Special Offer! Use our link https://joinnautilus.com/SABINE to get 15% off your membership!I recently read that you can have gravity without mass. Ha, no way…
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
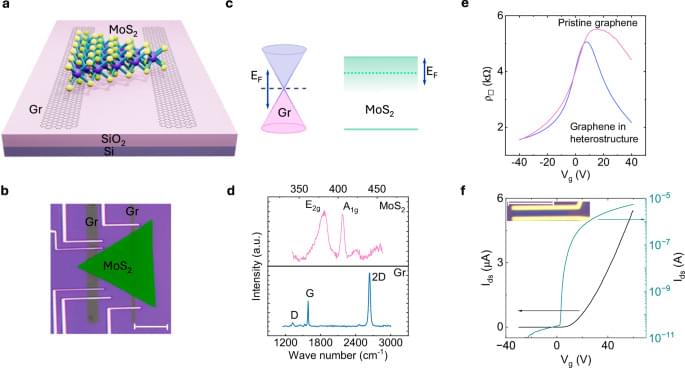
All-2D CVD-grown semiconductor field-effect transistors with van der Waals graphene contacts
Hoque, M.A., George, A., Ramachandra, V. et al. All-2D CVD-grown semiconductor field-effect transistors with van der Waals graphene contacts. npj 2D Mater Appl 8, 55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-024-00489-2
Ethics and benefits of gene editing
There are different types of biotechnology protocols for genome/gene editing (GE), but the preferred one is the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palynodromic Repeat (CRISPR) Cas9 system. Advantages include precision, the ability to design variants tailored to needs, and optimal operational cost and time.
The Universe is on the Move
Our universe is defined by the way it moves, and one way to describe the history of science is through our increasing awareness of the restlessness of the cosmos.
For millennia the brightest scientific minds in Europe and the Middle East believed that the Earth was perfectly still and that the heavens revolved around it, with a series of nested crystal spheres carrying each of the heavenly objects. Those early astronomers busied themselves with attempts to explain and predict the motion of those objects – the Sun, the Moon, each of the known planets, and the stars. Those predictions were excellent, and their systems able to explain the data well into the 16th century.
But that cosmological system of motion, initially developed by Claudius Ptolemy in the 2nd century, wasn’t perfect. In fact, it was an ungainly mathematical mess, relying on small circular orbits nested within larger ones, with some centered on the Earth and some centered on other points. On his deathbed in 1,543, the Polish astronomer Nicolas Copernicus published On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres, a radical reformulation of the old Ptolemaic system that put the Sun at the center of the universe – still and motionless – with the Earth set in motion around it along with all the other planets.
US achieves superconductor breakthrough, can benefit quantum computing
A team of scientists in the United States has achieved a notable milestone in the domain of superconductors. This progress may have considerable consequences for the future of quantum computing.
The research details the development of a novel superconductor material that has the potential to transform quantum computing and potentially function as a “topological superconductor.”
A topological superconductor is a special kind of material that exhibits superconductivity (zero electrical resistance) and also has unique properties related to its shape or topology.
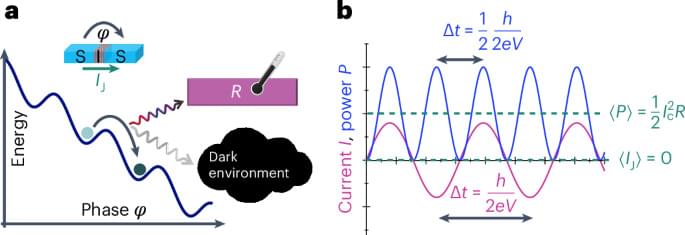
Bolometric detection of Josephson radiation
An on-chip nano-bolometer integrated with a Josephson junction quantitatively measures the Josephson radiation up to about 100 GHz frequency. This wide-band, thermal detection scheme of microwave photons provides a sensitive detector of Josephson dynamics beyond the standard conductance measurements.
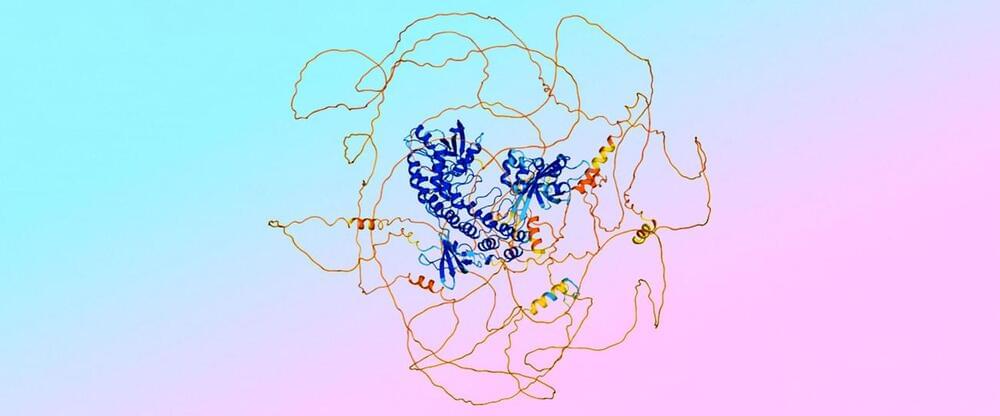

AlphaFold 3: Stepping into the future of structure prediction
We’ve all heard about the potential of artificial intelligence in the life sciences field. In 2020, the launch of AlphaFold 2, pioneered by Google DeepMind, took the world by storm and marked a new age in protein structure prediction. But now, AlphaFold 3 is transforming the landscape again. In this news highlight, we explore the new tech, compare it to its predecessor and take a look to the future.
Before the AI revolution, protein structure prediction heavily relied on experimental methods, such as X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy and, later, some complex computational methods like homology modelling. These methods were time consuming and costly, and were a major limiting step in drug discovery and development processes in particular. For years, scientists have been attempting to integrate the latest and greatest AI models into the field, in order to speed up the process and improve accuracy.
Enter AlphaFold, an artificial intelligence tool developed by Google’s DeepMind. The first version of the technology was released in 2018, but it was 2020’s AlphaFold 2 that made headlines – winning the prestigious Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) 14 competition. Having gone through multiple major iterations, the most recent release, AlphaFold 3, is set to further transform the protein space. But what does it do, and how may it outperform its predecessor?

UC Irvine discovery of ‘item memory’ brain cells offers new Alzheimer’s treatment target
Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have discovered the neurons responsible for “item memory,” deepening our understanding of how the brain stores and retrieves the details of “what” happened and offering a new target for treating Alzheimer’s disease.
Memories include three types…
Finding significantly deepens understanding of crucial component of cognitive function.
AERWINS XTURISMO the World’s First Flying Bike
face_with_colon_three year 2023.