The new AI system can estimate cosmological parameters with stunning precision, and it could help astronomers unpick one of the thorniest problems in the field.



Chinese scientists have developed a method using genetic engineering to potentially enhance brain-computer interface (BCI) technology by enlarging neurons for better signal transmission.
The researchers, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ National Centre for Nanoscience…
Gene sequence could be implanted with electrodes to make neurons larger and easier to ‘read’ in quest for better mind control of devices.

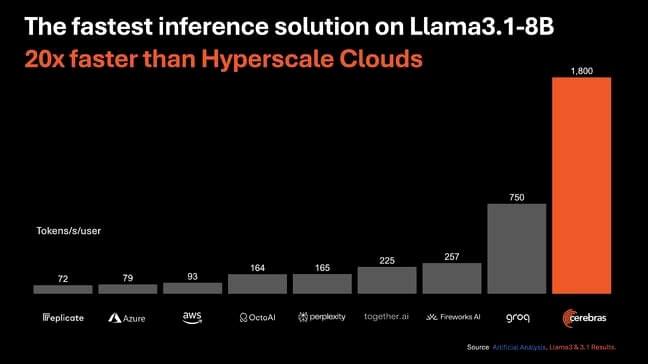
A new study looking at the potentially hazardous asteroid 99,942 Apophis has suggested that the odds of an impact in 2029 or 2036 is ever so slightly higher than we thought.
When Apophis was first discovered in 2004, observations briefly placed it at level 4 on the Torino impact hazard scale, with a score of 0 meaning the likelihood of impact is zero or thereabouts, and 10 meaning “a collision is certain, capable of causing global climatic catastrophe that may threaten the future of civilization as we know it, whether impacting land or ocean.”
While level 4 might sound low, it is the highest level of any object that has been discovered since NASA first started monitoring potentially hazardous Near-Earth Objects (NEOs).

IT is the backbone of modern healthcare, from patient records and medication management to diagnostic equipment, networking and communication systems. These healthcare IT professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy, security, reliability and accessibility of health data. Hospital IT professionals also ensure that the technological backbones of these hospital systems operate correctly.
They ensure that doctors have real-time access to patient information, nurses can track medication schedules accurately and communication between departments is fluid and efficient. Without this critical support, the efficiency and safety of patient care is severely compromised. Simply put, the work of hospital IT teams is vital to the smooth operation of hospitals.
It is fair and appropriate to say that hospital IT teams are unsung heroes. The nature of working in IT is to keep everything running smoothly at all times. These dedicated, talented and hardworking IT experts are often ignored unless the infrastructure is not working or has failed. Nobody notices when hospital IT systems are operating properly; the IT teams only get noticed when things go wrong, and typically receive negative attention.
Synthetic Plants For A Sustainable Future — Dr. Angie Burnett, Ph.D. — Program Director, Advanced Research + Invention Agency (ARIA)
Dr. Angie Burnett, Ph.D. is Program Director at the Advanced Research and Invention Agency (ARIA — https://www.aria.org.uk/), a UK organization created by an Act of Parliament, and sponsored by the Department for Science, Innovation, and Technology, to fund projects across a full spectrum of R\&D disciplines, approaches, and institutions, per the ARIA mission statement to “Look beyond what exists today to the breakthroughs we’ll need tomorrow”
Prior to this role, Dr. Burnett was a Research Associate in the Department of Plant Sciences, and a former David MacKay Research Associate at Darwin College and Cambridge Zero where her work focused on understanding the response of maize plants to high light and cold temperature stresses, and the genetic basis for stress tolerance, so that breeders can produce plants which are better able to withstand environmental stress.
Dr. Burnett’s background is in plant physiology. She holds a BA from the University of Cambridge and a PhD from the University of Sheffield, where she was awarded the inaugural PhD studentship from the Society for Experimental Biology. Before commencing her role at the University of Cambridge, she worked as a postdoctoral research associate at Brookhaven National Laboratory in the USA and as a Consultant at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations in Italy.
Important Episode Links.
A clever use of machine learning guides researchers to a missing term that’s needed to accurately describe the dynamics of a complex fluid system.
Physical theories and machine-learning (ML) models are both judged on their ability to predict results in unseen scenarios. However, the bar for the former is much higher. To become accepted knowledge, a theory must conform to known physical laws and—crucially—be interpretable. An interpretable theory is capable of explaining why phenomena occur rather than simply predicting their form. Having such an interpretation can inform the scope of a new theory, allowing it to be applied in new contexts, while also connecting it to and incorporating prior knowledge. To date, researchers have largely struggled to get ML models (or any automated optimization process) to produce new theories that meet these standards. Jonathan Colen and Vincenzo Vitelli of the University of Chicago and their colleagues now show success at harnessing ML not as a stand-in for a researcher but rather as a guide to aid building a model of a complex system [1].
The observation of quantum modifications to a well-known chemical law could lead to performance improvements for quantum information storage.
The Arrhenius law says that the rate of a chemical reaction should decrease steadily as you increase the energy barrier between initial and final states. Now researchers have found a system that obeys a quantum version of the Arrhenius law, where the rate does not drop smoothly but instead decreases in a staircase pattern [1]. The system is a type of quantum bit (qubit) that is particularly robust against environmental disturbances. The researchers demonstrated that they can take advantage of this quantum effect to improve the qubit’s performance.
Technologies such as quantum computers and quantum cryptography use qubits to store information, and one of the continuing challenges is that uncontrolled environmental effects can change the state of a qubit. The most common solutions require large amounts of hardware, but an alternative method is to use qubits that are more error resistant, such as so-called cat qubits. The information in these qubits is stored in robust combinations of quantum states that resemble the states in Schrödinger’s famous feline thought experiment (see Synopsis: Quantum-ness Put on the Scale).