Noetik will use its multimodal AI models to identify which patients will most likely benefit from Agenus’s lead immuno-oncology combination, BOT/BAL.


MCKINNEY, Texas — Ultra-low-cost carrier Avelo Airlines is in talks with McKinney to be among the first to fly commercial passengers following the city’s airport controversial expansion, a letter from the Texas Attorney General’s Office indicated.
Houston-based Avelo already flies from DFW International Airport to its hub in New Haven, Connecticut, but its self-described strategy is to fly into smaller and “more convenient” airports.
McKinney plans to break ground on a controversial expansion to its airport this summer, with the goal of commercial flights taking off by the end of next year.
Using advanced computational modelling, a research team led by the University of Oxford, working in partnership with the Instituto Superior Técnico in the University of Lisbon, has achieved the first-ever real-time, three-dimensional simulations of how intense laser beams alter the ‘quantum vacuum’ — a state once assumed to be empty, but which quantum physics predicts is full of virtual electron-positron pairs.
Insulin resistance detected by routine triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index can flag people with early Alzheimer’s who are four times more likely to present rapid cognitive decline, according to new research presented at the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) Congress 2025.
Neurologists at the University of Brescia reviewed records of 315 non-diabetic patients with cognitive deficits, including 200 with biologically confirmed Alzheimer’s disease. All subjects underwent an assessment of insulin resistance using the TyG index and a clinical follow-up of three years.
The work is published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia.

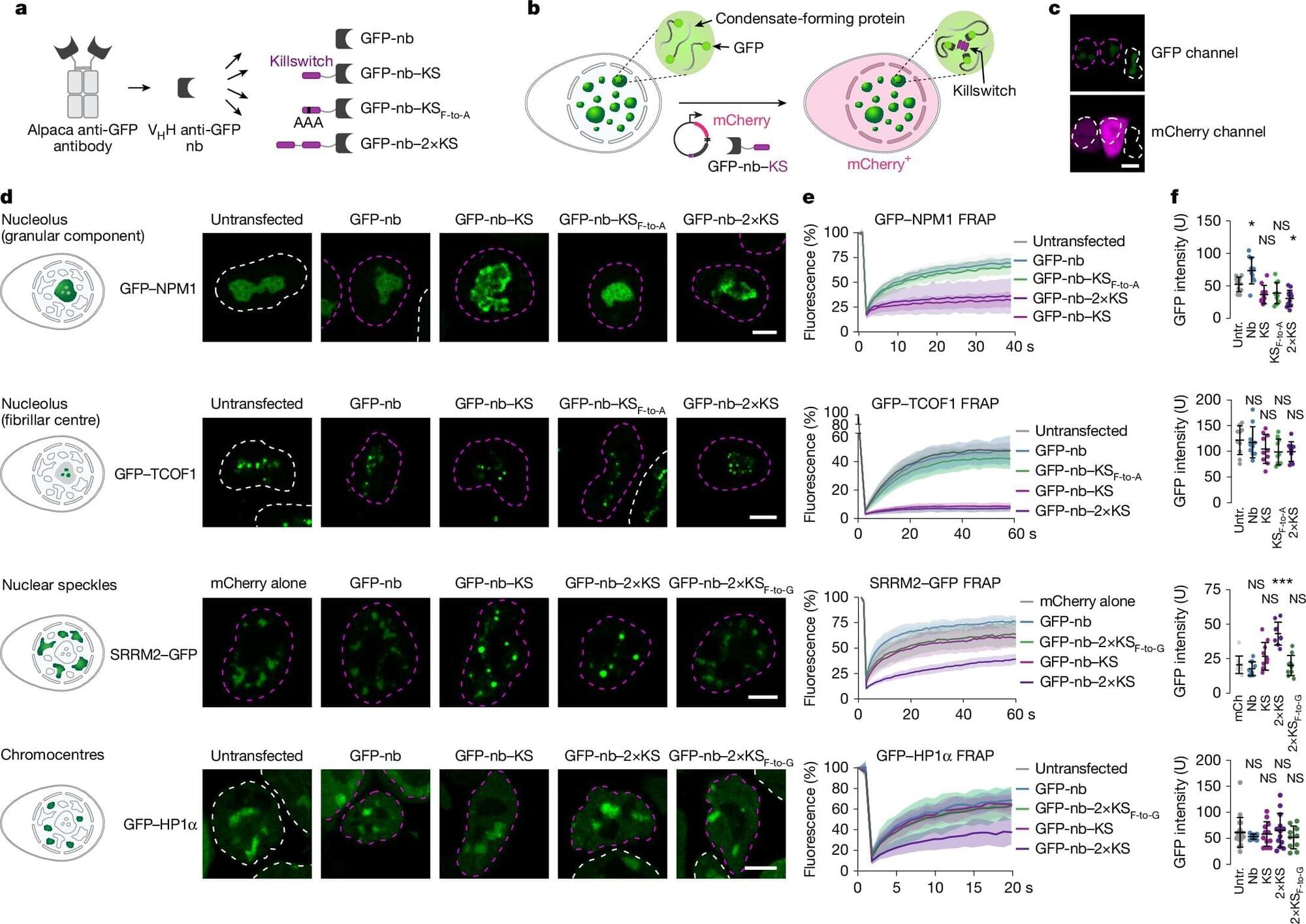
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics have developed a novel synthetic micropeptide termed the “killswitch” to selectively immobilize proteins within cellular condensates, unveiling crucial connections between condensate microenvironments and their biological functions.
Biomolecular condensates are specialized regions inside cells, existing without membranes, where critical biochemical reactions occur. Their importance in health and disease is well established, including roles in cancer progression and viral infection.
Methods to precisely probe and manipulate condensates in living cells remain limited. Existing strategies lack specificity, either dissolving condensates indiscriminately or requiring artificial protein overexpression, which obscures the natural behavior of native cellular proteins.
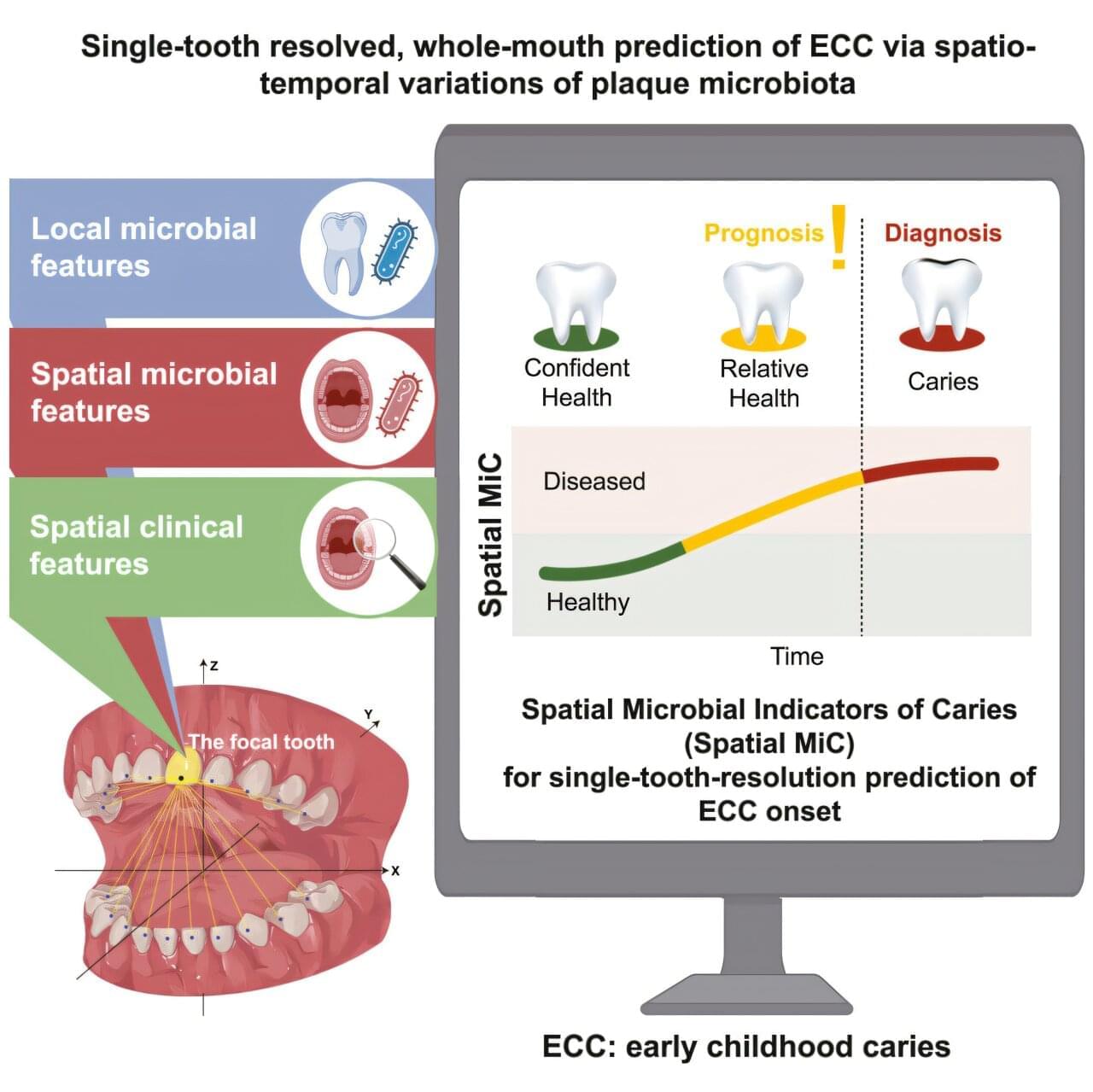
Early childhood caries (ECC)—the world’s most prevalent chronic childhood disease—disproportionately targets specific teeth, a mystery that has remained unresolved until now.
A collaborative research team from the Faculty of Dentistry of the University of Hong Kong (HKU), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS-QIBEBT), Qingdao Stomatological Hospital, and Qingdao Women and Children’s Hospital has made a discovery that could revolutionize the prevention of childhood tooth decay.
The team has developed the world’s first artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of predicting early childhood caries risk for individual teeth based on microbial characteristics, achieving an accuracy rate of more than 90%. The study is published in Cell Host & Microbe.