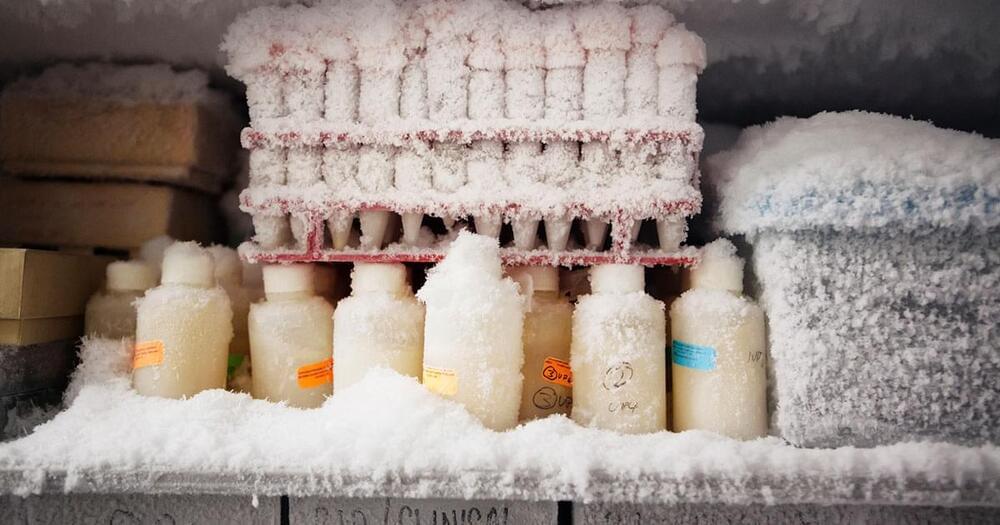
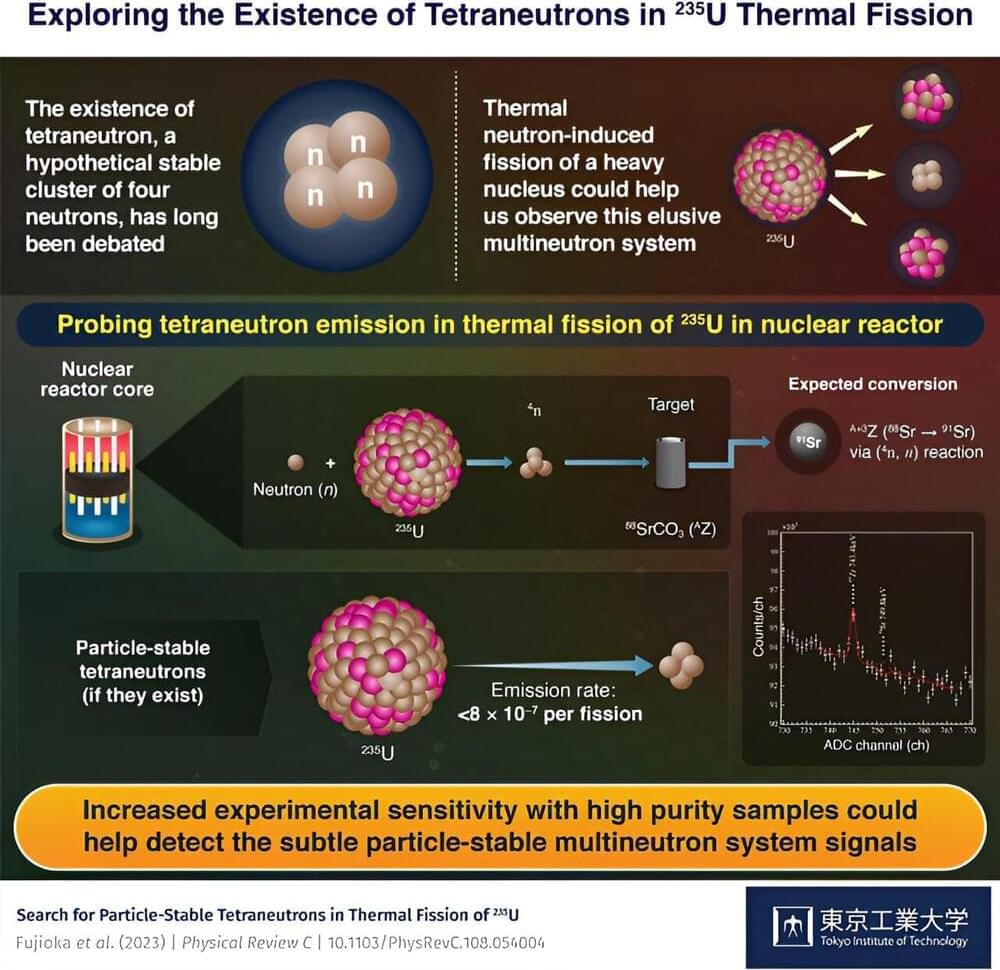
In an apparent attempt to turn off a beeping noise he allegedly deemed annoying, a janitor turned off the breaker to a freezer that contained extremely valuable cell cultures, samples, and other research.
The freezer, which was set to minus-112 degrees Fahrenheit, as the Times Union reports, warmed up to a catastrophic minus-25.6 degrees, damaging and destroying much of the decades of work.
At least, that’s what happened according to a lawsuit filed by the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute lab against the janitor’s employer.