A medical breakthrough that could save lives.
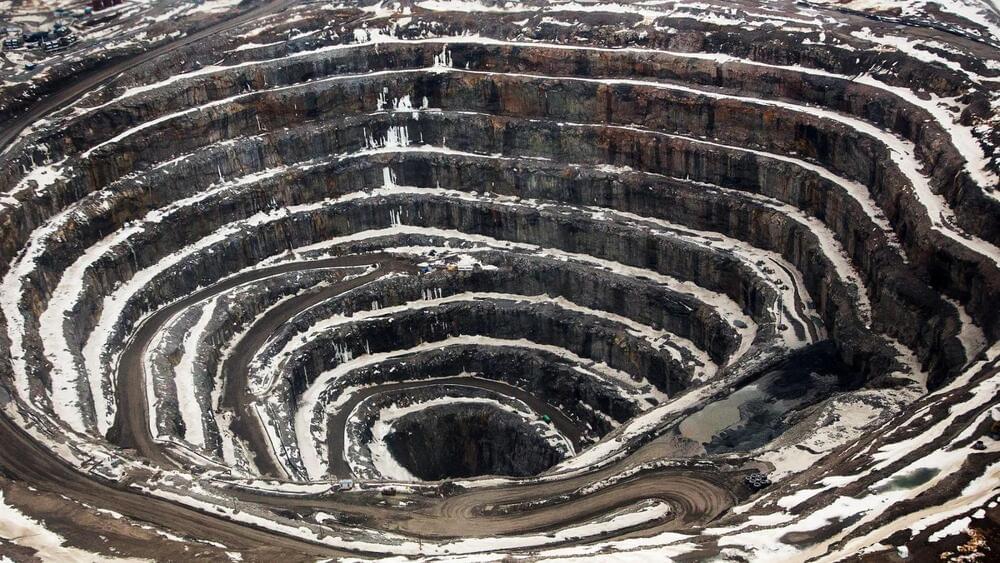



Rio Tinto has ambitious goals when it comes to sustainability. According to the company’s website, it aims to transition all its facilities and operations to net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. To achieve this, the company is working with governments to scale up renewable energy resources where it works. For example, Rio Tinto invested more than $500 million to partner with the Canadian government to decarbonize an iron and titanium mine in Quebec.
Mining companies like Rio Tinto provide necessary metals and minerals for global clients. The company’s products and resources are used all over the world in items that people use in their daily lives. Unfortunately, mining with diesel fuel produces carbon dioxide. Rio Tinto is exploring the effectiveness of renewable energy sources in its operations to try and reduce the negative impacts mining has on the Earth.
The Diavik diamond mine features a historic solar power plant that can produce up to 4.2GW hours of electricity for its operations. The solar panels on-site use both the light of the sun as well as light reflected off of snow to generate electricity.
“If a tree falls in the forest, and no one hears it, does it make a sound?” I remember seeing an actual argument get started on this subject—a fully naive argument that went nowhere near Berkeleyan subjectivism. Just:
“It makes a sound, just like any other falling tree!” “But how can there be a sound that no one hears?”
The standard rationalist view would be that the first person is speaking as if “sound” means acoustic vibrations in the air; the second person is speaking as if “sound” means an auditory experience in a brain. If you ask “Are there acoustic vibrations?” or “Are there auditory experiences?”, the answer is at once obvious. And so the argument is really about the definition of the word “sound”

In North Africa, some of the driest places on Earth have seen five times their average September rainfall. Flooding has affected more than 4 million people in 14 countries, according to the U.N. World Food Program. Heavy rain and floods have killed or displaced thousands and disrupted farming activities in areas where there already isn’t enough food for the population.
A northward shift in the region of clouds and rain that circles Earth near the equator is responsible for the flooding and greening. In this area, called the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), Southern Hemisphere winds blowing from the southeast converge with Northern Hemisphere winds blowing from the northeast. The combination of converging winds, strong sun and warm ocean water leads to rising, moist air and constant clouds, showers and thunderstorms.
The movement of the ITCZ north and south of the equator during the year is primarily driven by the difference in temperature between the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It drifts toward the warmer hemisphere, which means it resides north of the equator during the Northern Hemisphere summer, usually reaching its northernmost point in August or September.
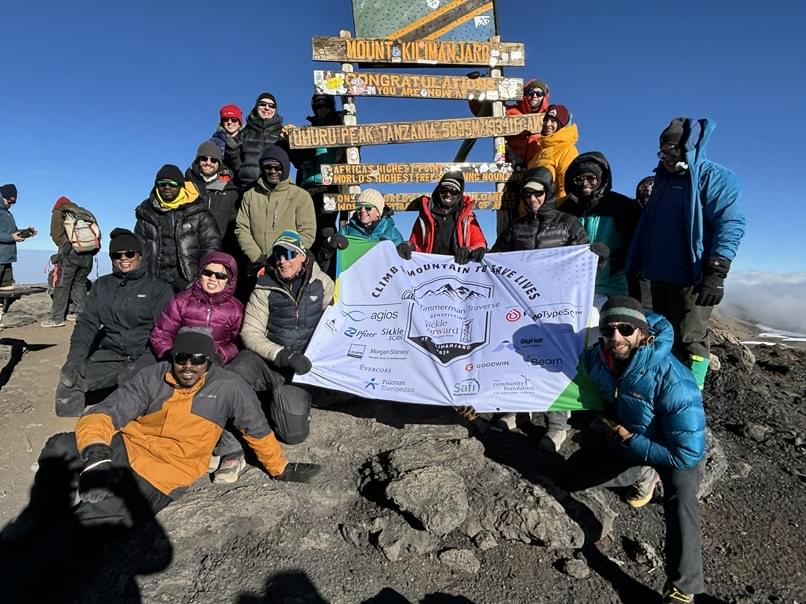

Four years after being functionally cured of sickle cell disease with a CRISPR gene-editing therapy, Jimi Olaghere has set a new world record for patients with this chronic and deadly disease.
Olaghere, a 39-year-old business owner from Atlanta, became the world’s first patient with sickle cell disease to reach the summit of Kilimanjaro at 7:30 am Tanzania time on Sept. 16. It’s the highest peak in Africa at 19,341 feet above sea level.
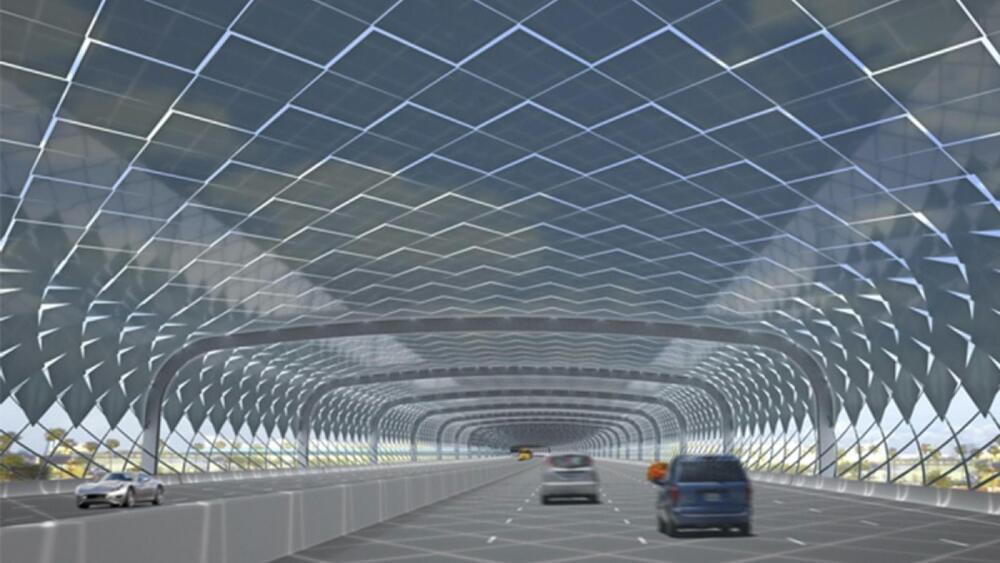

52 billion solar panels could soon be covering the American highway network. Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University, Chinese Academy of Geosciences, and Columbia University have proposed a historic initiative which could see major global highways covered with solar panels.
The researchers publication “Roofing Highways With Solar Panels Substantially Reduces Carbon Emissions and Traffic Losses” in Earth’s Future advocate for the deployment of solar technology across the global highway network which spans up to 3.2 million kilometers.
In doing so, the researchers estimate that up to 17,578 TWh of electricity could be generated annually. This figure is equivalent to more than a staggering 60% of 2023’s energy consumption. This could offset up to 28% of global carbon emissions and reduce road accident incidences up to 11%.
Sierra Space’s oxygen tech boosts lunar sustainability, aiding NASA’s Artemis goal for a permanent moon base and future Mars missions.

Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini excel at being trained on large data-sets to generate informative responses to prompts. Yi Cao, an assistant professor of accounting at the Donald G. Costello College of Business at George Mason University, and Long Chen, associate professor and area chair of accounting at Costello, are actively exploring how individual investors can use LLMs to glean market insights from the dizzying array of available data about companies.
Their new working paper, appearing in SSRN Electronic Journal and co-authored with Jennifer Wu Tucker of the University of Florida and Chi Wan of University of Massachusetts Boston, examines AI’s ability to identify “peer firms,” or product market competitors in an industry.
Cao explains the significance of selecting peers by relating this process to the real-estate market. “The capital market is similar to the real-estate market in that a firm’s value is partially determined by the value of its peers. In the real-estate market, we price a home based on the value of comparable properties in the neighborhood, or the so-called ‘comps.’ In our paper, we aim to leverage the power of LLMs to identify comps for evaluating firm value.”
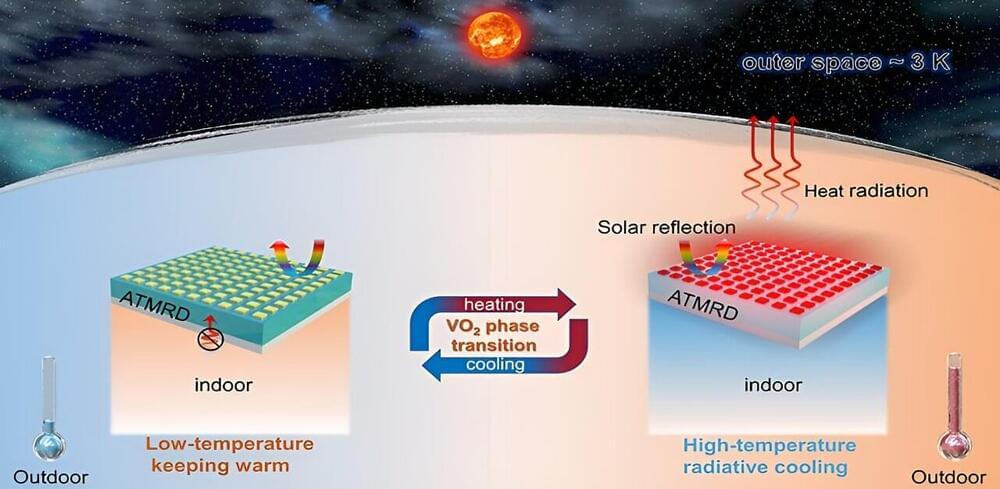
As the global energy crisis intensifies and climate change accelerates, finding sustainable solutions for energy management is increasingly urgent. One promising approach is passive radiative cooling, a technology that allows objects to cool by emitting heat directly into space, requiring no additional energy.

Summery:
(
Mousavi, S., Seyedmirzaei, H., Shahrokhi Nejad, S. et al. Sci Rep 14, 21,936 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-73277-z.