Will future humans use warp drives to explore the cosmos? We’re in no position to eliminate the possibility. But if our distant descendants ever do, it won’t involve dilithium crystals, and Scottish accents will have evaporated into history by then.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
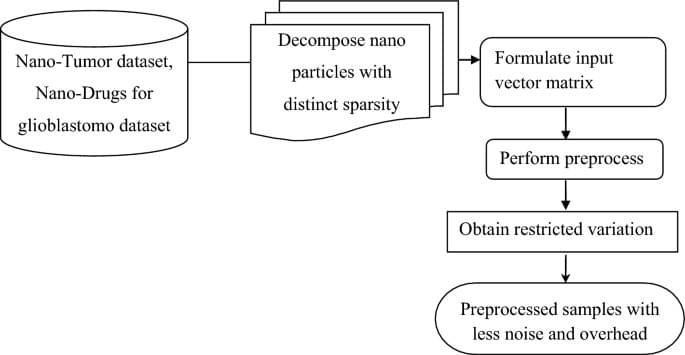
Point biserial correlation symbiotic organism search nanoengineering based drug delivery for tumor diagnosis
Shukla, G., Singh, S., Dhule, C. et al. Sci Rep 14, 6,530 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55159-6

New dark energy data could change our understanding of the universe
Are scientists wrong about dark energy? It looks like that could be the case.
Let’s dive into some recent findings from DESI, or the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument, to talk about its weird findings and how that might change our understanding of the universe.
Dark energy is not related to dark matter, even though they have similar names. They’re both called “dark,” though, because they’re not directly observable. We infer their existence based on how we’ve observed our universe behaves.
Black Hole and General relativity — gravity theory ‚Einstein field ‚sch equation|Ramanujan number
#blackhole Physics lecture video link, just click on the link for knowledge.
Here I discused general relativity — gravitytheory, Einstein field, schwarzchild equation, Black hall definition, Ramanujan numbers. Here I explain only static blackhole.
theory of general relativity.
special relativity vs general relativity.
einstein’s theory of general relativity.
general relativity equation.
special and general relativity.
spacetime and geometry an introduction to general relativity.
general relativity vs quantum mechanics.
a first course in general relativity.
general relativity and quantum mechanics.
general relativity and gravitation.
general relativity and black holes.
general relativity and time.
general relativity and special relativity.
general relativity astronomy.
general relativity assignment.
general relativity and gravity.
a new way to visualize general relativity.
albert einstein’s theory of general relativity.
albert einstein general relativity.
applications of general relativity.
alternatives to general relativity.
a first course in general relativity 3rd edition.
advanced general relativity.
a short course in general relativity.
general relativity black holes.
general relativity basics.
general relativity course.
general relativity course online.
general relativity class.
covariant derivative general relativity.
conformal transformation general relativity.
general relativity definition.
general relativity diagram.
general relativity definition in physics.
derivation of general relativity.
general relativity examples.
general relativity equation explained.
general relativity einstein paper.
general relativity equation derivation.
equation of general relativity.
einstein paper on general relativity.
einstein 1916 paper on general relativity.
general relativity field equations.
general relativity full equation.
field equations of general relativity.
formula for general relativity.
feynman general relativity.
general relativity gravity.
general relativity graviton lance.
general relativity geodesic.
general relativity geometry.
general relativity geodesic equation.
general relativity vs special relativity.
general relativity theory.
general relativity time dilation.
general relativity history.
general relativity homework solutions.
general relativity hilbert.
general relativity hamiltonian.
what is general relativity.
history of general relativity.
how did einstein discover general relativity.
general relativity in black holes.
general relativity inertial frame.
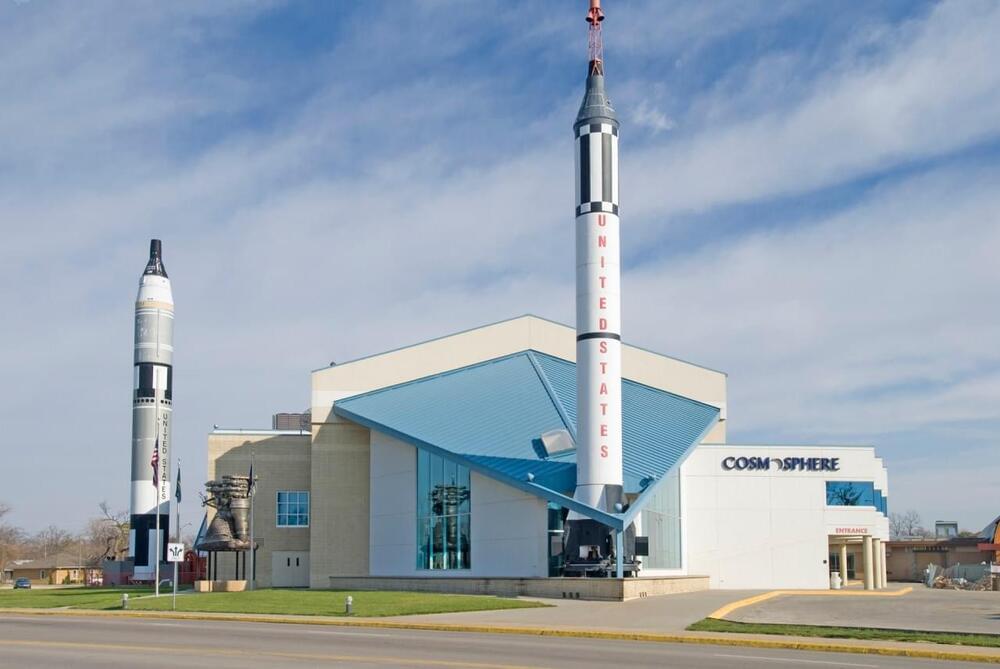

Cosmosphere gifted rocket engine from SpaceX
“The Cosmosphere is grateful to receive a flown Merlin engine from SpaceX,” said Jim Remar, Cosmosphere president and CEO. “The inclusion of the engine in our museum reaffirms the fact that the Cosmosphere houses one of the greatest collections of space exploration hardware.”
The Cosmosphere has been undergoing renovations since January. The Merlin engine will go on display in the new rocket gallery, which is expected to open in late 2024.
For more about the renovations underway at the Cosmosphere or to see upcoming events and programs, click here.
Subcutaneous Versus IV Nivolumab for Kidney Cancer
For people with advanced kidney cancer, an injectable form of nivolumab (Opdivo) is a suitable alternative to the original intravenous form, early results from a clinical trial have shown. Experts say the injectable form makes the treatment quicker and easier for patients to receive.
As a result, “patients’ treatment experience will be significantly improved,” said the trial’s leader, Saby George, M.D., of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, NY.
The clinical trial involved nearly 500 people with advanced or metastatic kidney cancer. All participants were randomly assigned to receive a new form of nivolumab that is given as injection under the skin (subcutaneous) or the original form, which is given through a vein (an intravenous infusion, or IV).

