Astronauts content themselves with freeze-dried gruel, but plans for crewed missions to Mars mean scientists need to create more delicious, nutritious menus by James Shackell.
A brief flash of green light was recently spotted coming from Venus in the night sky. The colorful shimmer has only been seen a handful of times before.
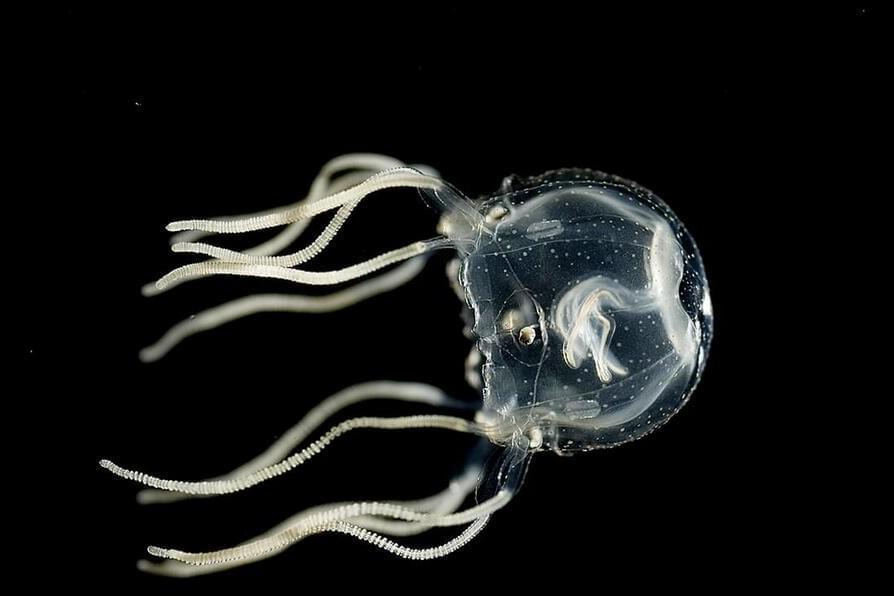
Despite lacking a centralized brain, the translucent creatures can learn from past experiences to avoid bumping into obstacles.
The team was thrilled with this discovery and saw the potential for creating durable patterns on the glass surface that could produce electricity when illuminated. This is a significant breakthrough because the technique does not require any additional materials, and all that is needed is tellurite glass and a femtosecond laser to create an active photoconductive material.
“Tellurium being semiconducting, based on this finding we wondered if it would be possible to write durable patterns on the tellurite glass surface that could reliably induce electricity when exposed to light, and the answer is yes,” explains Yves Bellouard who runs EPFL’s Galatea Laboratory.
Dr. David Sinclair’s groundbreaking research indicates a pill capable of reversing aging at a cellular level is possible and that even a high school student…
Mainly this is about vertical farming.
In this eye-opening video, we explore the complex Environmental Impacts of an Aging Cure, delving into how extending Human Lifespan and pursuing Longevity could reshape our planet. We investigate the potential for increased Population Growth, the challenges of Sustainability, and the implications for Resource Consumption. Our analysis covers the Ecological Footprint of a world where aging is a thing of the past, addressing both the ethical dilemmas and the potential for Biomedical Advances in Age-Related Research. As concerns about Overpopulation and the need for Renewable Resources come to the forefront, we examine Eco-friendly Technologies and their role in supporting an age-extended society. Join us in this critical discussion about the intersection of Environmental Ethics and the quest for Age Extension.
Don’t forget to subscribe for more thought-provoking content on the cutting-edge topics of our time. #AgingCure #EnvironmentalImpact #Sustainability.
Make a tax deductible Donation to support Longevity Advocacy and Research at:
LIKE WHAT WE DO?
Five-second clips generated with Lumiere show how the AI tools can create video from a prompt with realistic motion.
Lumiere can edit videos or create whole new ones from a prompt.
In a 1938 article, MIT’s president argued that technical progress didn’t mean fewer jobs. He’s still right.
Sewage surveillance has helped us track polio, covid, mpox, and more. Why not measles?
Shazam now lets you identify music while wearing headphones, the Apple-owned company announced this week. All you need to do is open the app, check for the headphone icon to confirm your headphones are connected and then start identifying music playing around you or within apps like TikTok and YouTube. The new update works with both wired and Bluetooth headphones.
Say you’re watching TikTok with headphones and come across a song you like in a video. You can open up the Shazam app, click to Shazam and then head back to TikTok. After a few seconds, the music will stop for a split second and then you can go back to the Shazam app to see the title and artist of the song.
Or, say you’re wearing headphones in a coffeeshop and want to know what song is playing in the café. You can now Shazam the song without having to remove your headphones.