Lithium iron phosphate is one of the most important materials for batteries in electric cars, stationary energy storage systems and tools. It has a long service life, is comparatively inexpensive and does not tend to spontaneously combust. Energy density is also making progress. However, experts are still puzzled as to why lithium iron phosphate batteries undercut their theoretical electricity storage capacity by up to 25% in practice.
In order to utilize this dormant capacity reserve, it would be crucial to know exactly where and how lithium ions are stored in and released from the battery material during the charging and discharging cycles.
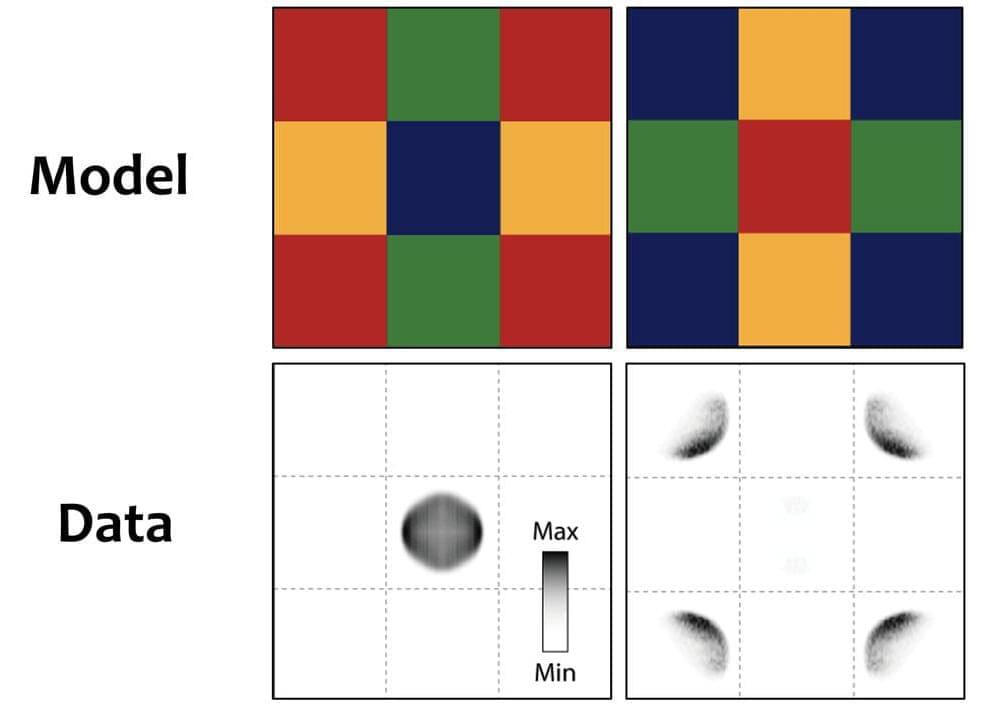
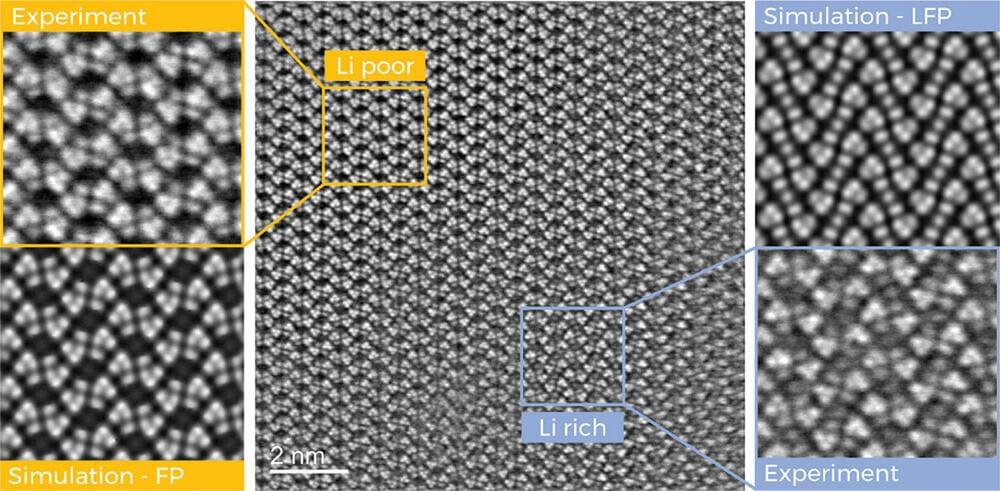
Researchers at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) have now taken a significant step in this direction. Using transmission electron microscopes, they were able to systematically track the lithium ions as they traveled through the battery material, map their arrangement in the crystal lattice of an iron phosphate cathode with unprecedented resolution and precisely quantify their distribution in the crystal.