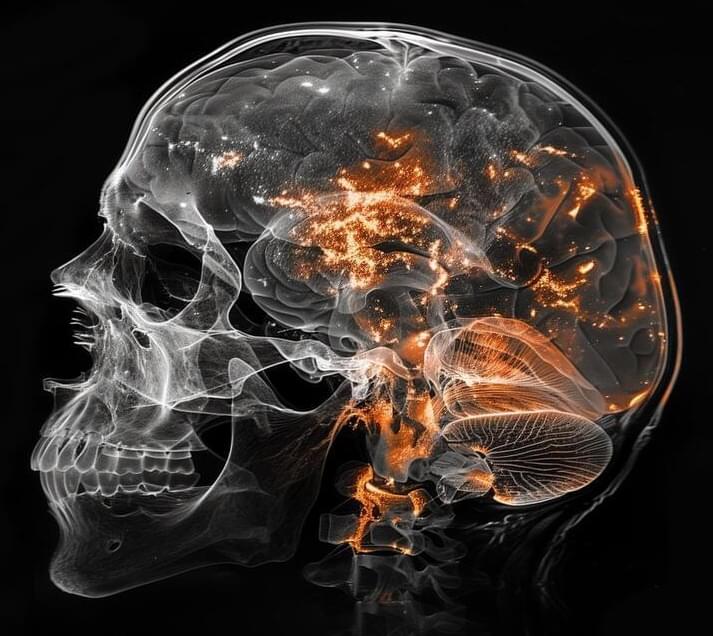
UC Davis researchers have identified new cell clusters in the amygdala that could hold keys to treating anxiety and depression.
Effective treatment for anxiety, depression, and other emotional disorders may rely on the amygdala—a part of the brain that regulates strong emotional responses, particularly fear. Until recently, understanding of this structure was limited. Now, researchers at the University of California, Davis, have identified distinct clusters of cells in the amygdala of humans and non-human primates, each with unique patterns of gene expression. This discovery could pave the way for more targeted treatments for conditions like anxiety, which impact tens of millions worldwide.
The findings were published on October 30 in the American Journal of Psychiatry.