this video comes from: Star Trek: The Next Generation, and baby Groot — Guardians of the Galaxy II.
PATREON
The first volume of ‘The Encyclopedia of the Future’ is available on my Patreon.
Along with: Timelapse of Future Technology (Master List)
Part of my ‘The Future Archive Files’ collection.
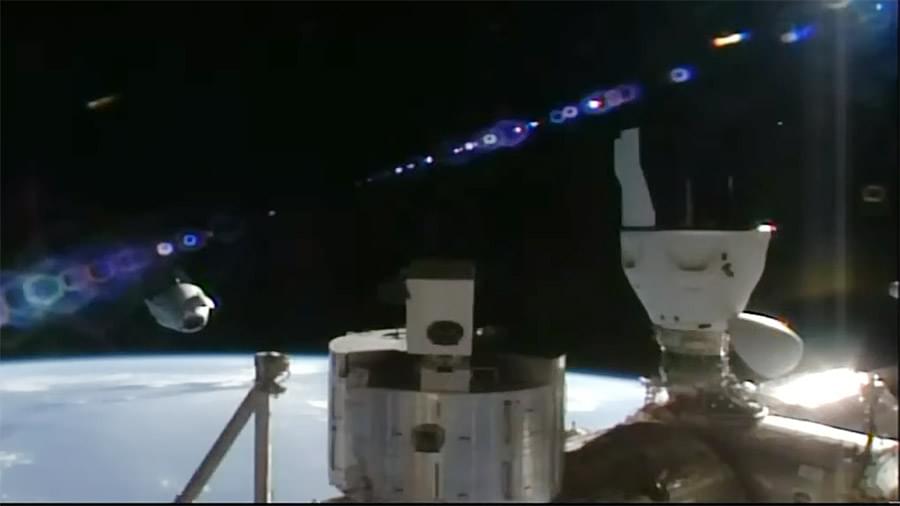

The SpaceX Dragon spacecraft undocked from the space-facing port of the International Space Station’s Harmony module at 9:20 a.m. EST over the Pacific Ocean, west of Ecuador, to complete the third all-private astronaut mission to the orbiting laboratory, Axiom Mission 3 (Ax-3).
Dragon is slowly maneuvering away from the orbital laboratory into an orbital track that will return the astronaut crew and its cargo safely to Earth, targeting a splashdown off the coast of Daytona, Florida, at approximately 8:30 a.m. EST Friday, Feb. 9.
Ax-3 astronauts Michael López-Alegría, Walter Villadei, Marcus Wandt, and Alper Gezeravci will complete 18 days aboard the orbiting laboratory at the conclusion of their mission. The SpaceX Dragon will return to Earth with more than 550 pounds of science and supplies, including NASA experiments and hardware.

Battelle Memorial Institute, Columbus, Ohio (FA8684-24D-B018); The Boeing Co., St. Louis, Missouri (FA8684-24D-B019); The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory Inc., Cambridge, Massachusetts (FA8684-24D-B014); Chip Scan Inc., Rockaway Beach, New York (FA8684-24D-B004); General Dynamics Mission Systems Inc., Dedham, Massachusetts (FA8684-24D-B006); GE Aviation Systems LLC Grand Rapids, Michigan (FA8684-24D-B008); Honeywell International, Clearwater, Florida (FA8684-24D-B010); Idaho Scientific LLC, Boise, Idaho (FA8684-24D-B012); Kratos SRE Inc., San Diego, California (FA8684-24D-B005); L3Harris Technologies Inc., Palm Bay, Florida (FA8684-24D-B007); Lockheed Martin Corp., Orlando, Florida (FA8684-24D-B009); Mercury Systems Inc., Andover, Massachusetts (FA8684-24D-B016); Microsemi SOC Corp., San Jose, California (FA8684-24D-B011); Northrop Grumman Systems Corp., Linthicum Heights, Maryland (FA8684-24D-B003); Radiance Technologies Inc., Huntsville, Alabama (FA8684-24D-B013); Raytheon Co., McKinney, Texas (FA8684-24D-B015); and Sabre Systems Inc., Warminster, Pennsylvania (FA8684-24D-B017), were awarded a $499,000,000 multiple award, indefinite-delivery/indefinite-quantity contract for the design, build, test, and delivery of functioning anti-tamper solutions that will be ready for follow-on production to be integrated into a broad range of Department of Defense programs. The development of these solutions enables the necessary protection of critical program information from adversarial tamper efforts. Work will be performed in the continental United States and is expected to be completed Feb. 28, 2030. This contract was a competitive acquisition, and 20 offers were received. Fiscal 2024 research, development, test, and evaluation funds in the amount of $1,000 per awardee are being obligated at time of award. The Air Force Life Cycle Management, Wright Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, is the contracting activity.
Roundhouse PBN LLC, Colorado Springs, Colorado, was awarded a $13,619,953 commercial, fixed-firm-price contract for a temporary and relocatable Program Integration Office/Program Management Office facility for the Sentinel Program at F. E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming. This contract provides for a one-time procurement for a secure, prefabricated, nominal 26,000-square-foot temporary facility, that will satisfy immediate requirements for additional office space for up to 200 Sentinel project personnel. This will be a commercial supply contract to procure a facility and furnishings, with a limited construction service component to conduct site preparation. Work will be performed at F.E. Warren AFB, Wyoming, and is expected to be completed by Feb. 7, 2025. This contract was a sole source acquisition. Fiscal 2024 operation and maintenance funds in the amount of $1,923,839; and fiscal 2024 procurement funds in the amount of $11,696,114, are being obligated at time of award.