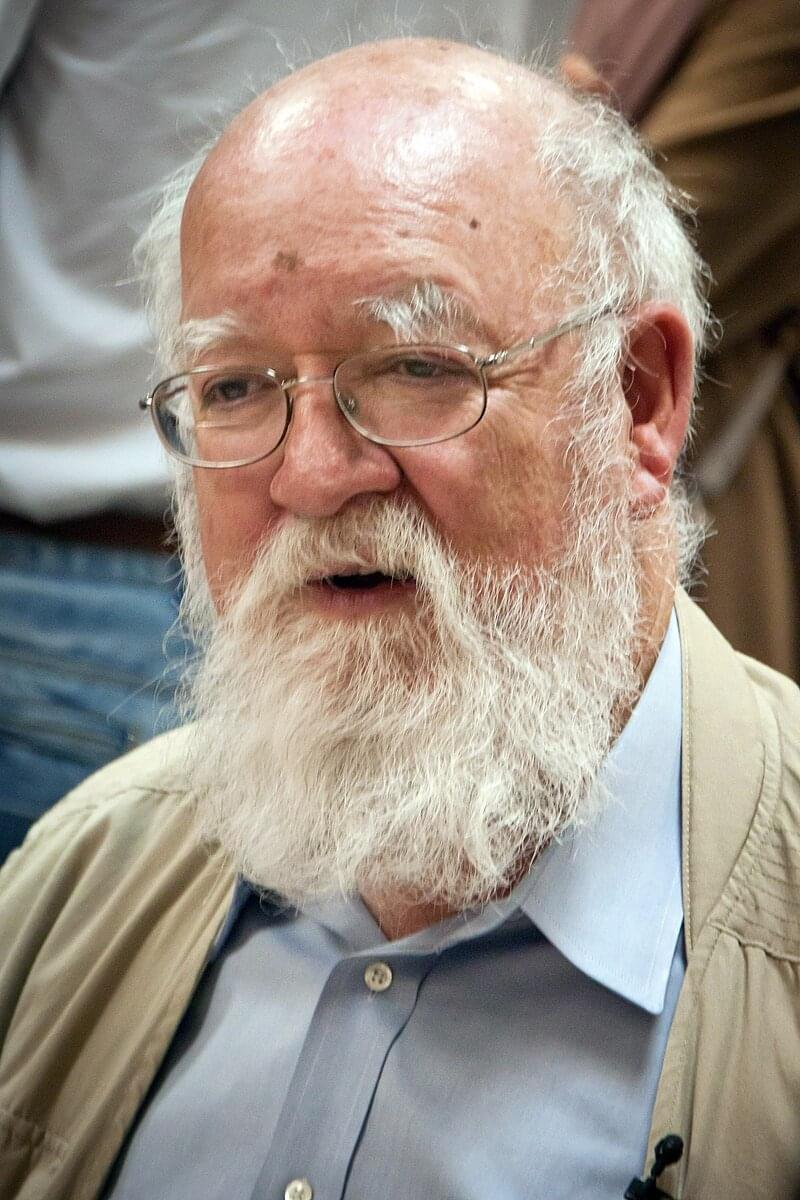
Hoboken, April 20, 2024. Daniel Dennett’s death feels like the end of an era, the era of ultra-materialist, ultra-Darwinian, swaggering, know-it-all scientism. Who’s left? Dawkins? Dennett isn’t as smart as he thinks he is, I liked to say, because no one is. He lacked the self-doubt gene, but he forced me to doubt myself, he made me rethink what I think, and what more can you ask of a philosopher? I first encountered Dennett’s in-your-face brilliance in 1981 when I read The Mind’s I, and his name popped up at a consciousness shindig I attended just last week. To honor Dennett, I’m posting a free, revised version of my 2017 critique of his claim that consciousness is an “illusion.” I’m also coining a phrase, “the Dennett Paradox,” explained below.— John Horgan
Of all the odd notions to emerge from debates over consciousness, the oddest is that it doesn’t exist, at least not in the way we think it does. It is an illusion, like “Santa Claus” or “American democracy.”
Descartes said consciousness is the one undeniable fact of our existence, and I find it hard to disagree. I’m conscious right now, as I type this sentence, and you are presumably conscious as you read it (although I can’t be absolutely sure).