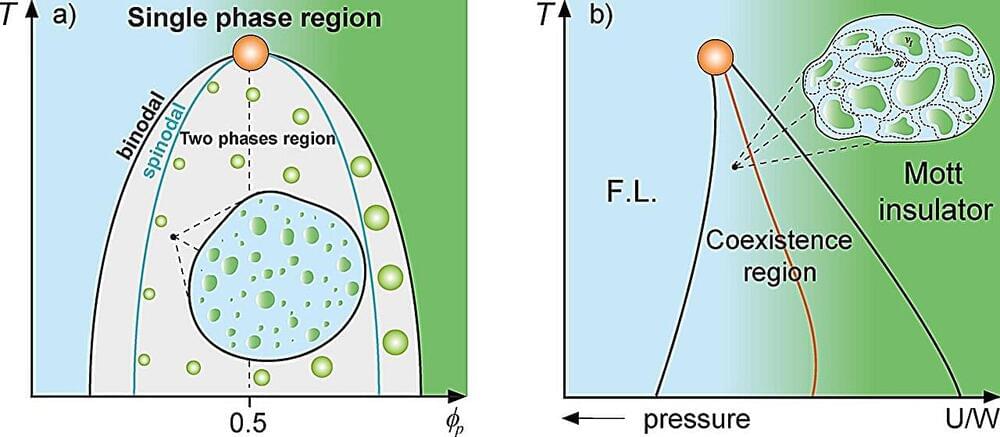
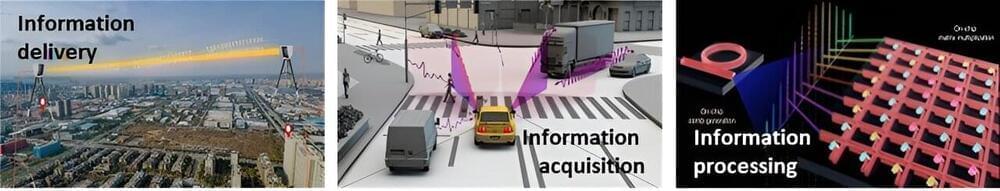
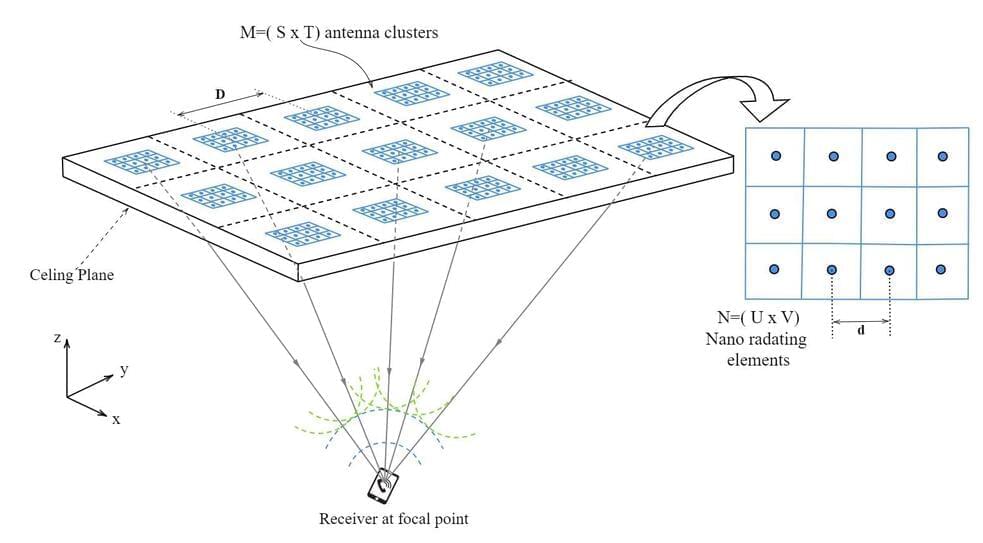
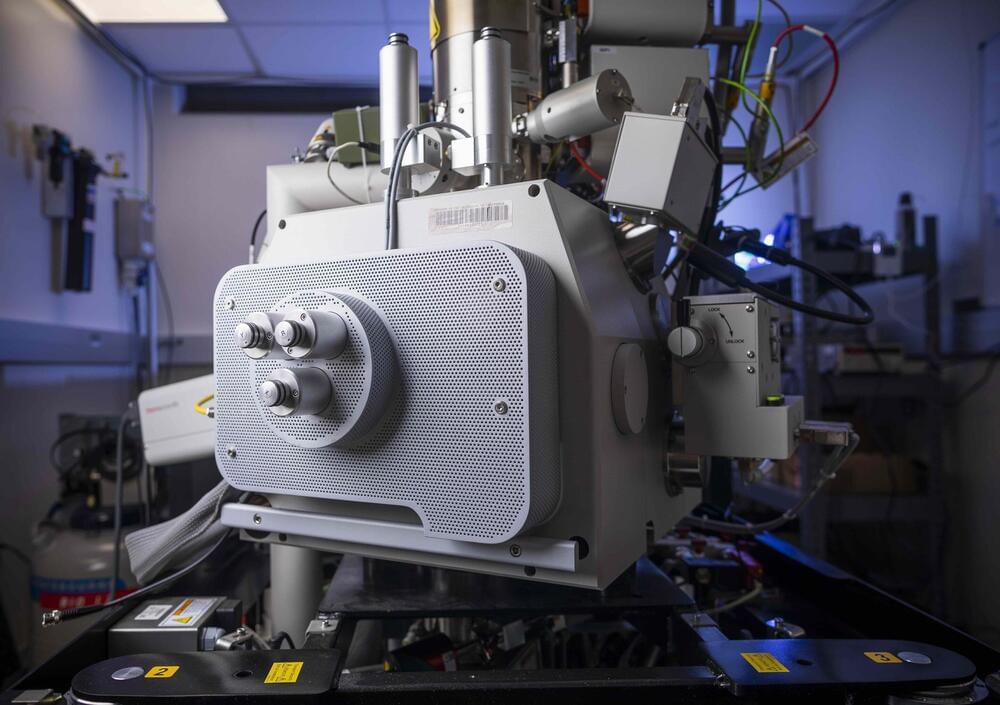
The word laser usually conjures up an image of a strongly concentrated and continuous light beam. Lasers that produce such light are, in fact, very common and useful. However, science and industry often also require very short and strong pulses of laser light.