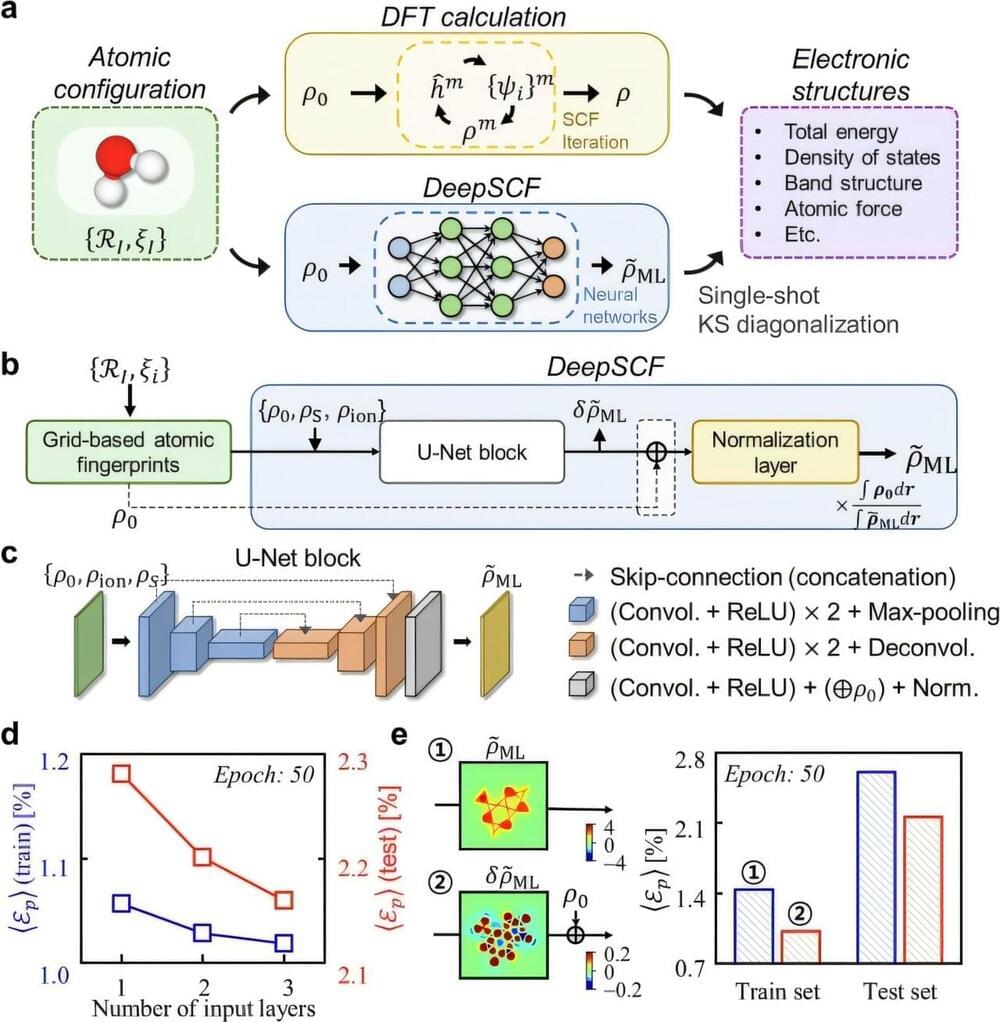
The close relationship between AI and highly complicated scientific computing can be seen in the fact that both the 2024 Nobel Prizes in Physics and Chemistry were awarded to scientists for devising AI for their respective fields of study. KAIST researchers have now succeeded in dramatically shortening the calculation time of highly sophisticated quantum mechanical computer simulations by predicting atomic-level chemical bonding information distributed in 3D space using a novel approach to teach AI.