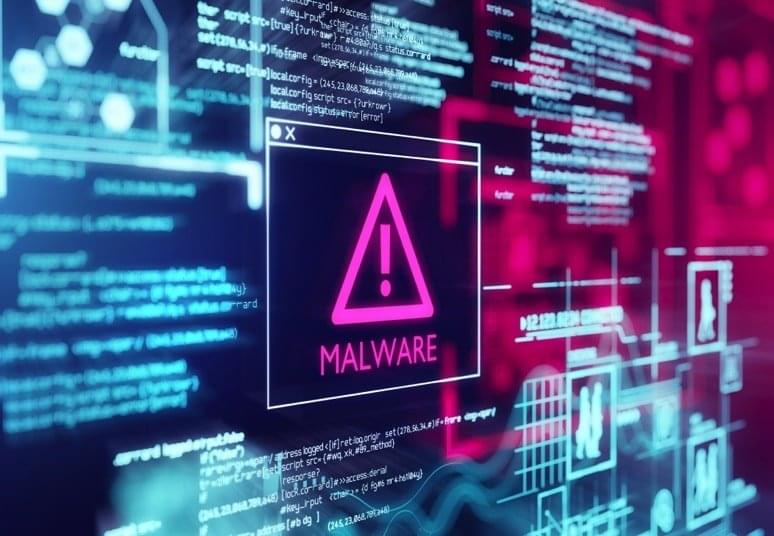
In the intricate landscape of global cybersecurity, Webwyrm malware has surfaced as a formidable adversary, casting its ominous shadow across 50 nations and leaving in its wake over 100,000 compromised victims. This insidious digital menace successfully emulates in excess of 1,000 reputable companies globally, with the ensuing potential financial fallout estimated to surpass a staggering $100 million. It is imperative for cybersecurity professionals and organizations alike to comprehend the multifaceted nature of this threat to devise and implement robust defensive strategies effectively.
In the dynamic realm of cyber threats, malicious actors incessantly refine their Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs), exploiting extant vulnerabilities and augmenting the efficacy of their malicious campaigns. Webwyrm epitomizes this relentless pursuit of evolution, embodying a level of sophistication reminiscent of infamous cyber threats of yore, such as the notorious ‘Blue Whale Challenge.’
WebWyrm malware orchestrates a complex, deceptive narrative aimed at duping unsuspecting job seekers into relinquishing their cryptocurrency. Initiating contact predominantly via WhatsApp, the malefactors likely leverage data procured from employment portals to pinpoint and engage individuals predisposed to their deceptive overtures. Prospective victims are enticed with promises of lucrative weekly remuneration, ranging between $1200 and $1500, contingent upon the completion of daily task “packets” or “resets.”