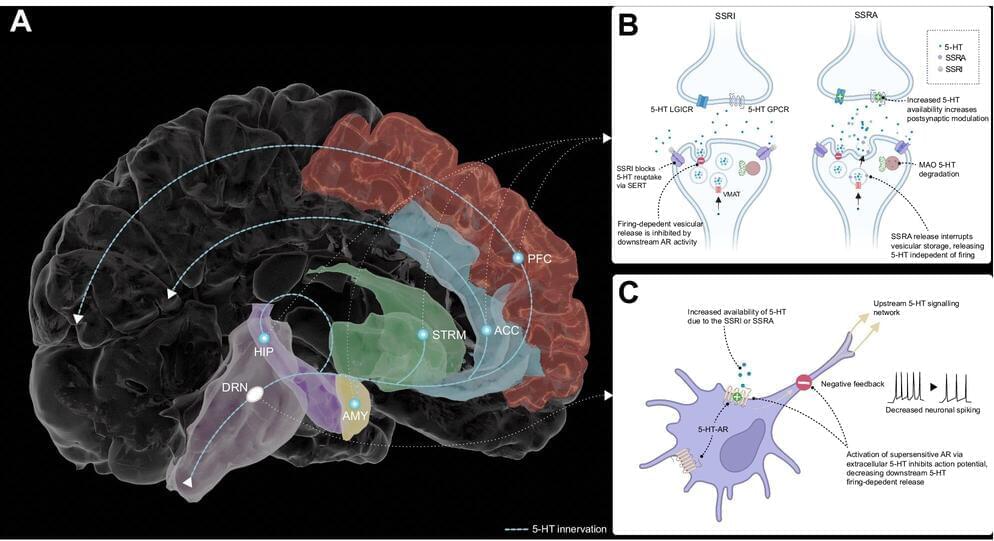
Increasing serotonin can change how people learn from negative information, as well as improving how they respond to it, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Communications.
The study by scientists at the University of Oxford’s Department of Psychiatry and the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Oxford Health Biomedical Research Center (OH BRC) found people with increased serotonin levels had reduced sensitivity to punishing outcomes (for example, losing money in a game) without significantly affecting sensitivity to rewarding ones (winning money).
The study involved 26 participants who were given the drug to increase serotonin, with a further 27 in a control group, who were asked to do a series of tasks measuring learning and behavioral control. State-of-the-art models were then used to understand participant behavior.