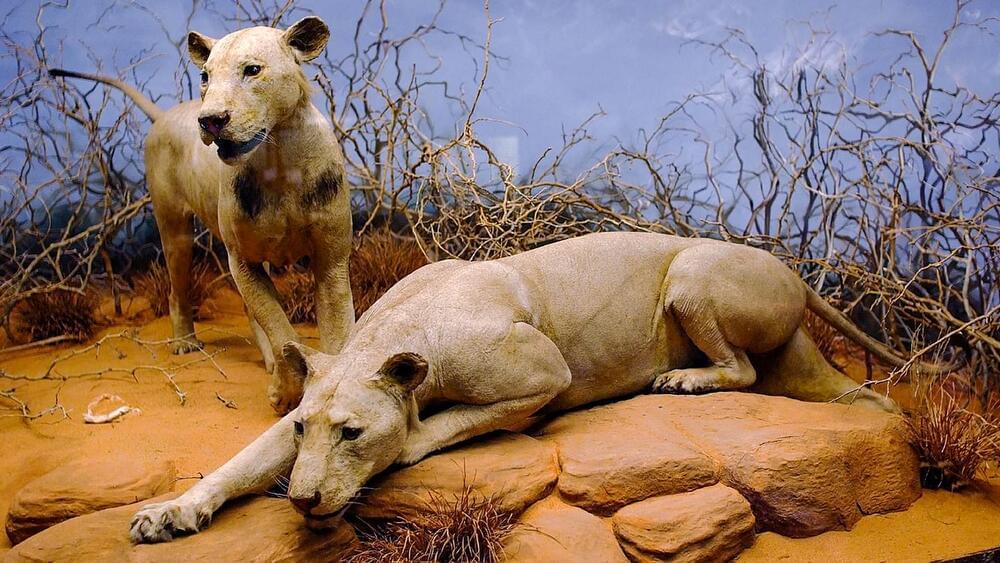
Genetic analysis of cavity crud from two famed man-eating lions suggests the method could re-create diets of predators that lived thousands of years ago.



“What the FBI uncovered in this case is essentially a new twist to old-school financial crime,” Jodi Cohen, the special agent in charge of the FBI’s Boston division, said in a statement. “What we uncovered has resulted in charges against the leadership of four cryptocurrency companies, and four crypto ‘market makers’ and their employees who are accused of spearheading a sophisticated trading scheme that allegedly bilked honest investors out of millions of dollars.”
Liu Zhou, a “market maker” working with MyTrade MM, allegedly told promoters of NexFundAI that MyTrade MM was better than its competitors because they “control the pump and dump” allowing them to “do inside trading easily.”
An FBI spokesperson told CoinDesk that there was limited trading activity on the coin but didn’t share additional information. On a Wednesday press call, Joshua Levy, the acting US attorney for the District of Massachusetts, said trading on the token was disabled, according to CoinDesk.
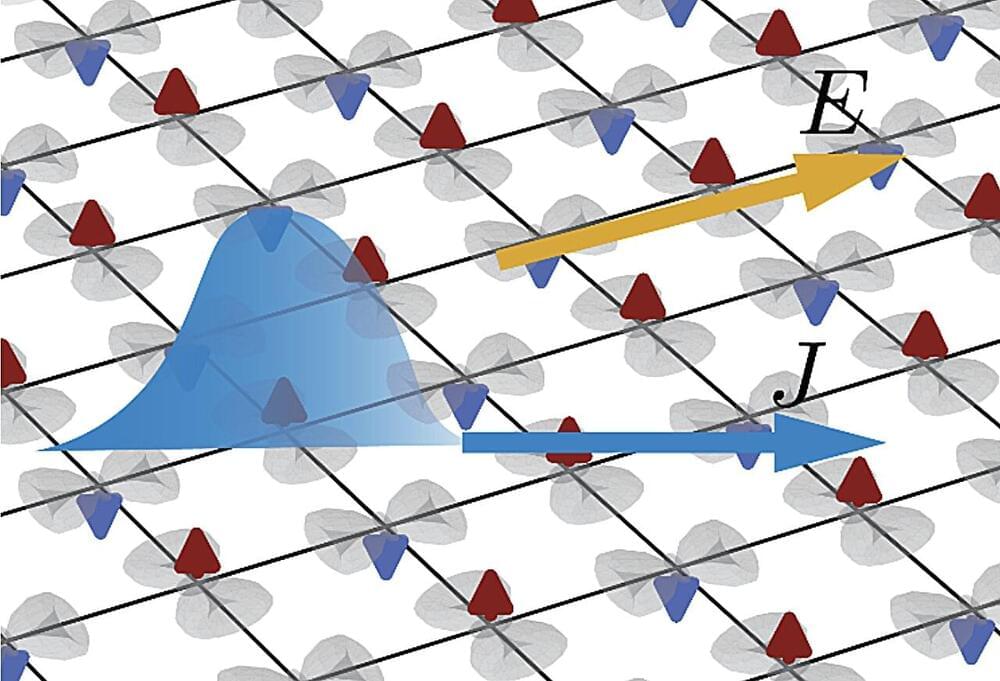
In the quantum world, materials called “altermagnets” behave in unique ways that could pave the way for new technologies.
This unique magnetism makes altermagnets highly promising for the development of new spintronic and electronic devices. It also opens new possibilities for the study of topological materials (i.e., systems with unique electronic properties originating from their electronic structure’s topology).
Researchers at Stony Brook University carried out a study aimed at better understanding the nonlinear response of planar altermagnets. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, reports the observation of a non-linear response in these materials derived from their quantum geometry.
“Recently, two experiments have confirmed the predicted role of quantum geometry in the second-order response of the conventional PT-symmetric antiferromagnets,” Sayed Ali Akbar Ghorashi, co-author of the paper, told Phys.org.
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Riding along in the Tesla Robotaxi at the unveiling event. Shot on Phone 16 ProFull video coming soon.

Where you people most often get their information regarding cannabis? This is what a recent study published in the Journal of Cannabis Research hopes to address as a team of researchers led by the University of Michigan Medical School investigated the methods by which everyday citizens receive their information regarding cannabis, specifically pertaining to its legality, which comes on the heels of its classification from a Schedule I to Schedule III drug recently being recommended by the Department of Health and Human Services.
For the study, the researchers conducted a survey of 1,161 participants ages 18 and up regarding their cannabis use within the past year, reasons for use, and the sources where they obtain their information regarding cannabis. The participants consisted of 51 percent women and 49 percent men with 27 percent reporting using cannabis within the past year. Regarding their sources of information, 35.6 percent reported it was from family and friends, 33.7 percent reported it was from websites, 9.3 percent from healthcare providers, 8.6 percent from employees where the cannabis was purchased, and 4.7 percent was from government agencies.
The study concludes by saying, “In this nationally representative survey, we show that most people draw information about cannabis from friends and family or online, with very few consulting their healthcare provider or government agencies. As cannabis accessibility and legality is increasing, there is a strong need for better clinician education, public outreach strategies, and improved communication between patients and clinicians about cannabis.”


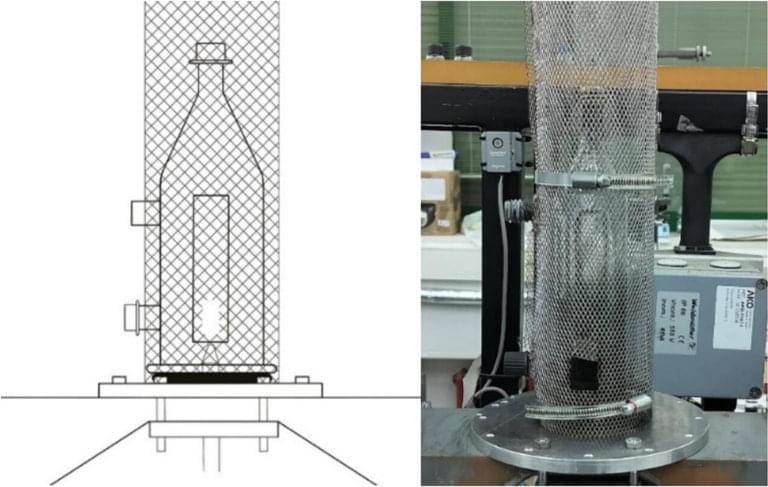
Harder than a diamond, stronger than steel, as flexible as rubber and lighter than aluminum. These are just some of the properties attributed to graphene. Although this material has sparked great interest in the scientific community in recent years, there is still no cheap and sustainable enough method for its high-quality manufacturing on an industrial scale.
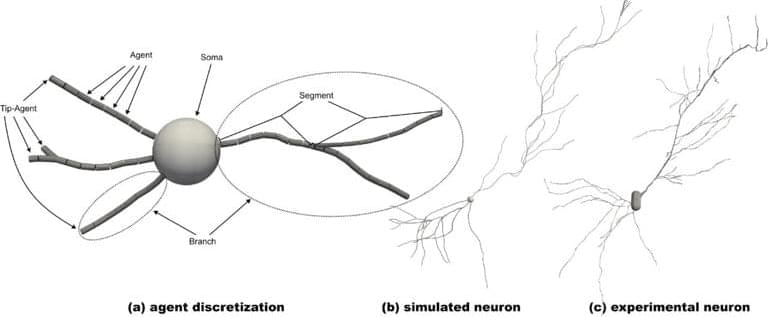
A new computer simulation of how our brains develop and grow neurons has been built by scientists from the University of Surrey. Along with improving our understanding of how the brain works, researchers hope that the models will contribute to neurodegenerative disease research and, someday, stem cell research that helps regenerate brain tissue.