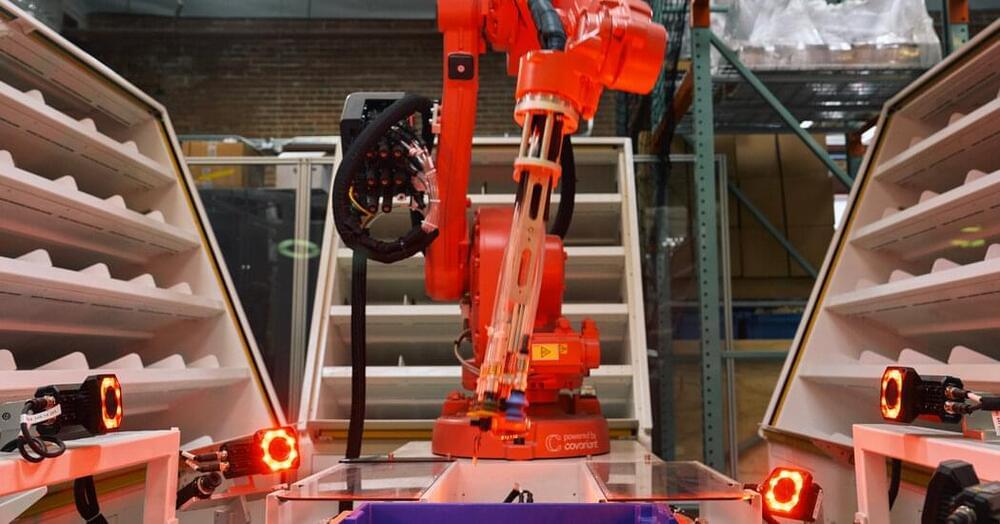
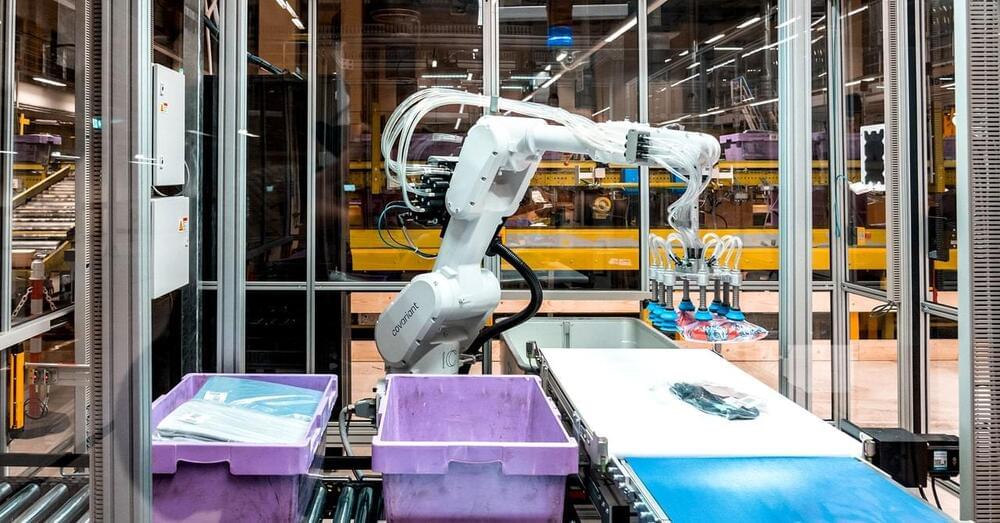
Covariant, a robotics start-up, is designing technology that lets robots learn skills much like chatbots do.



I have been engaged in the telecommunication industry for over 25 years, and it is so refreshing to see the positive energy moving into this sector as a result of applying generative AI technologies.
The telecom industry can accelerate growth from generative AI. Here are use cases for the telco industry.


From the article:
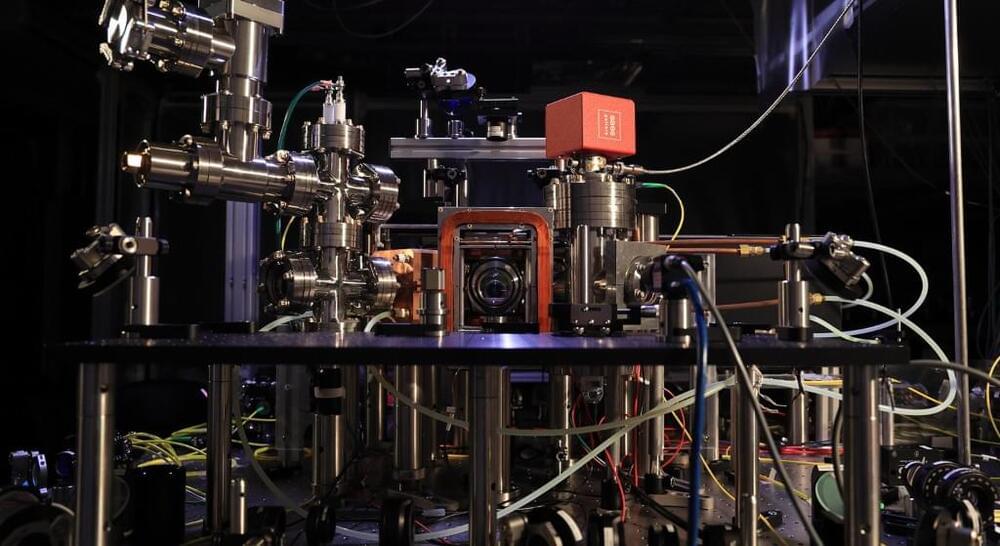
“Somewhere between one and ten million qubits are needed for a fault-tolerant quantum computer, whereas IBM has only just realized a 1,200-qubit computer,” says Aoki.
While this approach isn’t limited to any specific platform for quantum computers, it does lend itself to trapped ions and neutral atoms since they don’t need to be cooled to cryogenic temperatures, which makes them much easier to connect.
A hybrid approach
Aoki and his team are investigating the possibility of using a hybrid quantum system of atoms and photons known as a cavity quantum electrodynamics (QED) system as a promising way to connect units. “Cavity QED provides an ideal interface between optical qubits and atomic qubits for distributed quantum computing,” says Aoki. “Recently, key building blocks for realizing quantum computers based on cavity QED, such as single-photon sources and various quantum gates, have been demonstrated using free-space cavities.”


People in the daratumumab group who stayed MRD negative for at least a year were able to stop taking daratumumab as maintenance therapy and remained cancer free. That’s important, Dr. Sonneveld said, because taking fewer drugs long-term for maintenance therapy often translates to a better well-being and quality of life.
Adding daratumumab to the standard treatment resulted in a nearly 60% drop in the risk of cancer progression or death (hazard ratio of 0.42), the researchers determined.
The magnitude of that change is “unprecedented in these kinds of phase 3 trials [for] multiple myeloma,” Dr. Sonneveld said.

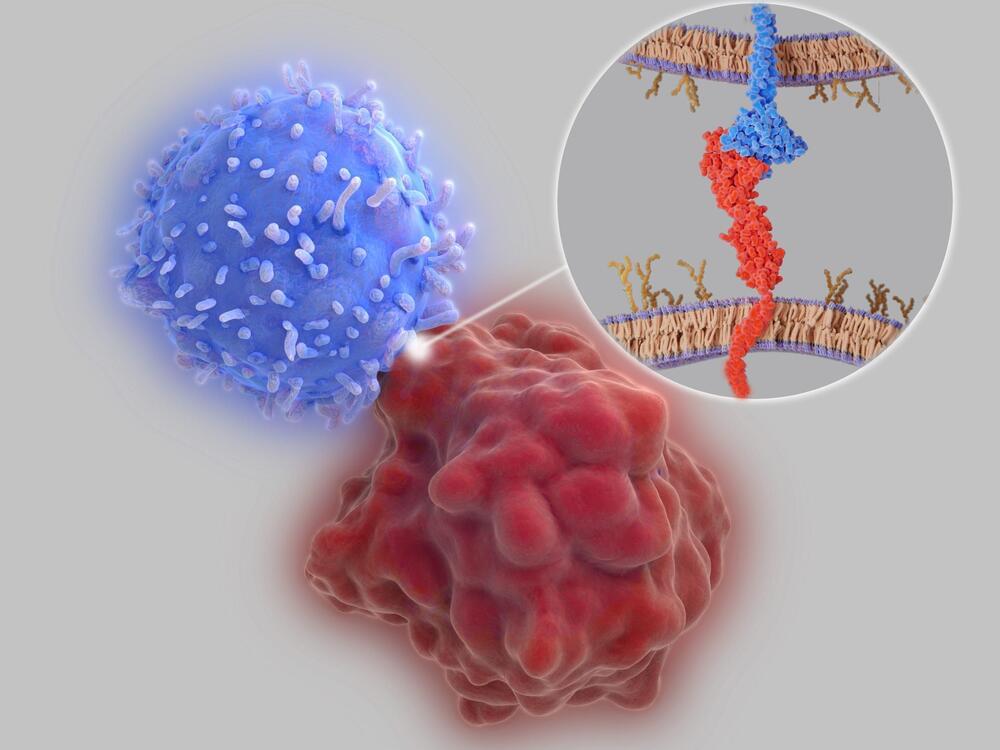
The authors cited results from a recent Phase II clinical trial reporting that Peresolimab, a PD-1 agonist monoclonal antibody, was effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis, but that the mechanism whereby peresolimab acts as an agonist was not reported. “Our characterization of PD-1 TMD dimerization may help inform evolving strategies for developing both agonists and antagonists,” they stated.
Co-senior investigator and cancer immunologist Jun Wang, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Pathology at NYU Grossman and Perlmutter, added, “Our findings offer new insights into the molecular workings of the PD-1 immune cell protein that have proven pivotal to the development of the current generation of anticancer immunotherapies, and which are proving essential in the design and developing of the next generation of immunotherapies for autoimmune diseases.”
Among the study’s findings was that a single change in the amino acid structure of the transmembrane segment can act to either enhance or diminish the inhibitory function of PD-1 in immune responses. The team plans further investigations of PD-1 inhibitors and agonists to see if they can tailor what they say are more effective, “rationally designed” therapies for both cancer and autoimmune disorders. Concluding on their findings in their paper, the team wrote, “In this study, we show that PD-1 and its ligands form dimers as a consequence of transmembrane domain (TMD) interactions and that propensity for dimerization correlates with PD-1 ability to inhibit immune responses, antitumor immunity, cytotoxic T cell function, and autoimmune tissue destruction. These observations contribute to our understanding of the PD-1 axis and how it can potentially be manipulated for improved treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases.”
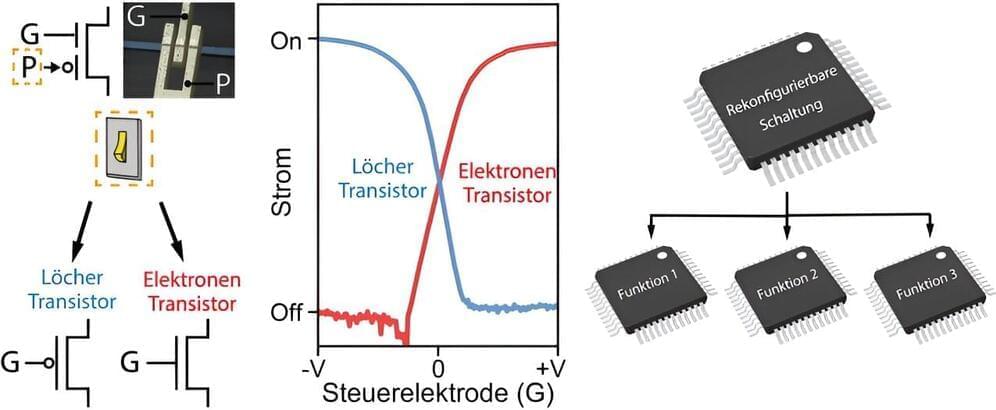
Even the most complicated data processing on a computer can be broken down into small, simple logical steps: You can add individual bits together, you can reverse logical states, you can use combinations such as “AND” or “OR.” Such operations are realized on the computer by very specific sets of transistors. These sets then form larger circuit blocks that carry out more complex data manipulations.