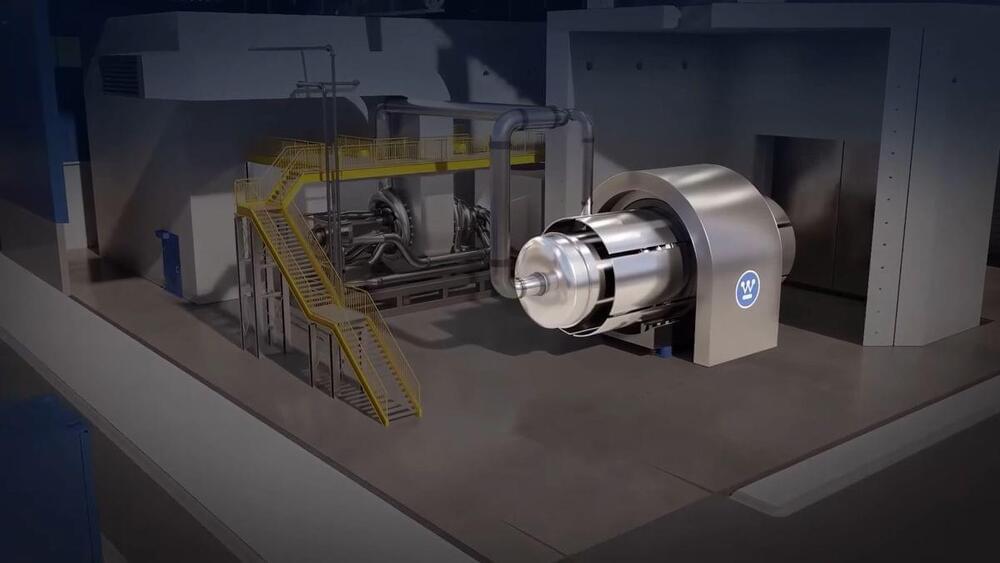
Small, easily transportable nukes could power our data driven future.

As President, Jimmy Carter established several science-related initiatives and policies.
Carter also sought to promote scientific research and development in a number of areas. He increased funding for basic science research in fields such as physics and chemistry, and established the National Commission on Excellence in Education to promote improvements in science and math education in American schools.
On top of that, Carter sought to address environmental issues through science policy. He established the Superfund program, which was created to clean up hazardous waste sites, and signed the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act, which protected millions of acres of land in Alaska.
Carter’s science policy emphasized the importance of science and technology in addressing pressing issues such as energy, the environment, and education.
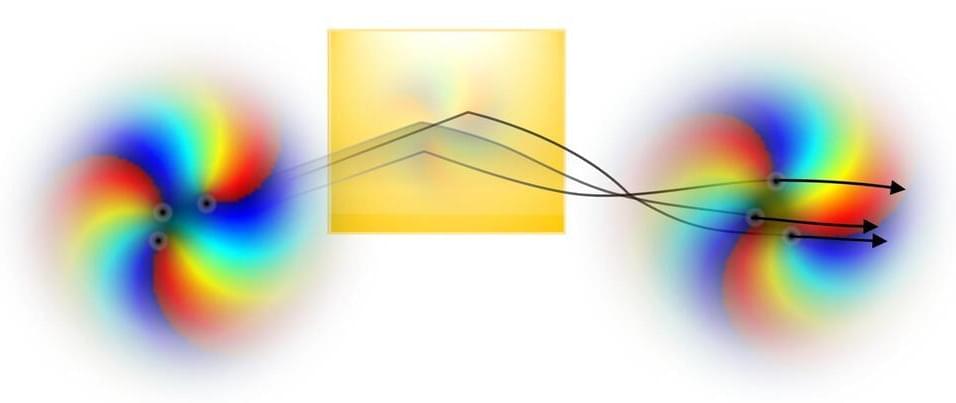

Researchers have recently observed a fascinating effect in the behavior of twisted light when it reflects off surfaces.
Everyday experience tells us that light reflected from a perfectly flat mirror will give us the correct image without any deformation. Interestingly, this is not the case when the light field itself is structured in a complex way. Tiny deformations appear.
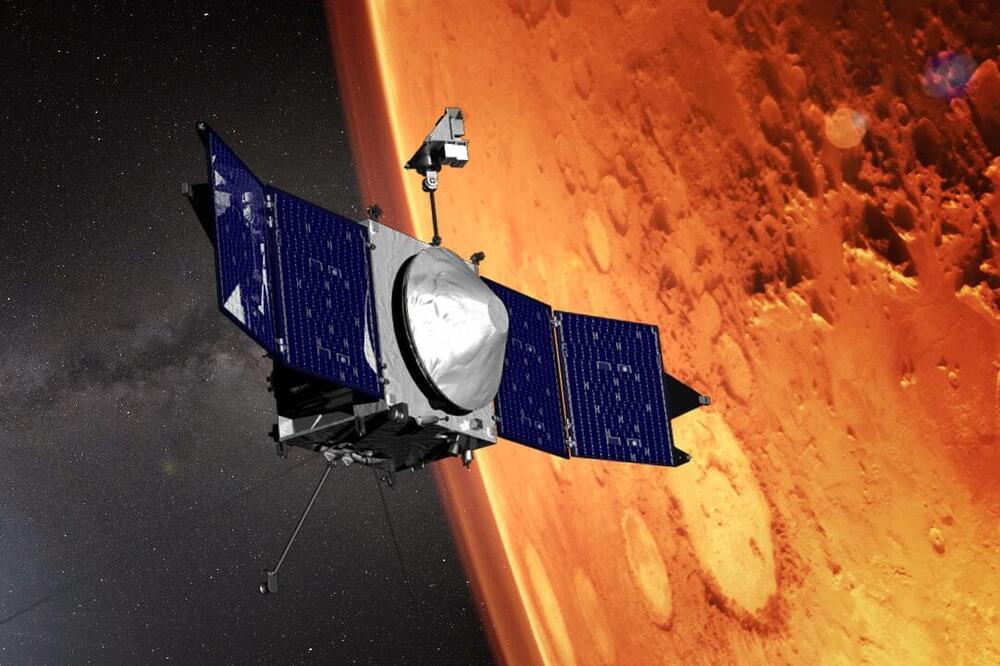

Dr Shannon Curry said she believes humans will first land on Mars — at the earliest — in 2040, but more realistically 2050. And 2075 before Mars colonization! Very realistic prediction, and I enthusiastically agree.
NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft, led by scientists at the University of Colorado Boulder, was supposed to operate for one year when it entered orbit on September 21, 2014. Ten years later, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution orbiter has been a boon to scientists studying the red planet and they hope it will remain in operation for years to come.
In May, MAVEN researchers got to watch as a huge solar storm hit the planet along with a massive dose of radiation. The MAVEN spacecraft is an orbiter, so it won’t ever land on the surface of Mars like the Curiosity and Perseverance rovers. Instead, it’s designed to examine the Martian atmosphere, which principal investigator Shannon Curry said “holds a number of secrets in terms of our past, present, and future.”
Here are some takeaways from Curry’s interview with Colorado Matters.
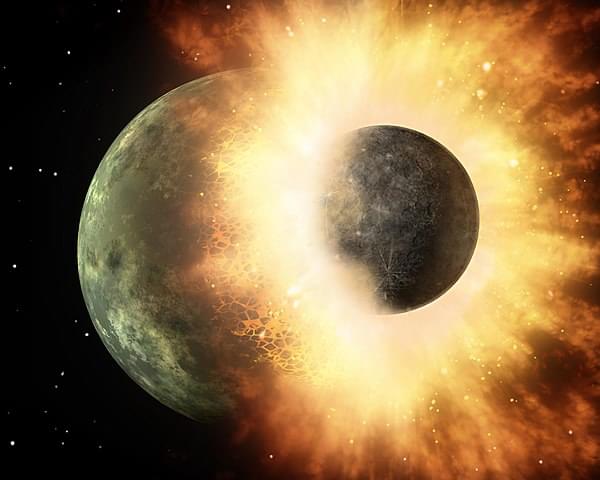

“No one knows how the moon was formed,” said Dr. Darren Williams. “For the last four decades, we have had one possibility for how it got there. Now, we have two. This opens a treasure trove of new questions and opportunities for further study.”
How did the Moon form? Was it from a collision, as has been the longstanding theory, or could it have been captured by the Earth early in our planet’s formation? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as two researchers from Penn State investigated a new model for how our Moon came to reside within its present orbit around the Earth. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the origin of our Moon, which could help explain how some moons throughout our solar system came to be orbiting their respective planets, as well.
For the study, the researchers performed a series of calculations aimed at ascertaining if a simulated binary object could end up in the Moon’s orbit. The argument the researchers make is that if the Moon was formed from a collision, then it would orbit above the Earth’s equator. In contrast, the Moon’s orbit follows a different orbit.
“The moon is more in line with the sun than it is with the Earth’s equator,” said Dr. Darren Williams, who is a professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State Behrend and lead author of the study.
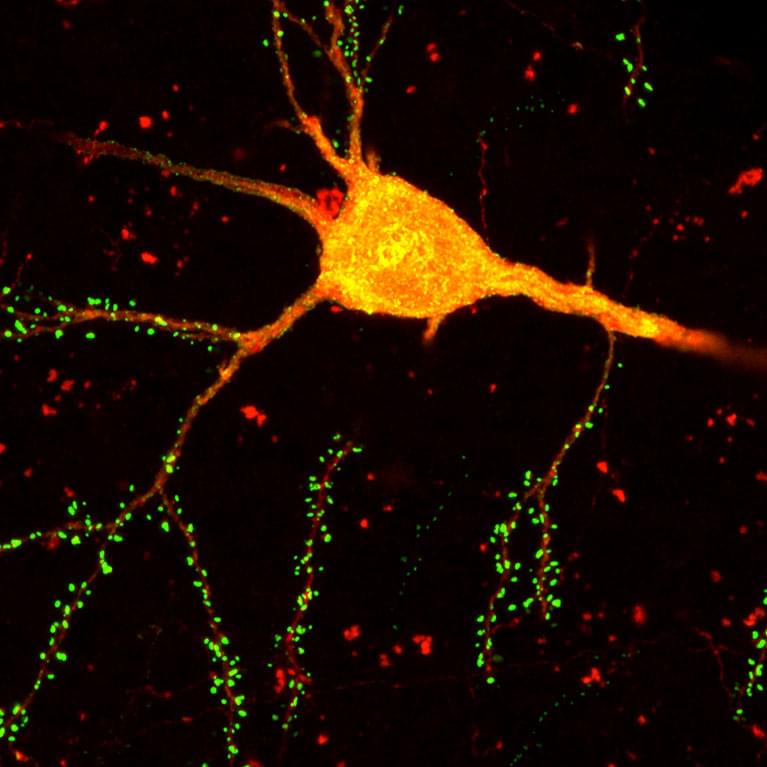
A new brain-mapping tool just dropped!
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute are unveiling a new brain-mapping neurotechnology called Single Transcriptome Assisted Rabies Tracing (START). The cutting-edge tool combines two advanced technologies—monosynaptic rabies virus tracing and single-cell transcriptomics—to map the brain’s intricate neuronal connections with unparalleled precision.
Using the technique, the researchers became the first to identify the patterns of connectivity made by transcriptomic subtypes of inhibitory neurons in the cerebral cortex. They say having this ability to map the connectivity of neuronal subtypes will drive the development of novel therapeutics that can target certain neurons and circuits with greater specificity. Such treatments could be more effective and produce fewer side effects than current pharmacological approaches.
The study, published on September 30, 2024, in Neuron, is the first to resolve cortical connectivity at the resolution of transcriptomic cell types.
Research videos aren’t known for their narrative arcs. Occasionally, however, you see one that keeps getting better the longer you watch. “Beyond Manual Dexterity” is one such video. It wows you in the first few seconds with a highly dexterous robotic gripper, and then things start to go off the rails.
The video debuted along with a research paper of the same name at IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Rotterdam this week. The work, conducted by Switzerland’s EPFL, explores ways in which robotic hands can grow beyond existing confines to grasp an even wider range of objects.
“The deep learning model has significantly advanced dexterous manipulation techniques for multi-fingered hand grasping,” the team notes. “However, the contact information-guided grasping in cluttered environments remains largely underexplored.”
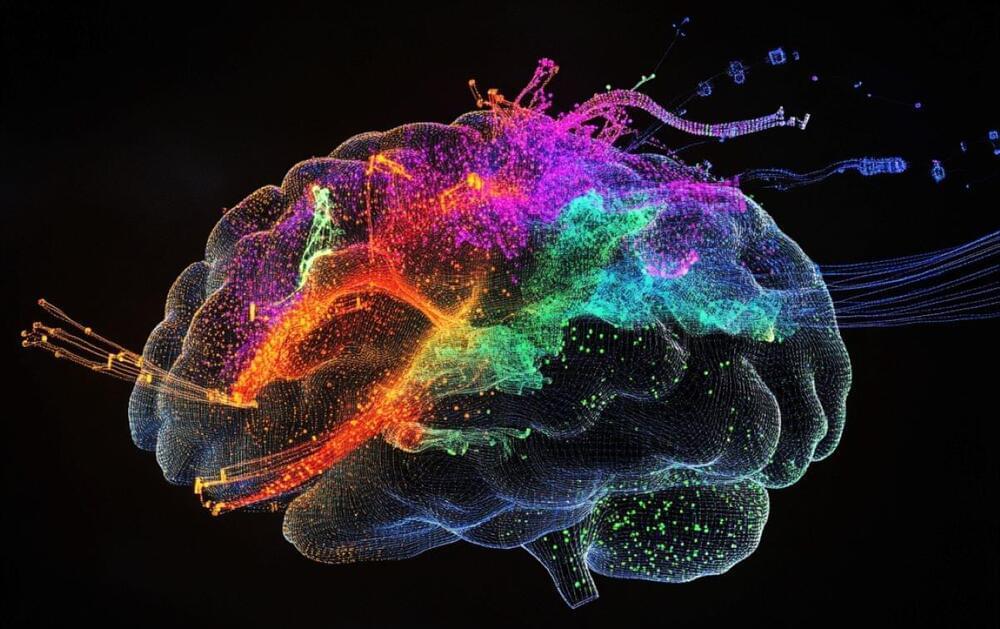
Source: Allen Institute.
The BRAIN Initiative® Cell Atlas Network (BICAN) has launched its first major data release, marking a significant milestone in the ambitious effort to map the whole human brain.
The data, accessible through the BICAN Rapid Release Inventory, includes single-cell and single-nucleus transcriptomic and epigenomic profiles from humans, mice, and 10 other mammalian species.

The LEV Foundation is a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing the field of rejuvenation biotechnology with the goal of reversing biological aging. Under the leadership of renowned gerontologist Aubrey de Grey, the foundation focuses on conducting early-stage research on animals, specifically testing combination therapies that aim to dramatically extend lifespan. LEV Foundation stands out in the aging research community by targeting middle-aged mice, developing treatments that could one day be applied to humans, helping achieve longevity escape velocity — the point at which aging can be controlled through medical interventions.