The ESA BioRock space experiment was carried into orbit, bound for the International Space Station (ISS), on 25 July 2019 as part of the SpaceX CRS-18 mission. CRS-18 lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, aboard a Falcon 9 launcher. The experiment will investigate the growth of biofilms and their ability to extract minerals and use them as nutrients (biomining) in microgravity conditions. This will be directly compared with results obtained under Mars and Earth gravity conditions simulated using a centrifuge on the ISS. The findings will contribute towards a better understanding of the growth of microorganisms in space, which is also key to bioregenerative life support systems, the formation of biofilms and microbial ore extraction. In future, such processes could be used in the biomining of economically valuable chemical elements such as copper on other planets. The German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) is playing a key role in the experiment.
Three species of bacteria are being investigated in the BioRock experiment: Sphingomonas desiccabilis, Bacillus subtilis and Cupriavidus metallidurans. “Our research focuses on the organism Bacillus subtilis,” says Petra Rettberg from the DLR Institute of Aerospace Medicine. “We are curious to see how well this bacterium can extract nutrients from the minerals of the basalt that was inoculated with Bacillus spores for the space experiment.” Over the coming weeks, the experiment will be put into operation on the ISS and is expected to remain in space until the end of August 2019. The experiment will then return to Earth for analysis and evaluation, with the samples later being examined in the astrobiological laboratories at the DLR site in Cologne.
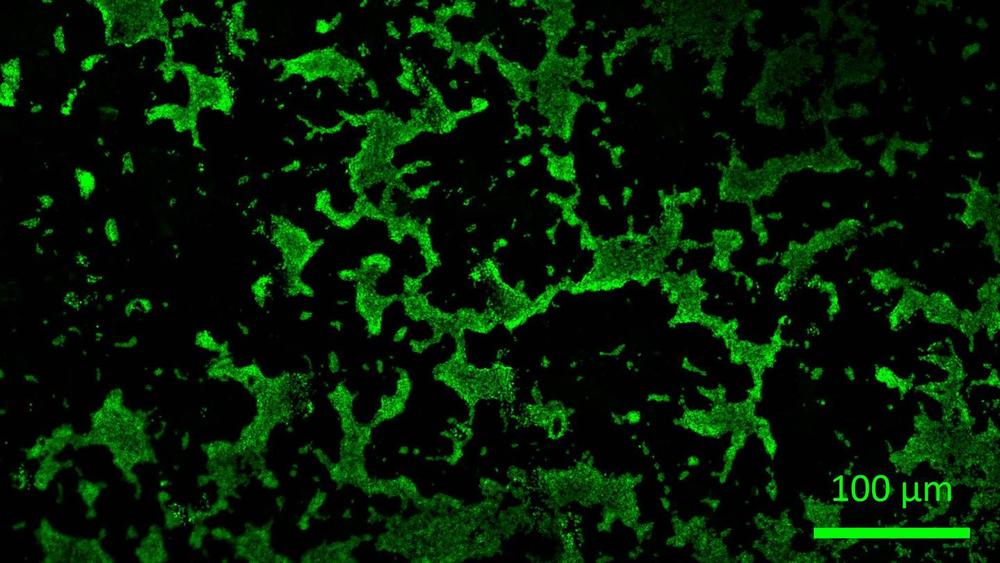
Biofilms are among the oldest visible signs of life on Earth and could also perhaps be found to be the earliest forms of life on other planets and moons in the Solar System. A biofilm is a structured community of microorganisms on a surface, encapsulated in a self-formed matrix made of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). This EPS matrix holds the microorganisms together in their three-dimensional arrangement and enables the biofilm to adhere to surfaces. The properties of microorganisms living within a biofilm generally differ substantially from those of microorganisms of the same species existing independently. The dense environment of the film allows them to cooperate with one another, interact in many ways and protects these minute organisms from external influences. This means that microorganisms in biofilms are highly resistant to various chemical and physical effects and can be used for a range of applications in space.