In the biotech and pharmaceutical industries, ELISA tests provide critical quality control during drug development and manufacturing. The tests can precisely quantify protein levels, but they also require hours of work by trained technicians and specialized equipment. That makes them prohibitively expensive, driving up the costs of drugs and putting research testing out of reach for many.
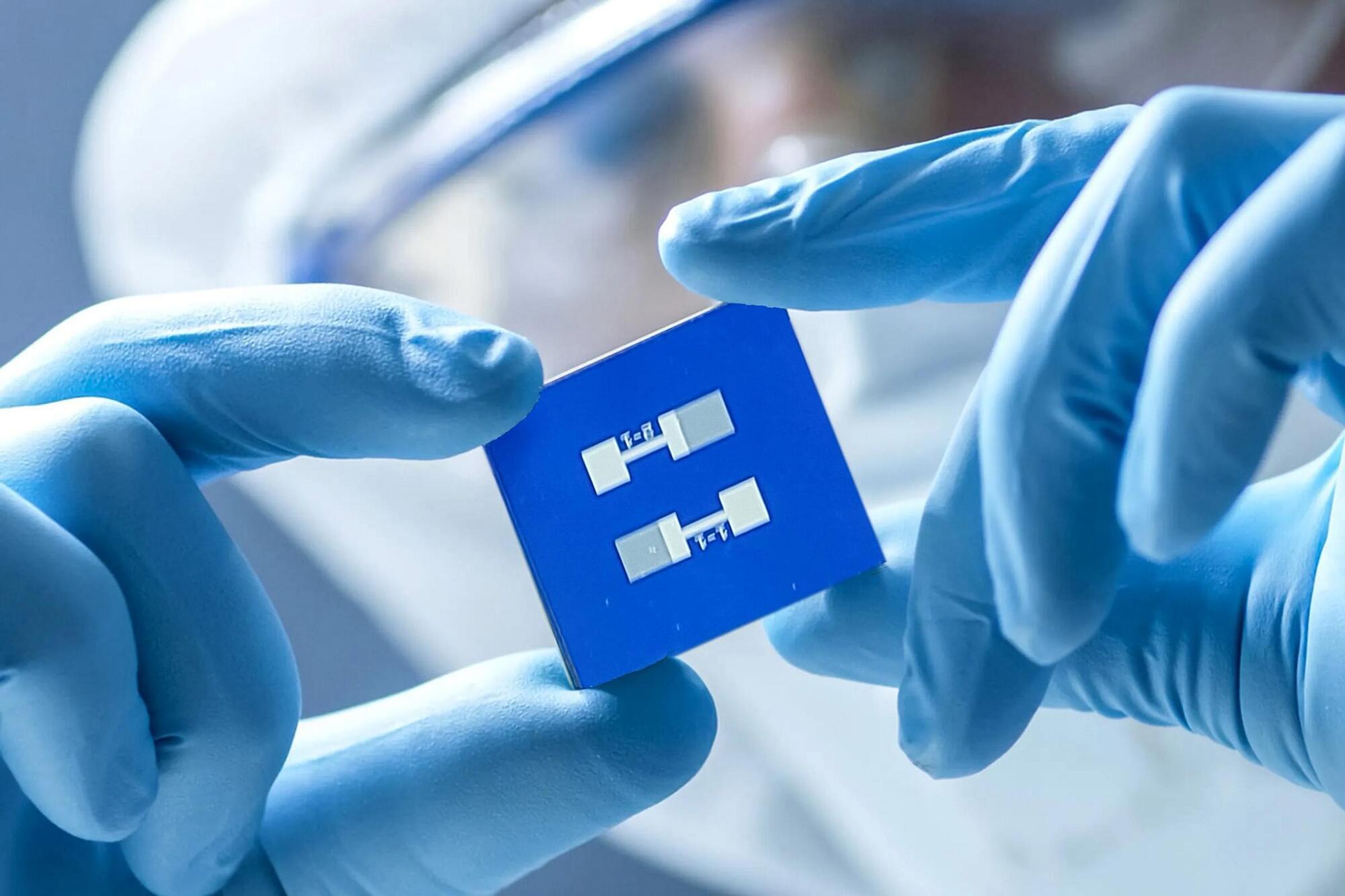
Now the Advanced Silicon Group (ASG), founded by Marcie Black ’94, MEng ’95, PhD ’03 and Bill Rever, is commercializing a new technology that could dramatically lower the time and costs associated with protein sensing. ASG’s proprietary sensor combines silicon nanowires with antibodies that can bind to different proteins to create a highly sensitive measurement of their concentration in a given solution.
The tests can measure the concentration of many different proteins and other molecules at once, with results typically available in less than 15 minutes. Users simply place a tiny amount of solution on the sensor, rinse the sensor, and then insert it into ASG’s handheld testing system.
“We’re making it 15 times faster and 15 times lower cost to test for proteins,” Black says. “That’s on the drug development side. This could also make the manufacturing of drugs significantly faster and more cost-effective. It could revolutionize how we create drugs in this country and around the world.”
Advanced Silicon Group, founded by MIT alumna Marcie Black, developed a protein sensor that could make drug development and manufacturing much faster and less expensive.