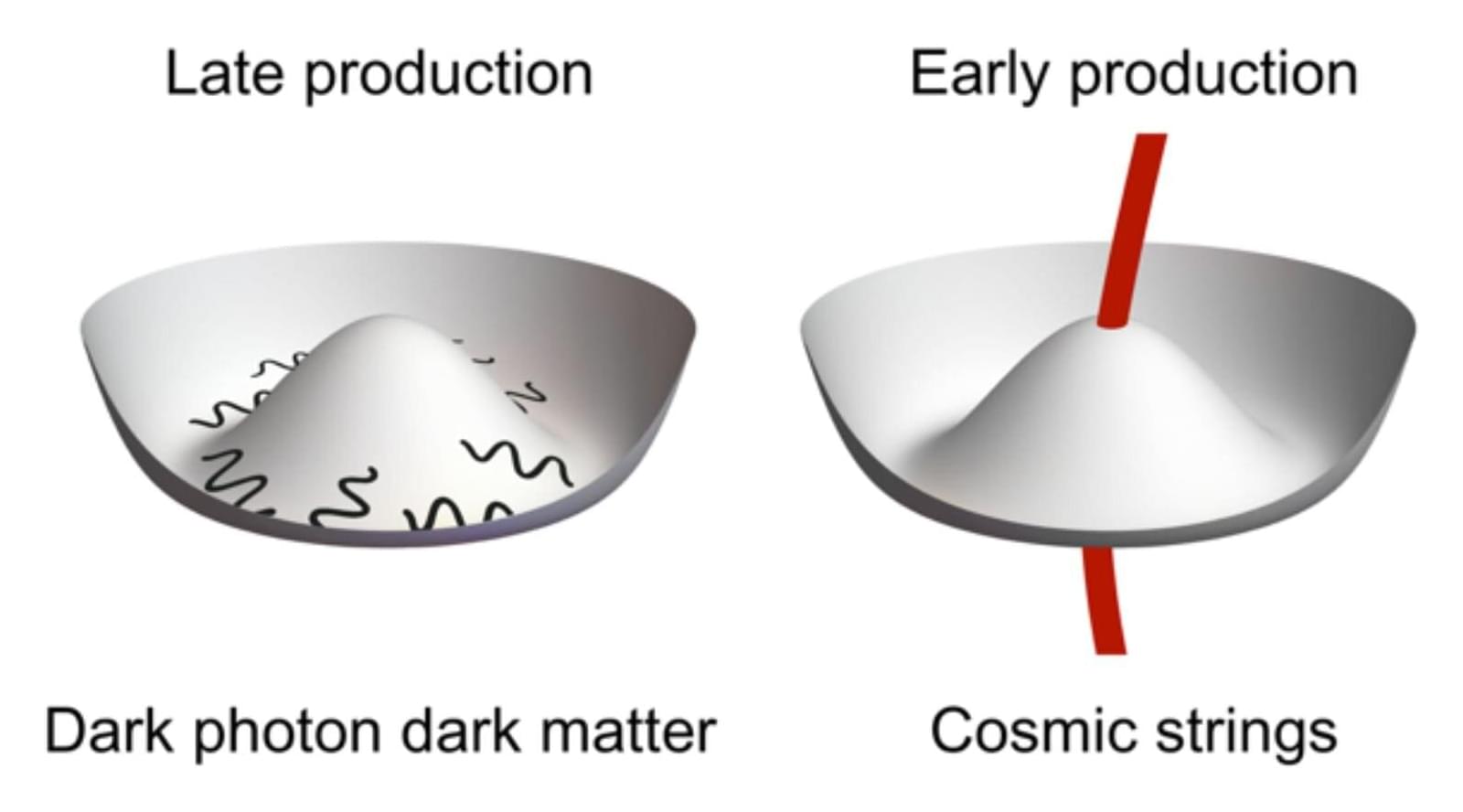
Researchers, in a recent Physical Review Letters paper, introduce a new mechanism that may finally allow ultralight dark photons to be considered serious candidates for dark matter, with promising implications for detection efforts.
Around 85% of all matter is believed to be dark matter, yet this elusive substance continues to puzzle scientists because it cannot be observed directly.
One of the candidates for dark matter particles is dark photons. These hypothetical particles are similar to regular photons but have mass and interact only weakly with normal matter.