Nearly 200 DeepMind workers signed a letter urging Google to drop military contracts, fearing AI misuse and violations of the company’s own rules.



What influence do global environmental stressors have on the ability of an ecosystem to withstand these stresses and rebuild itself? This is what a recent study published in Nature Geoscience hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated a correlation between environmental stressors and ecosystem resilience. This study comes as climate change continues to ravage the planet with more severe and frequent weather patterns, including increased temperatures and storms. This study holds the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, and the public better understand the short and long impacts of climate change on the environment and the steps that can be taken mitigate them.
“Terrestrial ecosystems are subject to a myriad of climate change and environmental degradation factors, including global warming, drought processes, atmospheric pollution, fires or overgrazing among many others. We know that these global change factors impact the ability of our ecosystems to provide services such as carbon sequestration or soil fertility that are key in the fight against climate change and in food production.” said Manuel Delgado Baquerizo, who leads the Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning Lab (BioFunLab) leader and is a co-author on the study.
For the study, the researchers conducted a global and elaborate study combining approximately 14,000 observations regarding ecosystems functions and biodiversity from a 15-year study with the goal of ascertaining an ecosystem’s ability to resist global environmental stressors, including those resulting from climate change. In the end, the team discovered a negative correlation between environmental stressors and an ecosystem’s resilience, meaning as these stressors increase the resilience of an ecosystem decreases. Additionally, they found the opposite regarding biodiversity, meaning its resilience increases to increasing global environmental stressors.

“This breakthrough enhances astronaut safety and makes long-term Mars missions a more realistic possibility,” said Dr. Dimitra Atri.
How will future Mars astronauts shield themselves from harmful space radiation? This is what a recent study published in The European Physical Journal Plus hopes to address as a pair of international researchers investigated what materials could be suited for providing the necessary shielding against solar and cosmic rays that could harm future Mars astronauts. This study holds the potential to help scientists and engineers better understand the mitigation measures that need to be taken to protect astronauts during long-term space missions.
For the study, the researchers used computer simulations to create Mars-like conditions, whose surface temperatures and pressures are much smaller than Earth’s, along with Mars completely lacking a protective magnetic field that provides our planet with protection from space radiation. Through this, the researchers tested a variety of materials to ascertain their effectiveness in shielding astronauts from space radiation.
In the end, they found that synthetic fibers, rubber, and plastics demonstrated the best performance of providing shielding. Additionally, the team found that Martian regolith (commonly called Martian “soil”) and aluminum combined with other materials could also be effective as a shielding agent, as well.
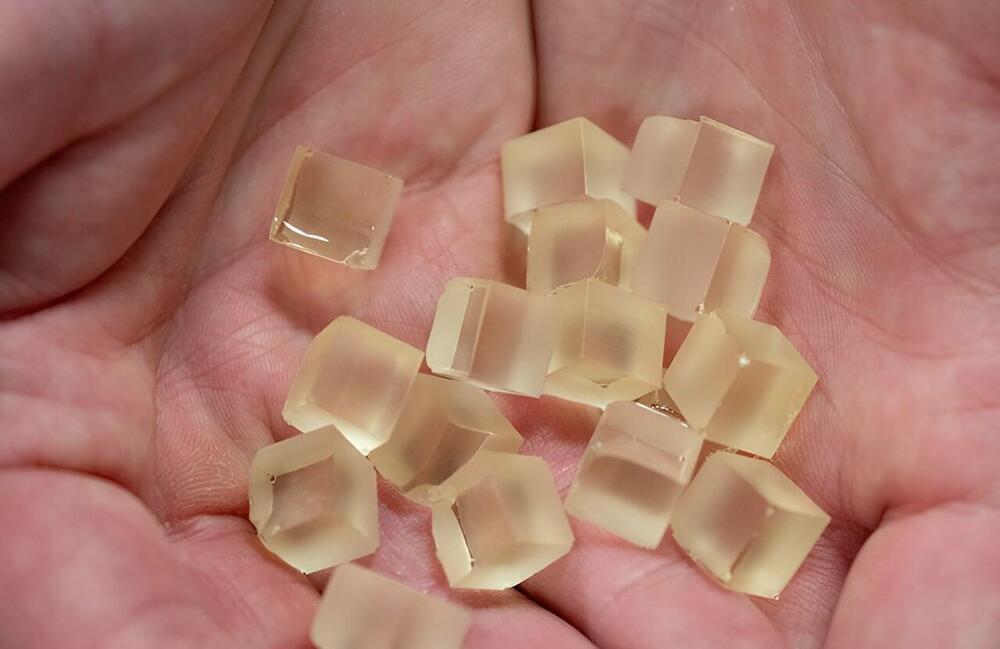

Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) see a realistic path forward to the manufacture of bio-derivable wind blades that can be chemically recycled and the components reused, ending the practice of old blades winding up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
The findings are published in the journal Science. The new resin, which is made of materials produced using bio-derivable resources, performs on par with the current industry standard of blades made from a thermoset resin and outperforms certain thermoplastic resins intended to be recyclable.
The researchers built a prototype 9-meter blade to demonstrate the manufacturability of an NREL-developed biomass-derivable resin nicknamed PECAN. The acronym stands for PolyEster Covalently Adaptable Network, and the manufacturing process dovetails with current methods.
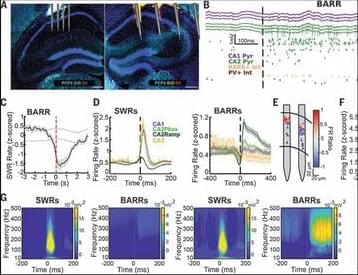
Memory consolidation involves the synchronous reactivation of hippocampal cells active during recent experience in sleep sharp-wave ripples (SWRs). How this increase in firing rates and synchrony after learning is counterbalanced to preserve network stability is not understood. We discovered a network event generated by an intrahippocampal circuit formed by a subset of CA2 pyramidal cells to cholecystokinin-expressing (CCK+) basket cells, which fire a barrage of action potentials (“BARR”) during non–rapid eye movement sleep. CA1 neurons and assemblies that increased their activity during learning were reactivated during SWRs but inhibited during BARRs. The initial increase in reactivation during SWRs returned to baseline through sleep. This trend was abolished by silencing CCK+ basket cells during BARRs, resulting in higher synchrony of CA1 assemblies and impaired memory consolidation.

The most recent email you sent was likely encrypted using a tried-and-true method that relies on the idea that even the fastest computer would be unable to efficiently break a gigantic number into factors.
Quantum computers, on the other hand, promise to rapidly crack complex cryptographic systems that a classical computer might never be able to unravel. This promise is based on a quantum factoring algorithm proposed in 1994 by Peter Shor, who is now a professor at MIT.
But while researchers have taken great strides in the last 30 years, scientists have yet to build a quantum computer powerful enough to run Shor’s algorithm.


A molecular biology research team at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine has become the first to map out how mitochondrial messenger RNA folds in human cells.
The research advances knowledge about the expression of genes in the mitochondria and paves the way for identification of therapeutic targets for mitochondrial neurodegenerative diseases.
“Dysfunctional mitochondria can cause devastating diseases, frequently with childhood-onset, known as mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Despite advances in identifying genes responsible for these disorders, their pathophysiological mechanisms have been poorly understood,” said Antoni Barrientos, Ph.D., professor of neurology and biochemistry and molecular biology at the Miller School. “This was partly due to a lack of a full understanding of mitochondrial gene expression. Specifically, nothing was known about how mitochondrial messenger RNA folds and how that could influence its stability and translation in health and disease.”