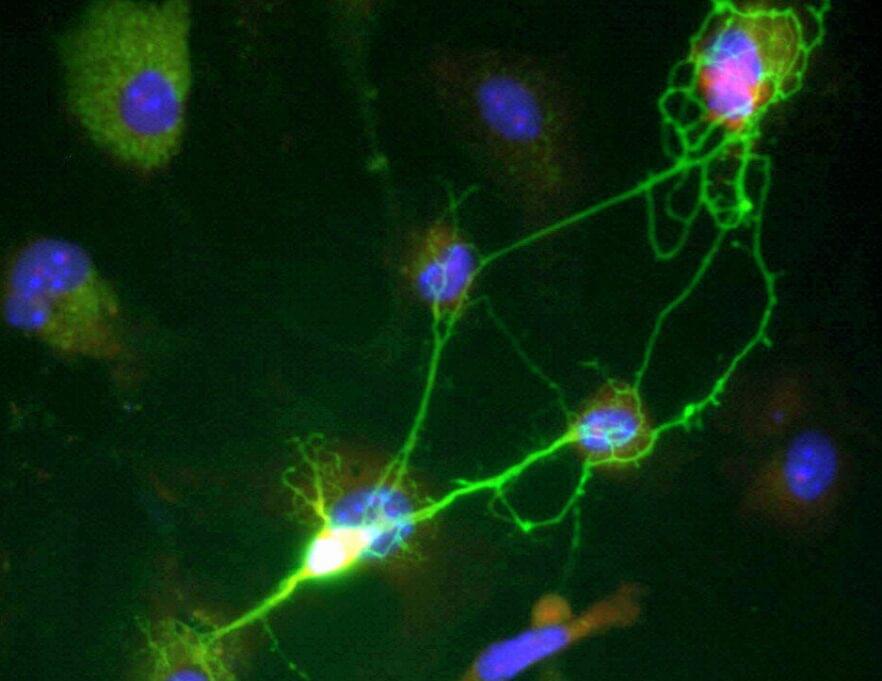
Estrogen, the major female ovarian hormone, can trigger nerve impulses within milliseconds to regulate a variety of physiological processes. At Baylor College of Medicine, Louisiana State University and collaborating institutions, researchers discovered that estrogen’s fast actions are mediated by the coupling of the estrogen receptor-alpha (ER-alpha) with an ion channel protein called Clic1.
Clic1 controls the fast flux of electrically charged chloride ions through the cell membrane, which neurons use for receiving, conducting and transmitting signals. The researchers propose that interacting with the ER-alpha-Clic1 complex enables estrogen to trigger fast neuronal responses through Clic1 ion currents. The study appears in Science Advances.
“Estrogen can act in the brain to regulate a variety of physiological processes, including female fertility, sexual behaviors, mood, reward, stress response, cognition, cardiovascular activities and body weight balance. Many of these functions are mediated by estrogen binding to one of its receptors, ER-alpha,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Yong Xu, professor of pediatrics—nutrition and associate director for basic sciences at the USDA/ARS Children’s Nutrition Research Center at Baylor.