This experiment offers new insights into quantum mechanics, simulating how an electron might spontaneously move backward in time.


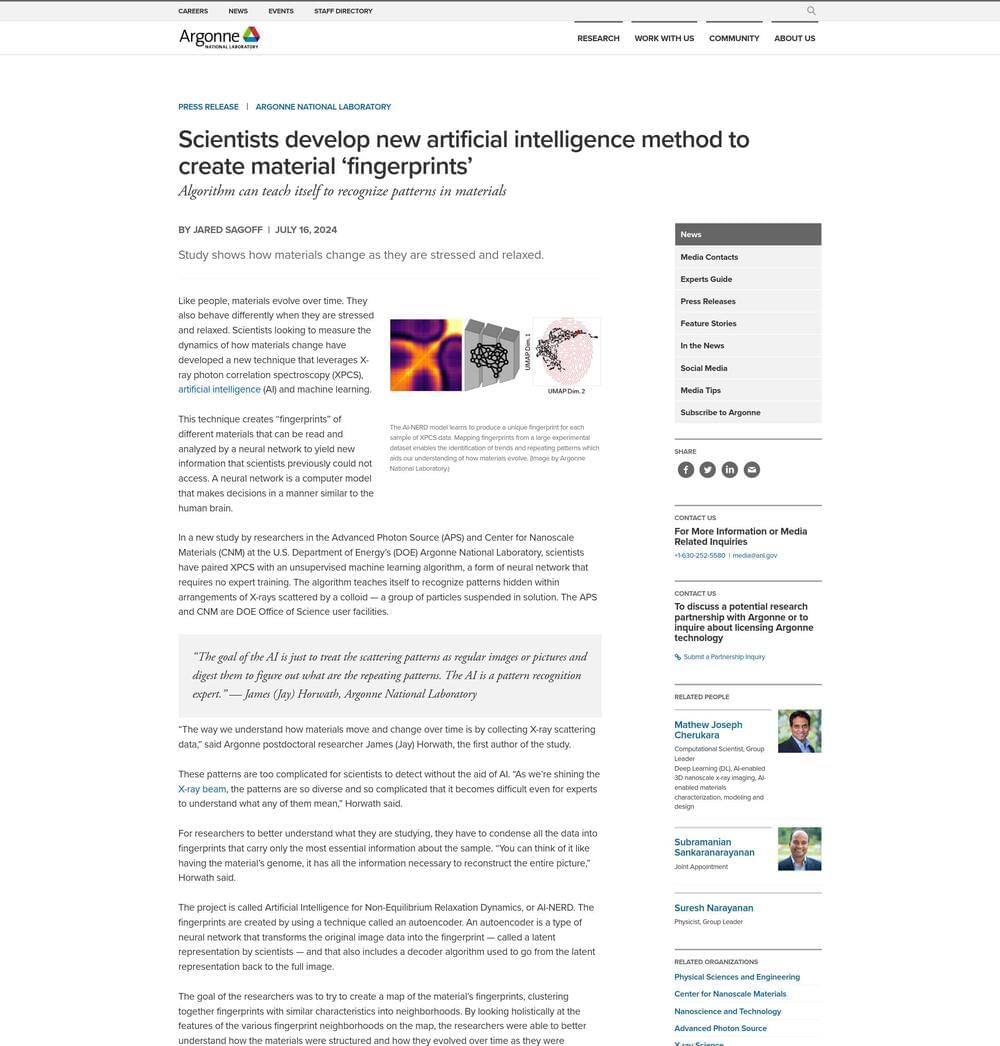
Researchers at Argonne have developed an innovative technique that creates “fingerprints” of different materials that can be read and analyzed by a neural network to yield previously inaccessible information — https://bit.ly/3LCklZw.
The goal of the AI is just to treat the scattering patterns as…
Study shows how materials change as they are stressed and relaxed.
Capone, C., Paolucci, P.S. Sci Rep 14, 14,656 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-65631-y.
Have you ever wonder how SNNs work and their difference from traditional neural networks? Or how SNNs play an important role in computing beyond the Moore’s Law?
What is SNN?
Spiking neural network (SNN) is a new form of neural networks with biologically realistic mechanisms designed to emulate the efficiency and effectiveness of the biological brain.
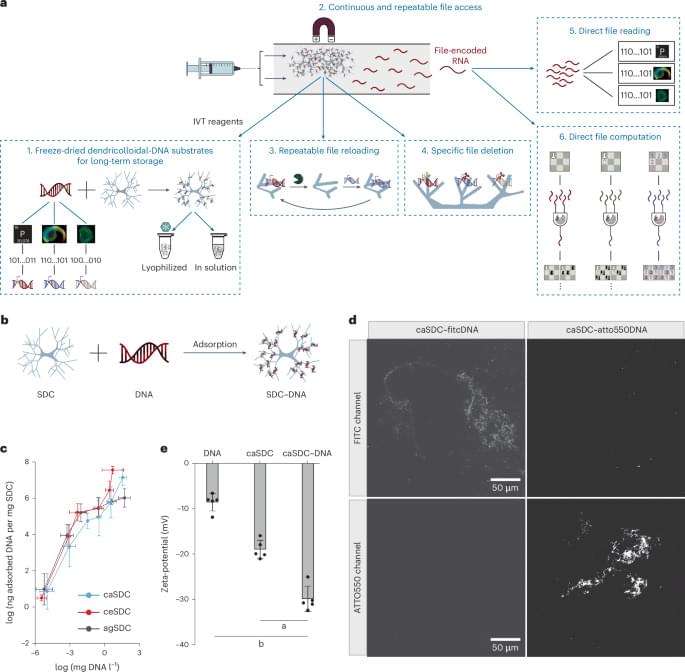
“DNA, RNA and proteins are the key players to regulate all processes in the cells of our body,” Leiden Professor John van Noort explains. “To understand the (mis-)functioning of these molecules, it is essential to uncover how their 3D structure depends on their sequence and for this it is necessary to measure them one molecule at a time. However, single-molecule measurements are laborious and slow, and the number of possible sequence variations is massive.”
Now the team of scientists developed an innovative tool, called SPARXS (Single-molecule Parallel Analysis for Rapid eXploration of Sequence space), that allows for studying millions of DNA molecules simultaneously.
“Traditional techniques that allow one sequence to be probed at a time usually take hours of measurement time per sequence. With SPARXS, we can measure millions of molecules within a day to a week. Without SPARXS, such a measurement would take several years to decades,” says Delft Professor Chirlmin Joo.

CRISPR-Cas systems, defense systems in bacteria, have become a plentiful source of technologies for molecular diagnostics. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) in Würzburg have expanded this extensive toolbox. Their novel method, called PUMA, enables the detection of RNA with Cas12 nucleases, which naturally target DNA. PUMA promises a wide range of applications and high accuracy.
The team published its results in the journal Nature Communications (“TracrRNA reprogramming enables direct PAM-independent detection of RNA with diverse DNA-targeting Cas12 nucleases”).
Bacteria have developed special defense mechanisms to protect themselves against viruses, which by no means infect only humans. As part of these so-called CRISPR-Cas systems, a CRISPR ribonucleic acid (crRNA), which serves as a “guide RNA,” recognizes regions of a foreign genome, such as viral DNA. The CRISPR-associated (Cas) nuclease, directed by a crRNA, then renders it harmless by cutting it like a pair of scissors.
Researchers worldwide can now create highly realistic brain cortical organoids — essentially miniature artificial brains with functioning neural networks — thanks to a proprietary protocol released this month by researchers at the University of California San Diego.
The new technique, published in Nature Protocols (“Generation of ‘semi-guided’ cortical organoids with complex neural oscillations”), paves the way for scientists to perform more advanced research regarding autism, schizophrenia and other neurological disorders in which the brain’s structure is usually typical, but electrical activity is altered. That’s according to Alysson Muotri, Ph.D., corresponding author and director of the UC San Diego Sanford Stem Cell Institute (SSCI) Integrated Space Stem Cell Orbital Research Center. The SSCI is directed by Dr. Catriona Jamieson, a leading physician-scientist in cancer stem cell biology whose research explores the fundamental question of how space alters cancer progression.
The newly detailed method allows for the creation of tiny replicas of the human brain so realistic that they rival “the complexity of the fetal brain’s neural network,” according to Muotri, who is also a professor in the UC San Diego School of Medicine’s Departments of Pediatrics and Cellular and Molecular Medicine. His brain replicas have already traveled to the International Space Station (ISS), where their activity was studied under conditions of microgravity.

In a study published in Cell Reports Physical Science (“Electro-Active Polymer Hydrogels Exhibit Emergent Memory When Embodied in a Simulated Game-Environment”), a team led by Dr Yoshikatsu Hayashi demonstrated that a simple hydrogel — a type of soft, flexible material — can learn to play the simple 1970s computer game ‘Pong’. The hydrogel, interfaced with a computer simulation of the classic game via a custom-built multi-electrode array, showed improved performance over time.
Dr Hayashi, a biomedical engineer at the University of Reading’s School of Biological Sciences, said: Our research shows that even very simple materials can exhibit complex, adaptive behaviours typically associated with living systems or sophisticated AI.
This opens up exciting possibilities for developing new types of ‘smart’ materials that can learn and adapt to their environment.

A research team at the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science has developed what it believes could be the template for the first building blocks for human-compatible organs printed on demand.
Liheng Cai, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering and chemical engineering, and his Ph.D. student, Jinchang Zhu, have made biomaterials with controlled mechanical properties matching those of various human tissues.
“That’s a big leap compared to existing bioprinting technologies,” Zhu said.