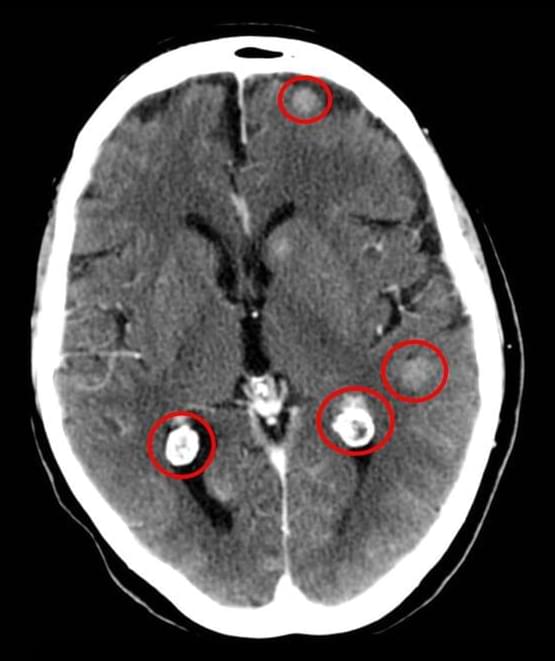
Although almost everyone in the world now breathes air that is polluted in some way, the unfolding story of air pollution is one of environmental inequality.
Every time Mithilesh turns on her stove to cook, her eyes begin to burn. The small home the 29-year-old housewife shares with her husband, daughter, son and elderly in-laws in the slums of the Indian capital Delhi quickly fills up with smoke, making it hard for anyone to see.
Mithilesh has cooked over a traditional chulha – a metal coated combustor stove that uses firewood as fuel – since she was 13 years old. She often has difficulty breathing and experiences uncontrolled bouts of coughing.